added arduino, modified build
This commit is contained in:
@@ -0,0 +1,494 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* FreeTouch, a QTouch-compatible library - tested on ATSAMD21 only!
|
||||
* The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2017 Limor 'ladyada' Fried for Adafruit Industries
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
|
||||
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
|
||||
* THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch(int p, oversample_t f, series_resistor_t r, freq_mode_t fh) {
|
||||
pin = p;
|
||||
oversample = f;
|
||||
seriesres = r;
|
||||
freqhop = fh;
|
||||
compcap = 0x2000;
|
||||
intcap = 0x3F;
|
||||
yline = -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::begin(void) {
|
||||
yline = getYLine(); // determine the Y0-15 #
|
||||
|
||||
if (yline == -1) // not all pins have Y line
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
setupClock();
|
||||
|
||||
ptcInitSettings();
|
||||
|
||||
enablePTC(false);
|
||||
|
||||
enableWCOint(false);
|
||||
enableEOCint(false);
|
||||
|
||||
// enable the sensor, only done once per line
|
||||
if (yline < 8) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YENABLEL.reg |= 1 << yline;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
} else if (yline < 16) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YENABLEH.reg |= 1 << (yline - 8);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
enablePTC(true);
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setupClock(void) {
|
||||
/* Setup and enable generic clock source for PTC module.
|
||||
struct system_gclk_chan_config gclk_chan_conf;
|
||||
system_gclk_chan_get_config_defaults(&gclk_chan_conf);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t channel = PTC_GCLK_ID;
|
||||
uint8_t source_generator = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// original line: system_gclk_chan_set_config(PTC_GCLK_ID, &gclk_chan_conf);
|
||||
uint32_t new_clkctrl_config = (channel << GCLK_CLKCTRL_ID_Pos); // from gclk.c
|
||||
|
||||
// original line: gclk_chan_conf.source_generator = GCLK_GENERATOR_1;
|
||||
/* Select the desired generic clock generator */
|
||||
new_clkctrl_config |= source_generator << GCLK_CLKCTRL_GEN_Pos; // from gclk.c
|
||||
|
||||
/* Disable generic clock channel */
|
||||
// original line: system_gclk_chan_disable(channel);
|
||||
noInterrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
/* Select the requested generator channel */
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg) = channel;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sanity check WRTLOCK */
|
||||
//Assert(!GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.WRTLOCK);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Switch to known-working source so that the channel can be disabled */
|
||||
uint32_t prev_gen_id = GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN;
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Disable the generic clock */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg &= ~GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN;
|
||||
while (GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg & GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN) {
|
||||
/* Wait for clock to become disabled */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Restore previous configured clock generator */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN = prev_gen_id;
|
||||
|
||||
//system_interrupt_leave_critical_section();
|
||||
interrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write the new configuration */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg = new_clkctrl_config;
|
||||
|
||||
// original line: system_gclk_chan_enable(PTC_GCLK_ID);
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg) = channel;
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg |= GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN; /* Enable the generic clock */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// original line: system_apb_clock_set_mask(SYSTEM_CLOCK_APB_APBC, PM_APBCMASK_PTC);
|
||||
PM->APBCMASK.reg |= PM_APBCMASK_PTC;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::measure(void) {
|
||||
uint16_t m;
|
||||
|
||||
m = measureRaw();
|
||||
if (m == -1) return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
// normalize the signal
|
||||
switch (oversample) {
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_1: return m;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_2: return m/2;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_4: return m/4;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_8: return m/8;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_16: return m/16;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_32: return m/32;
|
||||
case OVERSAMPLE_64: return m/64;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return -1; // shouldn't reach here but fail if we do!
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::measureRaw(void) {
|
||||
if (yline == -1)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
|
||||
runInStandby(true);
|
||||
enablePTC(true);
|
||||
// check if in progress
|
||||
// set up NVIC if using INT (we're not)
|
||||
enableWCOint(false);
|
||||
clearWCOintFlag();
|
||||
clearEOCintFlag();
|
||||
// enable_eoc_int(); // not using irq (for now)
|
||||
|
||||
// set up pin!
|
||||
//Serial.print("Y Line #"); Serial.println(yline);
|
||||
selectYLine();
|
||||
// set up sense resistor
|
||||
setSeriesResistor(seriesres);
|
||||
// set up prescalar
|
||||
setOversampling(oversample);
|
||||
// set up freq hopping
|
||||
setFreqHopping(freqhop, hops);
|
||||
// set up compensation cap + int (?) cap
|
||||
setCompCap(compcap);
|
||||
setIntCap(intcap);
|
||||
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->BURSTMODE.reg = 0xA4;
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return startPtcAcquire();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::startPtcAcquire(void) {
|
||||
ptcConfigIOpin();
|
||||
|
||||
ptcAcquire();
|
||||
|
||||
while (QTOUCH_PTC->CONVCONTROL.bit.CONVERT) {
|
||||
yield();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
uint16_t result = QTOUCH_PTC->RESULT.reg;
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*********************************** low level config **/
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::selectYLine(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (yline < 8) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YSELECTL.reg = 1 << yline;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YSELECTL.reg = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (yline > 7) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YSELECTH.reg = 1 << (yline - 8);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->YSELECTH.reg = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::getYLine(void) {
|
||||
int p = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin;
|
||||
if (g_APinDescription[pin].ulPort == PORTA) {
|
||||
if ((p >= 2) && (p <= 7)) {
|
||||
return (p - 2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (g_APinDescription[pin].ulPort == PORTB) {
|
||||
if ((p >= 0) && (p <= 9)) {
|
||||
return (p + 6);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// not valid
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setCompCap(uint16_t cc) {
|
||||
compcap = cc & 0x3FFF;
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->COMPCAPL.bit.VALUE = compcap & 0xFF;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->COMPCAPH.bit.VALUE = (compcap>>8) & 0x3F;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setIntCap(uint8_t ic) {
|
||||
intcap = ic & 0x3F;
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTCAP.bit.VALUE = intcap & 0x3F;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setOversampling(oversample_t lvl) {
|
||||
oversample = lvl; // back it up for later
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONVCONTROL.bit.ADCACCUM = lvl;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setSeriesResistor(series_resistor_t res) {
|
||||
seriesres = res;
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->SERRES.bit.RESISTOR = res;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::setFreqHopping(freq_mode_t fh, freq_hop_t hs) {
|
||||
freqhop = fh;
|
||||
hops = hs;
|
||||
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (fh == FREQ_MODE_NONE) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.bit.FREQSPREADEN = 0;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.bit.SAMPLEDELAY = 0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.bit.FREQSPREADEN = 1;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.bit.SAMPLEDELAY = hops;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::ptcInitSettings(void) {
|
||||
ptcConfigIOpin();
|
||||
|
||||
enablePTC(false);
|
||||
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->UNK4C04.reg &= 0xF7; //MEMORY[0x42004C04] &= 0xF7u;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->UNK4C04.reg &= 0xFB; //MEMORY[0x42004C04] &= 0xFBu;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->UNK4C04.reg &= 0xFC; //MEMORY[0x42004C04] &= 0xFCu;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.reg &= 0x9F; //MEMORY[0x42004C0C] &= 0x9Fu;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.reg &= 0xEF; //MEMORY[0x42004C0C] &= 0xEFu;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->FREQCONTROL.bit.SAMPLEDELAY = 0; //MEMORY[0x42004C0C] &= 0xF0u;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLC.bit.INIT = 1; //MEMORY[0x42004C05] |= 1u;
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLA.bit.RUNINSTANDBY = 1; //MEMORY[0x42004C00] |= 4u;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
enablePTC(true); //MEMORY[0x42004C00] |= 2u;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::ptcConfigIOpin(void) {
|
||||
uint32_t ulpin = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin;
|
||||
uint32_t ulport = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPort;
|
||||
|
||||
PORT->Group[ulport].PINCFG[ulpin].reg = 0x3; // pmuxen + input
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t curr_pmux = (PORT->Group[ulport].PMUX[ulpin/2].reg);
|
||||
|
||||
if (ulpin & 1) {
|
||||
// pmuxodd
|
||||
curr_pmux &= PORT_PMUX_PMUXE(0xF); // keep the even mux data
|
||||
curr_pmux |= PORT_PMUX_PMUXO(0x1); // set to mux B
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// pmuxeven
|
||||
curr_pmux &= PORT_PMUX_PMUXO(0xF); // keep the odd mux data
|
||||
curr_pmux |= PORT_PMUX_PMUXE(0x1); // set to mux B
|
||||
}
|
||||
PORT->Group[ulport].PMUX[ulpin/2].reg = curr_pmux;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::runInStandby(boolean en) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (en) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLA.bit.RUNINSTANDBY = 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLA.bit.RUNINSTANDBY = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::enablePTC(boolean en) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (en) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLA.bit.ENABLE = 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLA.bit.ENABLE = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::enableWCOint(boolean en) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (en) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTENABLE.bit.WCO = 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTDISABLE.bit.WCO = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::enableEOCint(boolean en) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
if (en) {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTENABLE.bit.EOC = 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTDISABLE.bit.EOC = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::clearWCOintFlag(void) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTFLAGS.bit.WCO = 1;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::clearEOCintFlag(void) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->INTFLAGS.bit.EOC = 1;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::ptcAcquire(void) {
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
QTOUCH_PTC->CONVCONTROL.bit.CONVERT = 1;
|
||||
sync_config();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::sync_config(void) {
|
||||
while (QTOUCH_PTC->CONTROLB.bit.SYNCFLAG) ;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************** DEBUGGING ASSIST *************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::snapshotRegsAndPrint(uint32_t base, uint8_t numregs) {
|
||||
volatile uint32_t addr = base;
|
||||
uint8_t datas[255];
|
||||
|
||||
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<numregs; i++) {
|
||||
datas[i] = *(uint8_t *)(addr+i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);
|
||||
printPTCregs(base, datas, numregs);
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<numregs; i++) {
|
||||
// Serial.print("$"); Serial.print(addr+i, HEX); Serial.print("\t0x");
|
||||
// printHex(datas[i]); Serial.println();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Print a hex with leading zero
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::printHex(uint8_t h, boolean newline) {
|
||||
if (h < 0x10) Serial.print("0");
|
||||
Serial.print(h, HEX);
|
||||
if (newline) Serial.println();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch::printPTCregs(uint32_t base, uint8_t *regs, uint8_t num) {
|
||||
Serial.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num; i++) {
|
||||
switch (i + base) {
|
||||
case 0x41004430: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PMUX0:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004431: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PMUX1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004432: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PMUX2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004433: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PMUX3:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
|
||||
case 0x41004440: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PCFG0:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004441: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PCFG1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004442: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PCFG2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004443: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PCFG3:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x41004444: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" PCFG4:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
case 0x42004C00: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Control A:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C01: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Sync: \t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C04: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Prescaler:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C05: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Init: \t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C08: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Disable Irq:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C09: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Enable Irq:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C0A: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Flags: \t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C0C: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Freq Cntl:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C0D: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Conv Cntl:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C10: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Y Select1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C11: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Y Select2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
/*
|
||||
case 0x42004C12: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" X Select1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C13: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" X Select2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
case 0x42004C14: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Y Enable1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C15: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Y Enable2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
/*
|
||||
case 0x42004C16: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" X Enable1:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C17: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+0x42004C00, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" X Enable2:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
case 0x42004C18: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Compcap L:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C19: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Compcap H:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C1A: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Intcap: \t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C1B: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Sense res:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C1C: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Result L:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
case 0x42004C1D: Serial.print("0x"); Serial.print(i+base, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(" Result H:\t\t0x"); printHex(regs[i], true); break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,428 @@
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_FREETOUCH_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_FREETOUCH_H
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** CONTROL A register ***************/
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONTROLA 0x42004C00
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_ENABLE 0x02
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_RUNINSTBY 0x04
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t SWRESET:1;
|
||||
uint8_t ENABLE:1;
|
||||
uint8_t RUNINSTANDBY:1;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:5;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_CONTROLA_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** CONTROL B register ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONTROLB 0x42004C01
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_SYNCFLAG 0x80
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:7;
|
||||
uint8_t SYNCFLAG:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_CONTROLB_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** UNK4C04 register ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_UNK4C04 0x42004C04
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_UNK4C04_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** CONTROL C register ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONTROLC 0x42004C05
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_INIT 0x01
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t INIT:1;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:7;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_CONTROLC_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** INT registers ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t EOC:1;
|
||||
uint8_t WCO:1;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:6;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_INT_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTDISABLE 0x42004C08
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTENABLE 0x42004C09
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_EOCINTEN 0x01
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_WCOINTEN 0x02
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTFLAGS 0x42004C0A
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_EOCINTFLAG 0x01
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_WCOINTFLAG 0x02
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** FREQ CONTROL reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t SAMPLEDELAY:4;
|
||||
uint8_t FREQSPREADEN:1;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:3;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} PTC_REG_FREQCONTROL_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_FREQCONTROL 0x42004C0C
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_FREQSPREADEN 0x10
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_SAMPLEDELAY_MASK 0x0F
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** CONVERT CONTROL reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t ADCACCUM:3;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:4;
|
||||
uint8_t CONVERT:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_CONVCONTROL_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONVCONTROL 0x42004C0D
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_CONVSTARTED 0x80
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_ADCACC_MASK 0x07
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** Y SELECT L+H reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t Y0:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y1:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y2:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y3:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y4:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y5:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y6:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y7:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_YSELECTL_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t Y8:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y9:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y10:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y11:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y12:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y13:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y14:1;
|
||||
uint8_t Y15:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_YSELECTH_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_YSELECT_L 0x42004C10
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_YSELECT_H 0x42004C11
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_YENABLE_L 0x42004C14
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_YENABLE_H 0x42004C15
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** X SELECT L+H reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t X0:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X1:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X2:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X3:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X4:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X5:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X6:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X7:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_XSELECTL_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t X8:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X9:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X10:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X11:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X12:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X13:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X14:1;
|
||||
uint8_t X15:1;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_XSELECTH_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_XSELECT_L 0x42004C12
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_XSELECT_H 0x42004C13
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_XENABLE_L 0x42004C16
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_XENABLE_H 0x42004C17
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** Compensation Cap reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t VALUE:8;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_COMPCAPL_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t VALUE:6;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:2;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_COMPCAPH_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_COMPCAPL 0x42004C18
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_COMPCAPH 0x42004C19
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** Int Cap reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t VALUE:6;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:2;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_INTCAP_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTCAP 0x42004C1A
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** Series resistor reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t RESISTOR:2;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:6;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_SERRES_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_SERIESRES 0x42004C1B
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** conversion result reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t LOWBYTE;
|
||||
uint8_t HIGHBYTE;
|
||||
} byte;
|
||||
uint16_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_CONVRESULT_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONVRESULT_L 0x42004C1C
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_CONVRESULT_H 0x42004C1D
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** burst mode reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
typedef union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
uint8_t __pad0__:2;
|
||||
uint8_t CTSLOWPOWER:1;
|
||||
uint8_t __pad1__:1;
|
||||
uint8_t BURSTMODE:4;
|
||||
} bit;
|
||||
uint8_t reg;
|
||||
} __attribute__ ((packed)) PTC_REG_BURSTMODE_Type;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_BURSTMODE 0x42004C20
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_BURSTMODE_MASK 0xF0
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_CTSLOWPOWER 0x04
|
||||
|
||||
/*************** etc unused reg ***************/
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_XYENABLE 0x42004C16
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_XYENABLE 0x02
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_WCO_MODE 0x42004C21
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_WCO_MODE_MASK 0x07
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_SET_WCO_THRESHHOLD_A_L 0x42004C24
|
||||
#define PTC_SET_WCO_THRESHHOLD_A_H 0x42004C25
|
||||
#define PTC_SET_WCO_THRESHHOLD_B_L 0x42004C26
|
||||
#define PTC_SET_WCO_THRESHHOLD_B_H 0x42004C27
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_CONTROLA_Type CONTROLA; // 0x42004C00
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_CONTROLB_Type CONTROLB; // 0x42004C01
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c02__; // 0x42004C02 unknown
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c03__; // 0x42004C03 unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_UNK4C04_Type UNK4C04; // 0x42004C04 unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_CONTROLC_Type CONTROLC; // 0x42004C05
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c06__; // 0x42004C06 unknown
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c07__; // 0x42004C07 unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_INT_Type INTDISABLE; // 0x42004C08
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_INT_Type INTENABLE; // 0x42004C09
|
||||
__I PTC_REG_INT_Type INTFLAGS; // 0x42004C0A
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c0b__; // 0x42004C0B unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_FREQCONTROL_Type FREQCONTROL; //0x42004C0C
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_CONVCONTROL_Type CONVCONTROL; // 0x42004C0D
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c0e__; // 0x42004C0E unknown
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c0f__; // 0x42004C0F unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_YSELECTL_Type YSELECTL; // 0x42004C10
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_YSELECTL_Type YSELECTH; // 0x42004C11
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_XSELECTL_Type XSELECTL; // 0x42004C12
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_XSELECTL_Type XSELECTH; // 0x42004C13
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_YSELECTL_Type YENABLEL; // 0x42004C14
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_YSELECTL_Type YENABLEH; // 0x42004C15
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_XSELECTL_Type XENABLEL; // 0x42004C16
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_XSELECTL_Type XENABLEH; // 0x42004C17
|
||||
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_COMPCAPL_Type COMPCAPL; // 0x42004C18
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_COMPCAPH_Type COMPCAPH; // 0x42004C19
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_INTCAP_Type INTCAP; // 0x42004C1A
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_SERRES_Type SERRES; // 0x42004C1B
|
||||
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_CONVRESULT_Type RESULT; // 0x42004C1C + 0x42004C1D
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c1e__; // 0x42004C1E unknown
|
||||
uint8_t __pad4c1f__; // 0x42004C1F unknown
|
||||
__IO PTC_REG_BURSTMODE_Type BURSTMODE; // 0x42004C20
|
||||
} Qtouch_Ptc;
|
||||
|
||||
#define QTOUCH_PTC (( Qtouch_Ptc *)0x42004C00U)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTDISABLE 0x42004C08
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTENABLE 0x42004C09
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_EOCINTEN 0x01
|
||||
#define PTC_BIT_WCOINTEN 0x02
|
||||
|
||||
#define PTC_REG_INTFLAGS 0x42004C0A
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Touch library oversampling (filter) setting */
|
||||
typedef enum tag_oversample_level_t {
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_1,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_2,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_4,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_8,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_16,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_32,
|
||||
OVERSAMPLE_64
|
||||
}
|
||||
oversample_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Touch library series resistor setting */
|
||||
typedef enum tag_series_resistor_t {
|
||||
RESISTOR_0,
|
||||
RESISTOR_20K,
|
||||
RESISTOR_50K,
|
||||
RESISTOR_100K,
|
||||
}
|
||||
series_resistor_t;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum tag_freq_mode_t {
|
||||
FREQ_MODE_NONE,
|
||||
FREQ_MODE_HOP,
|
||||
FREQ_MODE_SPREAD,
|
||||
FREQ_MODE_SPREAD_MEDIAN
|
||||
}
|
||||
freq_mode_t;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef enum tag_freq_hop_t {
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_1,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_2,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_3,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_4,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_5,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_6,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_7,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_8,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_9,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_10,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_11,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_12,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_13,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_14,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_15,
|
||||
FREQ_HOP_16
|
||||
}
|
||||
freq_hop_t;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_FreeTouch(int p = 0, oversample_t f = OVERSAMPLE_4, series_resistor_t r = RESISTOR_0, freq_mode_t fh = FREQ_MODE_NONE);
|
||||
bool begin(void);
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t measure(void);
|
||||
uint16_t measureRaw(void);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
void ptcInitSettings(void);
|
||||
void ptcConfigIOpin(void);
|
||||
uint16_t startPtcAcquire(void);
|
||||
|
||||
void setupClock(void);
|
||||
int getYLine(void);
|
||||
void selectYLine(void);
|
||||
void setOversampling(oversample_t lvl);
|
||||
void setSeriesResistor(series_resistor_t res);
|
||||
void setFreqHopping(freq_mode_t fh, freq_hop_t hops = FREQ_HOP_1);
|
||||
void setCompCap(uint16_t cc);
|
||||
void setIntCap(uint8_t ic);
|
||||
|
||||
void runInStandby(boolean en);
|
||||
void enablePTC(boolean en);
|
||||
void enableWCOint(boolean en);
|
||||
void enableEOCint(boolean en);
|
||||
void clearWCOintFlag(void);
|
||||
void clearEOCintFlag(void);
|
||||
void ptcAcquire(void);
|
||||
void sync_config(void);
|
||||
|
||||
// debugging helper!
|
||||
void snapshotRegsAndPrint(uint32_t base, uint8_t numregs);
|
||||
void printPTCregs(uint32_t base, uint8_t *regs, uint8_t num);
|
||||
void printHex(uint8_t h, boolean newline);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int pin; // arduino pin #
|
||||
int8_t yline; // the Y select line (see datasheet)
|
||||
oversample_t oversample;
|
||||
series_resistor_t seriesres;
|
||||
freq_mode_t freqhop;
|
||||
freq_hop_t hops;
|
||||
uint16_t compcap;
|
||||
uint8_t intcap;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,477 @@
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@file Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH.cpp
|
||||
@author K. Townsend / Limor Fried (Adafruit Industries)
|
||||
license BSD (see license.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
This is a library for the Adafruit LIS3DH Accel breakout board
|
||||
----> https://www.adafruit.com/products/2809
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
|
||||
please support Adafruit and open-source hardware by purchasing
|
||||
products from Adafruit!
|
||||
|
||||
v1.0 - First release
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#if ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Wire.h>
|
||||
#include <Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __SAMD21G18A__
|
||||
#define Wire Wire1 // CP Express has LIS on Wire1 bus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Instantiates a new LIS3DH class in I2C mode
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH()
|
||||
: _cs(-1), _mosi(-1), _miso(-1), _sck(-1), _sensorID(-1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Instantiates a new LIS3DH class in hardware SPI mode
|
||||
@param cspin the pin used as a chip select
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH(int8_t cspin)
|
||||
: _cs(cspin), _mosi(-1), _miso(-1), _sck(-1), _sensorID(-1)
|
||||
{ }
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Instantiates a new LIS3DH class in software SPI mode
|
||||
@param cspin the pin used as a chip select
|
||||
@param mosipin the pin used as master-out-slave-in
|
||||
@param misopin the pin used as master-in-slave-out
|
||||
@param sckpin the pin used as SPI serial clock
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH(int8_t cspin, int8_t mosipin, int8_t misopin, int8_t sckpin)
|
||||
: _cs(cspin), _mosi(mosipin), _miso(misopin), _sck(sckpin), _sensorID(-1)
|
||||
{ }
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Setups the HW (reads coefficients values, etc.)
|
||||
@param i2caddr the I2C address the device can be found on. defaults to 0x18
|
||||
@return true on success, false on any failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
bool Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::begin(uint8_t i2caddr) {
|
||||
_i2caddr = i2caddr;
|
||||
|
||||
if (_cs == -1) {
|
||||
// i2c
|
||||
Wire.begin();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, HIGH);
|
||||
pinMode(_cs, OUTPUT);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
if (_sck == -1) {
|
||||
// hardware SPI
|
||||
SPI.begin();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// software SPI
|
||||
pinMode(_sck, OUTPUT);
|
||||
pinMode(_mosi, OUTPUT);
|
||||
pinMode(_miso, INPUT);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<0x30; i++) {
|
||||
Serial.print("$");
|
||||
Serial.print(i, HEX); Serial.print(" = 0x");
|
||||
Serial.println(readRegister8(i), HEX);
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Check connection */
|
||||
uint8_t deviceid = readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_WHOAMI);
|
||||
if (deviceid != 0x33)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* No LIS3DH detected ... return false */
|
||||
//Serial.println(deviceid, HEX);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// enable all axes, normal mode
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL1, 0x07);
|
||||
// 400Hz rate
|
||||
setDataRate(LIS3DH_DATARATE_400_HZ);
|
||||
|
||||
// High res & BDU enabled
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL4, 0x88);
|
||||
|
||||
// DRDY on INT1
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL3, 0x10);
|
||||
|
||||
// Turn on orientation config
|
||||
//writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_PL_CFG, 0x40);
|
||||
|
||||
// enable adcs
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_TEMPCFG, 0x80);
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
for (uint8_t i=0; i<0x30; i++) {
|
||||
Serial.print("$");
|
||||
Serial.print(i, HEX); Serial.print(" = 0x");
|
||||
Serial.println(readRegister8(i), HEX);
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief read x, y, and z axis data and store in class variables.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::read(void) {
|
||||
// read x y z at once
|
||||
|
||||
if (_cs == -1) {
|
||||
// i2c
|
||||
Wire.beginTransmission(_i2caddr);
|
||||
Wire.write(LIS3DH_REG_OUT_X_L | 0x80); // 0x80 for autoincrement
|
||||
Wire.endTransmission();
|
||||
|
||||
Wire.requestFrom(_i2caddr, 6);
|
||||
x = Wire.read(); x |= ((uint16_t)Wire.read()) << 8;
|
||||
y = Wire.read(); y |= ((uint16_t)Wire.read()) << 8;
|
||||
z = Wire.read(); z |= ((uint16_t)Wire.read()) << 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
else {
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(500000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, LOW);
|
||||
spixfer(LIS3DH_REG_OUT_X_L | 0x80 | 0x40); // read multiple, bit 7&6 high
|
||||
|
||||
x = spixfer(); x |= ((uint16_t)spixfer()) << 8;
|
||||
y = spixfer(); y |= ((uint16_t)spixfer()) << 8;
|
||||
z = spixfer(); z |= ((uint16_t)spixfer()) << 8;
|
||||
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, HIGH);
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.endTransaction(); // release the SPI bus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
uint8_t range = getRange();
|
||||
uint16_t divider = 1;
|
||||
if (range == LIS3DH_RANGE_16_G) divider = 1365;
|
||||
if (range == LIS3DH_RANGE_8_G) divider = 4096;
|
||||
if (range == LIS3DH_RANGE_4_G) divider = 8190;
|
||||
if (range == LIS3DH_RANGE_2_G) divider = 16380;
|
||||
|
||||
x_g = (float)x / divider;
|
||||
y_g = (float)y / divider;
|
||||
z_g = (float)z / divider;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Read the auxilary ADC
|
||||
@param adc the adc number to read. Valid adc numbers are 1, 2, and 3.
|
||||
@return the measured value
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
int16_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::readADC(uint8_t adc) {
|
||||
if ((adc < 1) || (adc > 3)) return 0;
|
||||
uint16_t value;
|
||||
|
||||
adc--;
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t reg = LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC1_L + adc*2;
|
||||
|
||||
if (_cs == -1) {
|
||||
// i2c
|
||||
Wire.beginTransmission(_i2caddr);
|
||||
Wire.write(reg | 0x80); // 0x80 for autoincrement
|
||||
Wire.endTransmission();
|
||||
Wire.requestFrom(_i2caddr, 2);
|
||||
value = Wire.read(); value |= ((uint16_t)Wire.read()) << 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
else {
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(500000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, LOW);
|
||||
spixfer(reg | 0x80 | 0x40); // read multiple, bit 7&6 high
|
||||
|
||||
value = spixfer(); value |= ((uint16_t)spixfer()) << 8;
|
||||
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, HIGH);
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.endTransaction(); // release the SPI bus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set INT to output for single or double click
|
||||
@param c the number of taps to detect. pass 1 for single tap on all axis, 2 for double tap on all axis. Pass 0 to disable taps.
|
||||
@param clickthresh the threshold over which to register a tap.
|
||||
@param timelimit Optional time limit for a tap. Defaults to 10
|
||||
@param timelatency Optional tap latency. defaults to 20
|
||||
@param timewindow Optional time window. defaults to 255
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::setClick(uint8_t c, uint8_t clickthresh, uint8_t timelimit, uint8_t timelatency, uint8_t timewindow) {
|
||||
if (!c) {
|
||||
//disable int
|
||||
uint8_t r = readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL3);
|
||||
r &= ~(0x80); // turn off I1_CLICK
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL3, r);
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CLICKCFG, 0);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// else...
|
||||
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL3, 0x80); // turn on int1 click
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL5, 0x08); // latch interrupt on int1
|
||||
|
||||
if (c == 1)
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CLICKCFG, 0x15); // turn on all axes & singletap
|
||||
if (c == 2)
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CLICKCFG, 0x2A); // turn on all axes & doubletap
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CLICKTHS, clickthresh); // arbitrary
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_TIMELIMIT, timelimit); // arbitrary
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_TIMELATENCY, timelatency); // arbitrary
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_TIMEWINDOW, timewindow); // arbitrary
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get a tap reading
|
||||
@return the tap reading
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::getClick(void) {
|
||||
return readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CLICKSRC);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets the g range for the accelerometer
|
||||
@param range the desired range of the device. Pass LIS3DH_RANGE_2_G for highest sensitivity
|
||||
and lowest max/min value (+-2G), LIS3DH_RANGE_16_G for lowest sensitivity and highest max/min value (+-16G).
|
||||
Other acceptable values are LIS3DH_RANGE_4_G and LIS3DH_RANGE_8_G.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::setRange(lis3dh_range_t range)
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t r = readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL4);
|
||||
r &= ~(0x30);
|
||||
r |= range << 4;
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL4, r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets the g range for the accelerometer
|
||||
@return the range reading from the sensor.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
lis3dh_range_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::getRange(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Read the data format register to preserve bits */
|
||||
return (lis3dh_range_t)((readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL4) >> 4) & 0x03);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets the data rate for the LIS3DH (controls power consumption)
|
||||
@param dataRate the desired datarate.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::setDataRate(lis3dh_dataRate_t dataRate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t ctl1 = readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL1);
|
||||
ctl1 &= ~(0xF0); // mask off bits
|
||||
ctl1 |= (dataRate << 4);
|
||||
writeRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL1, ctl1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets the data rate for the LIS3DH (controls power consumption)
|
||||
@return the data rate reading from the sensor.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
lis3dh_dataRate_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::getDataRate(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return (lis3dh_dataRate_t)((readRegister8(LIS3DH_REG_CTRL1) >> 4)& 0x0F);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Gets the most recent sensor event
|
||||
@param event the pointer to place the event reading in
|
||||
@return none
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
bool Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::getEvent(sensors_event_t *event) {
|
||||
/* Clear the event */
|
||||
memset(event, 0, sizeof(sensors_event_t));
|
||||
|
||||
event->version = sizeof(sensors_event_t);
|
||||
event->sensor_id = _sensorID;
|
||||
event->type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER;
|
||||
event->timestamp = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
read();
|
||||
|
||||
event->acceleration.x = x_g * SENSORS_GRAVITY_STANDARD;
|
||||
event->acceleration.y = y_g * SENSORS_GRAVITY_STANDARD;
|
||||
event->acceleration.z = z_g * SENSORS_GRAVITY_STANDARD;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Gets the sensor_t data
|
||||
@param sensor the pointer to place sensor information into.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::getSensor(sensor_t *sensor) {
|
||||
/* Clear the sensor_t object */
|
||||
memset(sensor, 0, sizeof(sensor_t));
|
||||
|
||||
/* Insert the sensor name in the fixed length char array */
|
||||
strncpy (sensor->name, "LIS3DH", sizeof(sensor->name) - 1);
|
||||
sensor->name[sizeof(sensor->name)- 1] = 0;
|
||||
sensor->version = 1;
|
||||
sensor->sensor_id = _sensorID;
|
||||
sensor->type = SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER;
|
||||
sensor->min_delay = 0;
|
||||
sensor->max_value = 0;
|
||||
sensor->min_value = 0;
|
||||
sensor->resolution = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Low level SPI
|
||||
@param x the byte to transfer
|
||||
@return the read byte
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::spixfer(uint8_t x) {
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
return SPI.transfer(x);
|
||||
|
||||
// software spi
|
||||
//Serial.println("Software SPI");
|
||||
uint8_t reply = 0;
|
||||
for (int i=7; i>=0; i--) {
|
||||
reply <<= 1;
|
||||
digitalWrite(_sck, LOW);
|
||||
digitalWrite(_mosi, x & (1<<i));
|
||||
digitalWrite(_sck, HIGH);
|
||||
if (digitalRead(_miso))
|
||||
reply |= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return reply;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Writes 8-bits to the specified destination register
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::writeRegister8(uint8_t reg, uint8_t value) {
|
||||
if (_cs == -1) {
|
||||
Wire.beginTransmission((uint8_t)_i2caddr);
|
||||
Wire.write((uint8_t)reg);
|
||||
Wire.write((uint8_t)value);
|
||||
Wire.endTransmission();
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
else {
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(500000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, LOW);
|
||||
spixfer(reg & ~0x80); // write, bit 7 low
|
||||
spixfer(value);
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, HIGH);
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.endTransaction(); // release the SPI bus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Reads 8-bits from the specified register
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH::readRegister8(uint8_t reg) {
|
||||
uint8_t value;
|
||||
|
||||
if (_cs == -1) {
|
||||
Wire.beginTransmission(_i2caddr);
|
||||
Wire.write((uint8_t)reg);
|
||||
Wire.endTransmission();
|
||||
|
||||
Wire.requestFrom(_i2caddr, 1);
|
||||
value = Wire.read();
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
else {
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(500000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, LOW);
|
||||
spixfer(reg | 0x80); // read, bit 7 high
|
||||
value = spixfer(0);
|
||||
digitalWrite(_cs, HIGH);
|
||||
#if SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION
|
||||
if (_sck == -1)
|
||||
SPI.endTransaction(); // release the SPI bus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@file Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH.h
|
||||
@author K. Townsend / Limor Fried (Adafruit Industries)
|
||||
license BSD (see license.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
This is a library for the Adafruit LIS3DH Accel breakout board
|
||||
----> https://www.adafruit.com/products/2809
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
|
||||
please support Adafruit and open-source hardware by purchasing
|
||||
products from Adafruit!
|
||||
|
||||
v1.0 - First release
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_LIS3DH_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_LIS3DH_H
|
||||
|
||||
#if ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Wire.h>
|
||||
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny85__
|
||||
#include <SPI.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include "utility/Adafruit_CPlay_Sensor.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*=========================================================================
|
||||
I2C ADDRESS/BITS
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
#define LIS3DH_DEFAULT_ADDRESS (0x18) ///< default I2C address. if SDO/SA0 is 3V, its 0x19.
|
||||
/*=========================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief LIS3DH register definitions
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_STATUS1 = 0x07,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC1_L = 0x08,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC1_H = 0x09,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC2_L = 0x0A,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC2_H = 0x0B,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC3_L = 0x0C,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUTADC3_H = 0x0D,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_INTCOUNT = 0x0E,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_WHOAMI = 0x0F,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_TEMPCFG = 0x1F,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL1 = 0x20,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL2 = 0x21,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL3 = 0x22,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL4 = 0x23,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL5 = 0x24,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CTRL6 = 0x25,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_REFERENCE = 0x26,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_STATUS2 = 0x27,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_X_L = 0x28,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_X_H = 0x29,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_Y_L = 0x2A,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_Y_H = 0x2B,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_Z_L = 0x2C,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_OUT_Z_H = 0x2D,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_FIFOCTRL = 0x2E,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_FIFOSRC = 0x2F,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_INT1CFG = 0x30,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_INT1SRC = 0x31,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_INT1THS = 0x32,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_INT1DUR = 0x33,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CLICKCFG = 0x38,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CLICKSRC = 0x39,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_CLICKTHS = 0x3A,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_TIMELIMIT = 0x3B,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_TIMELATENCY = 0x3C,
|
||||
LIS3DH_REG_TIMEWINDOW = 0x3D,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief LIS3DH measurement ranges
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
typedef enum
|
||||
{
|
||||
LIS3DH_RANGE_16_G = 0b11, // +/- 16g
|
||||
LIS3DH_RANGE_8_G = 0b10, // +/- 8g
|
||||
LIS3DH_RANGE_4_G = 0b01, // +/- 4g
|
||||
LIS3DH_RANGE_2_G = 0b00 // +/- 2g (default value)
|
||||
} lis3dh_range_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief LIS3DH axis numbers
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
typedef enum
|
||||
{
|
||||
LIS3DH_AXIS_X = 0x0,
|
||||
LIS3DH_AXIS_Y = 0x1,
|
||||
LIS3DH_AXIS_Z = 0x2,
|
||||
} lis3dh_axis_t;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief LIS3DH datarates
|
||||
@note Used with register 0x2A (LIS3DH_REG_CTRL_REG1) to set bandwidth
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
typedef enum
|
||||
{
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_400_HZ = 0b0111, // 400Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_200_HZ = 0b0110, // 200Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_100_HZ = 0b0101, // 100Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_50_HZ = 0b0100, // 50Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_25_HZ = 0b0011, // 25Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_10_HZ = 0b0010, // 10 Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_1_HZ = 0b0001, // 1 Hz
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_POWERDOWN = 0,
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_LOWPOWER_1K6HZ = 0b1000,
|
||||
LIS3DH_DATARATE_LOWPOWER_5KHZ = 0b1001,
|
||||
|
||||
} lis3dh_dataRate_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Class that stores state and functions for LIS3DH accelerometer on the circuitPlayground board
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH : public Adafruit_Sensor {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH(void);
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH(int8_t cspin);
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_LIS3DH(int8_t cspin, int8_t mosipin, int8_t misopin, int8_t sckpin);
|
||||
|
||||
bool begin(uint8_t addr = LIS3DH_DEFAULT_ADDRESS);
|
||||
|
||||
void read();
|
||||
int16_t readADC(uint8_t a);
|
||||
|
||||
void setRange(lis3dh_range_t range);
|
||||
lis3dh_range_t getRange(void);
|
||||
|
||||
void setDataRate(lis3dh_dataRate_t dataRate);
|
||||
lis3dh_dataRate_t getDataRate(void);
|
||||
|
||||
bool getEvent(sensors_event_t *event);
|
||||
void getSensor(sensor_t *sensor);
|
||||
|
||||
void setClick(uint8_t c, uint8_t clickthresh, uint8_t timelimit = 10, uint8_t timelatency = 20, uint8_t timewindow = 255);
|
||||
uint8_t getClick(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief integer axis readings
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
int16_t x, ///> integer x-axis reading
|
||||
y, ///> integer y-axis reading
|
||||
z; ///> integer z-axis reading
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief floating point axis readings
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
float x_g, ///> floating point G reading for x axis
|
||||
y_g, ///> floating point G reading for y axis
|
||||
z_g; ///> floating point G reading for z axis
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t readRegister8(uint8_t reg);
|
||||
void writeRegister8(uint8_t reg, uint8_t value);
|
||||
uint8_t spixfer(uint8_t x = 0xFF);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t _sensorID;
|
||||
int8_t _i2caddr;
|
||||
|
||||
// SPI
|
||||
int8_t _cs, _mosi, _miso, _sck;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Circuit Playground microphone library
|
||||
// by Phil Burgess / Paint Your Dragon.
|
||||
// Fast Fourier transform section is derived from
|
||||
// ELM-ChaN FFT library (see comments in ffft.S).
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_CPlay_Mic.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
|
||||
#define SAMPLERATE_HZ 22000
|
||||
#define DECIMATION 64
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit_ZeroPDM Adafruit_CPlay_Mic::pdm = Adafruit_ZeroPDM(34, 35);
|
||||
|
||||
// a windowed sinc filter for 44 khz, 64 samples
|
||||
uint16_t sincfilter[DECIMATION] = {0, 2, 9, 21, 39, 63, 94, 132, 179, 236, 302, 379, 467, 565, 674, 792, 920, 1055, 1196, 1341, 1487, 1633, 1776, 1913, 2042, 2159, 2263, 2352, 2422,
|
||||
2474, 2506, 2516, 2506, 2474, 2422, 2352, 2263, 2159, 2042, 1913, 1776, 1633, 1487, 1341, 1196, 1055, 920, 792, 674, 565, 467, 379, 302, 236, 179, 132, 94, 63, 39, 21, 9, 2, 0, 0};
|
||||
|
||||
// a manual loop-unroller!
|
||||
#define ADAPDM_REPEAT_LOOP_16(X) X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
|
||||
|
||||
static bool pdmConfigured = false;
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define DC_OFFSET (1023 / 3)
|
||||
#define NOISE_THRESHOLD 3
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Reads ADC for given interval (in milliseconds, 1-65535). Uses ADC free-run mode w/polling on AVR.
|
||||
Any currently-installed ADC interrupt handler will be temporarily
|
||||
disabled while this runs.
|
||||
@param ms the number of milliseconds to sample
|
||||
@return max deviation from DC_OFFSET (e.g. 0-341)
|
||||
@deprecated THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED AND WILL BE REMOVED IN A FUTURE RELEASE.
|
||||
please use soundPressureLevel(ms) instead
|
||||
@note THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED AND WILL BE REMOVED IN A FUTURE RELEASE.
|
||||
please use soundPressureLevel(ms) instead
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
int Adafruit_CPlay_Mic::peak(uint16_t ms) {
|
||||
int val = soundPressureLevel(ms);
|
||||
val = map(val, 56, 130, 0, 350);
|
||||
return constrain(val, 0, 350);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief capture the passed number of samples and place them in buf.
|
||||
@param buf the buffer to store the samples in
|
||||
@param nSamples the number of samples to take
|
||||
|
||||
@note ON AVR: Captures ADC audio samples at maximum speed supported by 32u4 (9615 Hz).
|
||||
Ostensibly for FFT code (below), but might have other uses. Uses ADC
|
||||
free-run mode w/polling. Any currently-installed ADC interrupt handler
|
||||
will be temporarily disabled while this runs. No other interrupts are
|
||||
disabled; as long as interrupt handlers are minor (e.g. Timer/Counter 0
|
||||
handling of millis() and micros()), this isn't likely to lose readings.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Mic::capture(int16_t *buf, uint16_t nSamples) {
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
uint8_t admux_save, adcsra_save, adcsrb_save, timsk0_save, channel;
|
||||
int16_t adc;
|
||||
|
||||
channel = analogPinToChannel(4); // Pin A4 to ADC channel
|
||||
admux_save = ADMUX; // Save ADC config registers
|
||||
adcsra_save = ADCSRA;
|
||||
adcsrb_save = ADCSRB;
|
||||
|
||||
// Init ADC free-run mode; f = ( 8MHz/prescaler ) / 13 cycles/conversion
|
||||
ADCSRA = 0; // Stop ADC interrupt, if any
|
||||
ADMUX = _BV(REFS0) | channel; // Aref=AVcc, channel sel, right-adj
|
||||
ADCSRB = 0; // Free run mode, no high MUX bit
|
||||
ADCSRA = _BV(ADEN) | // ADC enable
|
||||
_BV(ADSC) | // ADC start
|
||||
_BV(ADATE) | // Auto trigger
|
||||
_BV(ADIF) | // Reset interrupt flag
|
||||
_BV(ADPS2) | _BV(ADPS1); // 64:1 / 13 = 9615 Hz
|
||||
|
||||
// ADC conversion-ready bit is polled for each sample rather than using
|
||||
// an interrupt; avoids contention with application or other library
|
||||
// using ADC ISR for other things (there can be only one) while still
|
||||
// providing the speed & precise timing of free-run mode (a loop of
|
||||
// analogRead() won't get you that).
|
||||
for(uint16_t i=0; i<nSamples; i++) {
|
||||
while(!(ADCSRA & _BV(ADIF))); // Wait for ADC result
|
||||
adc = ADC;
|
||||
ADCSRA |= _BV(ADIF); // Clear bit
|
||||
// FFT requires signed inputs; ADC output is unsigned. DC offset is
|
||||
// NOT 512 on Circuit Playground because it uses a 1.1V OpAmp input
|
||||
// as the midpoint, and may swing asymmetrically on the high side.
|
||||
// Sign-convert and then clip range to +/- DC_OFFSET.
|
||||
if(adc <= (DC_OFFSET - NOISE_THRESHOLD)) {
|
||||
adc -= DC_OFFSET;
|
||||
} else if(adc >= (DC_OFFSET + NOISE_THRESHOLD)) {
|
||||
adc -= DC_OFFSET;
|
||||
if(adc > (DC_OFFSET * 2)) adc = DC_OFFSET * 2;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
adc = 0; // Below noise threshold
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf[i] = adc;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ADMUX = admux_save; // Restore ADC config
|
||||
ADCSRB = adcsrb_save;
|
||||
ADCSRA = adcsra_save;
|
||||
(void)analogRead(A4); // Purge residue from ADC register
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
if(!pdmConfigured){
|
||||
pdm.begin();
|
||||
pdm.configure(SAMPLERATE_HZ * DECIMATION / 16, true);
|
||||
pdmConfigured = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t *ptr = buf;
|
||||
while(ptr < (buf + nSamples)){
|
||||
uint16_t runningsum = 0;
|
||||
uint16_t *sinc_ptr = sincfilter;
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t samplenum=0; samplenum < (DECIMATION/16) ; samplenum++) {
|
||||
uint16_t sample = pdm.read() & 0xFFFF; // we read 16 bits at a time, by default the low half
|
||||
|
||||
ADAPDM_REPEAT_LOOP_16( // manually unroll loop: for (int8_t b=0; b<16; b++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// start at the LSB which is the 'first' bit to come down the line, chronologically
|
||||
// (Note we had to set I2S_SERCTRL_BITREV to get this to work, but saves us time!)
|
||||
if (sample & 0x1) {
|
||||
runningsum += *sinc_ptr; // do the convolution
|
||||
}
|
||||
sinc_ptr++;
|
||||
sample >>= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// since we wait for the samples from I2S peripheral, we dont need to delay, we will 'naturally'
|
||||
// wait the right amount of time between analog writes
|
||||
//Serial.println(runningsum);
|
||||
|
||||
runningsum /= 64 ; // convert 16 bit -> 10 bit
|
||||
runningsum -= 512; // make it close to 0-offset signed
|
||||
|
||||
*ptr++ = runningsum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "no compatible architecture defined."
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Returns somewhat-calibrated sound pressure level.
|
||||
@param ms Milliseconds to continuously sample microphone over, 10ms is a good start.
|
||||
@returns Floating point Sound Pressure Level, tends to range from 40-120 db SPL
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
float Adafruit_CPlay_Mic::soundPressureLevel(uint16_t ms){
|
||||
float gain;
|
||||
int16_t *ptr;
|
||||
uint16_t len;
|
||||
int16_t minVal = 52;
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
gain = 1.3;
|
||||
len = 9.615 * ms;
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
gain = 9;
|
||||
len = (float)(SAMPLERATE_HZ/1000) * ms;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "no compatible architecture defined."
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
int16_t data[len];
|
||||
capture(data, len);
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t *end = data + len;
|
||||
float pref = 0.00002;
|
||||
|
||||
/*******************************
|
||||
* REMOVE DC OFFSET
|
||||
******************************/
|
||||
int32_t avg = 0;
|
||||
ptr = data;
|
||||
while(ptr < end) avg += *ptr++;
|
||||
avg = avg/len;
|
||||
|
||||
ptr = data;
|
||||
while(ptr < end) *ptr++ -= avg;
|
||||
|
||||
/*******************************
|
||||
* GET MAX VALUE
|
||||
******************************/
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t maxVal = 0;
|
||||
ptr = data;
|
||||
while(ptr < end){
|
||||
int32_t v = abs(*ptr++);
|
||||
if(v > maxVal) maxVal = v;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
float conv = ((float)maxVal)/1023 * gain;
|
||||
|
||||
/*******************************
|
||||
* CALCULATE SPL
|
||||
******************************/
|
||||
conv = 20 * log10(conv/pref);
|
||||
|
||||
if(isfinite(conv)) return conv;
|
||||
else return minVal;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief 16 bit complex data type
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
int16_t r; ///< real portion
|
||||
int16_t i; ///< imaginary portion
|
||||
} complex_t;
|
||||
|
||||
extern "C" { // In ffft.S
|
||||
void fft_input(const int16_t *, complex_t *),
|
||||
fft_execute(complex_t *),
|
||||
fft_output(complex_t *, uint16_t *);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief AVR ONLY: Performs one cycle of fast Fourier transform (FFT) with audio captured
|
||||
from mic on A4. Output is 32 'bins,' each covering an equal range of
|
||||
frequencies from 0 to 4800 Hz (i.e. 0-150 Hz, 150-300 Hz, 300-450, etc).
|
||||
Needs about 450 bytes free RAM to operate.
|
||||
@param spectrum the buffer to store the results in. Must be 32 bytes in length.
|
||||
|
||||
@note THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED AND WILL BE REMOVED IN A FUTURE RELEASE.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Mic::fft(
|
||||
uint16_t *spectrum) { // Spectrum output buffer, uint16_t[32]
|
||||
if(spectrum) {
|
||||
int16_t capBuf[64]; // Audio capture buffer
|
||||
complex_t butterfly[64]; // FFT "butterfly" buffer
|
||||
|
||||
capture(capBuf, 64); // Collect mic data into capBuf
|
||||
fft_input(capBuf, butterfly); // Samples -> complex #s
|
||||
fft_execute(butterfly); // Process complex data
|
||||
fft_output(butterfly, spectrum); // Complex -> spectrum (32 bins)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Circuit Playground microphone library
|
||||
// by Phil Burgess / Paint Your Dragon.
|
||||
// Fast Fourier transform section is derived from
|
||||
// ELM-ChaN FFT library (see comments in ffft.S).
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_MIC_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_MIC_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __GNUC__
|
||||
#define DEPRECATED(func) func __attribute__ ((deprecated))
|
||||
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
|
||||
#define DEPRECATED(func) __declspec(deprecated) func
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#pragma message("WARNING: You need to implement DEPRECATED for this compiler")
|
||||
#define DEPRECATED(func) func
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_ZeroPDM.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Class that stores state and functions for the microphone on CircuitPlayground boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class Adafruit_CPlay_Mic {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_Mic(void) {}; // Empty constructor
|
||||
int peak(uint16_t ms) __attribute__ ((deprecated));
|
||||
void capture(int16_t *buf, uint16_t nSamples),
|
||||
fft(uint16_t *spectrum);
|
||||
|
||||
float soundPressureLevel(uint16_t ms);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
static Adafruit_ZeroPDM pdm;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_MIC_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,740 @@
|
||||
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Arduino library to control a wide variety of WS2811- and WS2812-based RGB
|
||||
LED devices such as Adafruit FLORA RGB Smart Pixels and NeoPixel strips.
|
||||
Currently handles 400 and 800 KHz bitstreams on 8, 12 and 16 MHz ATmega
|
||||
MCUs, with LEDs wired for various color orders. 8 MHz MCUs provide
|
||||
output on PORTB and PORTD, while 16 MHz chips can handle most output pins
|
||||
(possible exception with upper PORT registers on the Arduino Mega).
|
||||
|
||||
Written by Phil Burgess / Paint Your Dragon for Adafruit Industries,
|
||||
contributions by PJRC, Michael Miller and other members of the open
|
||||
source community.
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit invests time and resources providing this open source code,
|
||||
please support Adafruit and open-source hardware by purchasing products
|
||||
from Adafruit!
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
This file is part of the Adafruit NeoPixel library.
|
||||
|
||||
NeoPixel is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
|
||||
published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of
|
||||
the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
NeoPixel is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License along with NeoPixel. If not, see
|
||||
<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Constructor when length, pin and type are known at compile-time
|
||||
@param n number of pixels
|
||||
@param p pin the pixels are attached to
|
||||
@param t the type of neopixel. can be NEO_KHZ800 or NEO_KHZ400
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel(uint16_t n, uint8_t p, neoPixelType t) :
|
||||
begun(false), brightness(0), pixels(NULL), endTime(0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
updateType(t);
|
||||
updateLength(n);
|
||||
setPin(p);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// via Michael Vogt/neophob: empty constructor is used when strand length
|
||||
// isn't known at compile-time; situations where program config might be
|
||||
// read from internal flash memory or an SD card, or arrive via serial
|
||||
// command. If using this constructor, MUST follow up with updateType(),
|
||||
// updateLength(), etc. to establish the strand type, length and pin number!
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief via Michael Vogt/neophob: empty constructor is used when strand length
|
||||
isn't known at compile-time; situations where program config might be
|
||||
read from internal flash memory or an SD card, or arrive via serial
|
||||
command. If using this constructor, MUST follow up with updateType(),
|
||||
updateLength(), etc. to establish the strand type, length and pin number!
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel() :
|
||||
is800KHz(true),
|
||||
begun(false), numLEDs(0), numBytes(0), pin(-1), brightness(0), pixels(NULL),
|
||||
rOffset(1), gOffset(0), bOffset(2), wOffset(1), endTime(0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::~Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel() {
|
||||
if(pixels) free(pixels);
|
||||
if(pin >= 0) pinMode(pin, INPUT);
|
||||
pixels = NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief initialize necessary hardware to drive the pixels.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::begin(void) {
|
||||
if(pin >= 0) {
|
||||
pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(pin, LOW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
begun = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set the number of pixels in the strip
|
||||
@param n the number of pixels in the strip
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::updateLength(uint16_t n) {
|
||||
if(pixels) free(pixels); // Free existing data (if any)
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocate new data -- note: ALL PIXELS ARE CLEARED
|
||||
numBytes = n * ((wOffset == rOffset) ? 3 : 4);
|
||||
if((pixels = (uint8_t *)malloc(numBytes))) {
|
||||
memset(pixels, 0, numBytes);
|
||||
numLEDs = n;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
numLEDs = numBytes = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief set the type of neopixel we are using
|
||||
@param t the type of neopixel. Can be NEO_KHZ800 or NEO_KHZ400
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::updateType(neoPixelType t) {
|
||||
boolean oldThreeBytesPerPixel = (wOffset == rOffset); // false if RGBW
|
||||
|
||||
wOffset = (t >> 6) & 0b11; // See notes in header file
|
||||
rOffset = (t >> 4) & 0b11; // regarding R/G/B/W offsets
|
||||
gOffset = (t >> 2) & 0b11;
|
||||
bOffset = t & 0b11;
|
||||
is800KHz = (t < 256); // 400 KHz flag is 1<<8
|
||||
|
||||
// If bytes-per-pixel has changed (and pixel data was previously
|
||||
// allocated), re-allocate to new size. Will clear any data.
|
||||
if(pixels) {
|
||||
boolean newThreeBytesPerPixel = (wOffset == rOffset);
|
||||
if(newThreeBytesPerPixel != oldThreeBytesPerPixel) updateLength(numLEDs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Write data to the neopixels
|
||||
@note this disables interrupts on the chip until the write is complete.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::show(void) {
|
||||
|
||||
if(!pixels) return;
|
||||
|
||||
// Data latch = 50+ microsecond pause in the output stream. Rather than
|
||||
// put a delay at the end of the function, the ending time is noted and
|
||||
// the function will simply hold off (if needed) on issuing the
|
||||
// subsequent round of data until the latch time has elapsed. This
|
||||
// allows the mainline code to start generating the next frame of data
|
||||
// rather than stalling for the latch.
|
||||
while(!canShow());
|
||||
// endTime is a private member (rather than global var) so that mutliple
|
||||
// instances on different pins can be quickly issued in succession (each
|
||||
// instance doesn't delay the next).
|
||||
|
||||
// In order to make this code runtime-configurable to work with any pin,
|
||||
// SBI/CBI instructions are eschewed in favor of full PORT writes via the
|
||||
// OUT or ST instructions. It relies on two facts: that peripheral
|
||||
// functions (such as PWM) take precedence on output pins, so our PORT-
|
||||
// wide writes won't interfere, and that interrupts are globally disabled
|
||||
// while data is being issued to the LEDs, so no other code will be
|
||||
// accessing the PORT. The code takes an initial 'snapshot' of the PORT
|
||||
// state, computes 'pin high' and 'pin low' values, and writes these back
|
||||
// to the PORT register as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
noInterrupts(); // Need 100% focus on instruction timing
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
// AVR MCUs -- ATmega & ATtiny (no XMEGA) ---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint16_t
|
||||
i = numBytes; // Loop counter
|
||||
volatile uint8_t
|
||||
*ptr = pixels, // Pointer to next byte
|
||||
b = *ptr++, // Current byte value
|
||||
hi, // PORT w/output bit set high
|
||||
lo; // PORT w/output bit set low
|
||||
|
||||
// Hand-tuned assembly code issues data to the LED drivers at a specific
|
||||
// rate. There's separate code for different CPU speeds (8, 12, 16 MHz)
|
||||
// for both the WS2811 (400 KHz) and WS2812 (800 KHz) drivers. The
|
||||
// datastream timing for the LED drivers allows a little wiggle room each
|
||||
// way (listed in the datasheets), so the conditions for compiling each
|
||||
// case are set up for a range of frequencies rather than just the exact
|
||||
// 8, 12 or 16 MHz values, permitting use with some close-but-not-spot-on
|
||||
// devices (e.g. 16.5 MHz DigiSpark). The ranges were arrived at based
|
||||
// on the datasheet figures and have not been extensively tested outside
|
||||
// the canonical 8/12/16 MHz speeds; there's no guarantee these will work
|
||||
// close to the extremes (or possibly they could be pushed further).
|
||||
// Keep in mind only one CPU speed case actually gets compiled; the
|
||||
// resulting program isn't as massive as it might look from source here.
|
||||
|
||||
// 8 MHz(ish) AVR ---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
#if (F_CPU >= 7400000UL) && (F_CPU <= 9500000UL)
|
||||
|
||||
if(is800KHz) {
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint8_t n1, n2 = 0; // First, next bits out
|
||||
|
||||
// Squeezing an 800 KHz stream out of an 8 MHz chip requires code
|
||||
// specific to each PORT register. At present this is only written
|
||||
// to work with pins on PORTD or PORTB, the most likely use case --
|
||||
// this covers all the pins on the Adafruit Flora and the bulk of
|
||||
// digital pins on the Arduino Pro 8 MHz (keep in mind, this code
|
||||
// doesn't even get compiled for 16 MHz boards like the Uno, Mega,
|
||||
// Leonardo, etc., so don't bother extending this out of hand).
|
||||
// Additional PORTs could be added if you really need them, just
|
||||
// duplicate the else and loop and change the PORT. Each add'l
|
||||
// PORT will require about 150(ish) bytes of program space.
|
||||
|
||||
// 10 instruction clocks per bit: HHxxxxxLLL
|
||||
// OUT instructions: ^ ^ ^ (T=0,2,7)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Same as above, just switched to PORTB and stripped of comments.
|
||||
hi = PORTB | pinMask;
|
||||
lo = PORTB & ~pinMask;
|
||||
n1 = lo;
|
||||
if(b & 0x80) n1 = hi;
|
||||
|
||||
asm volatile(
|
||||
"cp_headB:" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n1]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 6" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n2]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 5" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n1]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 4" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n2]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 3" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n1]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 2" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n2]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 1" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n1]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 0" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n2] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbiw %[count], 1" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[n2]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"ld %[byte] , %a[ptr]+" "\n\t"
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 7" "\n\t"
|
||||
"mov %[n1] , %[hi]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"out %[port] , %[lo]" "\n\t"
|
||||
"brne cp_headB" "\n"
|
||||
: [byte] "+r" (b), [n1] "+r" (n1), [n2] "+r" (n2), [count] "+w" (i)
|
||||
: [port] "I" (_SFR_IO_ADDR(PORTB)), [ptr] "e" (ptr), [hi] "r" (hi),
|
||||
[lo] "r" (lo));
|
||||
|
||||
} else { // end 800 KHz, do 400 KHz
|
||||
|
||||
// Timing is more relaxed; unrolling the inner loop for each bit is
|
||||
// not necessary. Still using the peculiar RJMPs as 2X NOPs, not out
|
||||
// of need but just to trim the code size down a little.
|
||||
// This 400-KHz-datastream-on-8-MHz-CPU code is not quite identical
|
||||
// to the 800-on-16 code later -- the hi/lo timing between WS2811 and
|
||||
// WS2812 is not simply a 2:1 scale!
|
||||
|
||||
// 20 inst. clocks per bit: HHHHxxxxxxLLLLLLLLLL
|
||||
// ST instructions: ^ ^ ^ (T=0,4,10)
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint8_t next, bit;
|
||||
|
||||
hi = *port | pinMask;
|
||||
lo = *port & ~pinMask;
|
||||
next = lo;
|
||||
bit = 8;
|
||||
|
||||
asm volatile(
|
||||
"cp_head20:" "\n\t" // Clk Pseudocode (T = 0)
|
||||
"st %a[port], %[hi]" "\n\t" // 2 PORT = hi (T = 2)
|
||||
"sbrc %[byte] , 7" "\n\t" // 1-2 if(b & 128)
|
||||
"mov %[next], %[hi]" "\n\t" // 0-1 next = hi (T = 4)
|
||||
"st %a[port], %[next]" "\n\t" // 2 PORT = next (T = 6)
|
||||
"mov %[next] , %[lo]" "\n\t" // 1 next = lo (T = 7)
|
||||
"dec %[bit]" "\n\t" // 1 bit-- (T = 8)
|
||||
"breq cp_nextbyte20" "\n\t" // 1-2 if(bit == 0)
|
||||
"rol %[byte]" "\n\t" // 1 b <<= 1 (T = 10)
|
||||
"st %a[port], %[lo]" "\n\t" // 2 PORT = lo (T = 12)
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t" // 2 nop nop (T = 14)
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t" // 2 nop nop (T = 16)
|
||||
"rjmp .+0" "\n\t" // 2 nop nop (T = 18)
|
||||
"rjmp cp_head20" "\n\t" // 2 -> head20 (next bit out)
|
||||
"cp_nextbyte20:" "\n\t" // (T = 10)
|
||||
"st %a[port], %[lo]" "\n\t" // 2 PORT = lo (T = 12)
|
||||
"nop" "\n\t" // 1 nop (T = 13)
|
||||
"ldi %[bit] , 8" "\n\t" // 1 bit = 8 (T = 14)
|
||||
"ld %[byte] , %a[ptr]+" "\n\t" // 2 b = *ptr++ (T = 16)
|
||||
"sbiw %[count], 1" "\n\t" // 2 i-- (T = 18)
|
||||
"brne cp_head20" "\n" // 2 if(i != 0) -> (next byte)
|
||||
: [port] "+e" (port),
|
||||
[byte] "+r" (b),
|
||||
[bit] "+r" (bit),
|
||||
[next] "+r" (next),
|
||||
[count] "+w" (i)
|
||||
: [hi] "r" (hi),
|
||||
[lo] "r" (lo),
|
||||
[ptr] "e" (ptr));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "CPU SPEED NOT SUPPORTED"
|
||||
#endif // end F_CPU ifdefs on __AVR__
|
||||
|
||||
// END AVR ----------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAMD21G18A__) // Arduino Zero / CP Express
|
||||
|
||||
// Tried this with a timer/counter, couldn't quite get adequate
|
||||
// resolution. So yay, you get a load of goofball NOPs...
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t *ptr, *end, p, bitMask, portNum;
|
||||
uint32_t pinMask;
|
||||
|
||||
portNum = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPort;
|
||||
pinMask = 1ul << g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin;
|
||||
ptr = pixels;
|
||||
end = ptr + numBytes;
|
||||
p = *ptr++;
|
||||
bitMask = 0x80;
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint32_t *set = &(PORT->Group[portNum].OUTSET.reg),
|
||||
*clr = &(PORT->Group[portNum].OUTCLR.reg);
|
||||
|
||||
if(is800KHz) {
|
||||
for(;;) {
|
||||
*set = pinMask;
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
if(p & bitMask) {
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
*clr = pinMask;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*clr = pinMask;
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(bitMask >>= 1) {
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if(ptr >= end) break;
|
||||
p = *ptr++;
|
||||
bitMask = 0x80;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // 400 KHz bitstream
|
||||
for(;;) {
|
||||
*set = pinMask;
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
if(p & bitMask) {
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
*clr = pinMask;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*clr = pinMask;
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;"
|
||||
"nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
if(bitMask >>= 1) {
|
||||
asm("nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop; nop;");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if(ptr >= end) break;
|
||||
p = *ptr++;
|
||||
bitMask = 0x80;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "CPU ARCHITECTURE NOT SUPPORTED"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// END ARCHITECTURE SELECT ------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
interrupts();
|
||||
endTime = micros(); // Save EOD time for latch on next call
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set the output pin number
|
||||
@param p the pin number
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::setPin(uint8_t p) {
|
||||
if(begun && (pin >= 0)) pinMode(pin, INPUT);
|
||||
pin = p;
|
||||
if(begun) {
|
||||
pinMode(p, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(p, LOW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
port = portOutputRegister(digitalPinToPort(p));
|
||||
pinMask = digitalPinToBitMask(p);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set pixel color from separate R,G,B components:
|
||||
@param n the pixel number to set
|
||||
@param r the red component
|
||||
@param g the green component
|
||||
@param b the blue component
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::setPixelColor(
|
||||
uint16_t n, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) {
|
||||
|
||||
if(n < numLEDs) {
|
||||
if(brightness) { // See notes in setBrightness()
|
||||
r = (r * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
g = (g * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
b = (b * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint8_t *p;
|
||||
if(wOffset == rOffset) { // Is an RGB-type strip
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 3]; // 3 bytes per pixel
|
||||
} else { // Is a WRGB-type strip
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 4]; // 4 bytes per pixel
|
||||
p[wOffset] = 0; // But only R,G,B passed -- set W to 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p[rOffset] = r; // R,G,B always stored
|
||||
p[gOffset] = g;
|
||||
p[bOffset] = b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set pixel color from separate R,G,B,W components:
|
||||
@param n the pixel number to set
|
||||
@param r the red component
|
||||
@param g the green component
|
||||
@param b the blue component
|
||||
@param w the white component
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::setPixelColor(
|
||||
uint16_t n, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b, uint8_t w) {
|
||||
|
||||
if(n < numLEDs) {
|
||||
if(brightness) { // See notes in setBrightness()
|
||||
r = (r * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
g = (g * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
b = (b * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
w = (w * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint8_t *p;
|
||||
if(wOffset == rOffset) { // Is an RGB-type strip
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 3]; // 3 bytes per pixel (ignore W)
|
||||
} else { // Is a WRGB-type strip
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 4]; // 4 bytes per pixel
|
||||
p[wOffset] = w; // Store W
|
||||
}
|
||||
p[rOffset] = r; // Store R,G,B
|
||||
p[gOffset] = g;
|
||||
p[bOffset] = b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Set pixel color from 'packed' 32-bit RGB color:
|
||||
@param n the pixel number to set
|
||||
@param c the packed 32-bit color data
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::setPixelColor(uint16_t n, uint32_t c) {
|
||||
if(n < numLEDs) {
|
||||
uint8_t *p,
|
||||
r = (uint8_t)(c >> 16),
|
||||
g = (uint8_t)(c >> 8),
|
||||
b = (uint8_t)c;
|
||||
if(brightness) { // See notes in setBrightness()
|
||||
r = (r * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
g = (g * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
b = (b * brightness) >> 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(wOffset == rOffset) {
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 3];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 4];
|
||||
uint8_t w = (uint8_t)(c >> 24);
|
||||
p[wOffset] = brightness ? ((w * brightness) >> 8) : w;
|
||||
}
|
||||
p[rOffset] = r;
|
||||
p[gOffset] = g;
|
||||
p[bOffset] = b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Convert separate R,G,B into packed 32-bit RGB color.
|
||||
@param r the red component
|
||||
@param g the green component
|
||||
@param b the blue component
|
||||
@return the converted 32-bit color
|
||||
|
||||
@note Packed format is always RGB, regardless of LED strand color order.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint32_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::Color(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) {
|
||||
return ((uint32_t)r << 16) | ((uint32_t)g << 8) | b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Convert separate R,G,B,W into packed 32-bit WRGB color.
|
||||
@param r the red component
|
||||
@param g the green component
|
||||
@param b the blue component
|
||||
@param w the white component
|
||||
@return the converted 32-bit color
|
||||
|
||||
@note Packed format is always WRGB, regardless of LED strand color order.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint32_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::Color(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b, uint8_t w) {
|
||||
return ((uint32_t)w << 24) | ((uint32_t)r << 16) | ((uint32_t)g << 8) | b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Query color from previously-set pixel (returns packed 32-bit RGB value)
|
||||
@param n the number of the pixel to check
|
||||
@return the 32-bit color of the pixel
|
||||
|
||||
@note this does not read from the pixel itself. It just checks the value that was previously set.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint32_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::getPixelColor(uint16_t n) const {
|
||||
if(n >= numLEDs) return 0; // Out of bounds, return no color.
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t *p;
|
||||
|
||||
if(wOffset == rOffset) { // Is RGB-type device
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 3];
|
||||
if(brightness) {
|
||||
// Stored color was decimated by setBrightness(). Returned value
|
||||
// attempts to scale back to an approximation of the original 24-bit
|
||||
// value used when setting the pixel color, but there will always be
|
||||
// some error -- those bits are simply gone. Issue is most
|
||||
// pronounced at low brightness levels.
|
||||
return (((uint32_t)(p[rOffset] << 8) / brightness) << 16) |
|
||||
(((uint32_t)(p[gOffset] << 8) / brightness) << 8) |
|
||||
( (uint32_t)(p[bOffset] << 8) / brightness );
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// No brightness adjustment has been made -- return 'raw' color
|
||||
return ((uint32_t)p[rOffset] << 16) |
|
||||
((uint32_t)p[gOffset] << 8) |
|
||||
(uint32_t)p[bOffset];
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // Is RGBW-type device
|
||||
p = &pixels[n * 4];
|
||||
if(brightness) { // Return scaled color
|
||||
return (((uint32_t)(p[wOffset] << 8) / brightness) << 24) |
|
||||
(((uint32_t)(p[rOffset] << 8) / brightness) << 16) |
|
||||
(((uint32_t)(p[gOffset] << 8) / brightness) << 8) |
|
||||
( (uint32_t)(p[bOffset] << 8) / brightness );
|
||||
} else { // Return raw color
|
||||
return ((uint32_t)p[wOffset] << 24) |
|
||||
((uint32_t)p[rOffset] << 16) |
|
||||
((uint32_t)p[gOffset] << 8) |
|
||||
(uint32_t)p[bOffset];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Returns pointer to pixels[] array. Pixel data is stored in device-
|
||||
native format and is not translated here. Application will need to be
|
||||
aware of specific pixel data format and handle colors appropriately.
|
||||
@return pointer to the pixel array.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint8_t *Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::getPixels(void) const {
|
||||
return pixels;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get the number of pixels in the strip
|
||||
@return the number of pixels
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint16_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::numPixels(void) const {
|
||||
return numLEDs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Adjust output brightness; 0=darkest (off), 255=brightest.
|
||||
@param b the brightness to set
|
||||
@return the number of pixels
|
||||
|
||||
@note This does NOT immediately affect what's currently displayed on the LEDs. The
|
||||
next call to show() will refresh the LEDs at this level. However,
|
||||
this process is potentially "lossy," especially when increasing
|
||||
brightness. The tight timing in the WS2811/WS2812 code means there
|
||||
aren't enough free cycles to perform this scaling on the fly as data
|
||||
is issued. So we make a pass through the existing color data in RAM
|
||||
and scale it (subsequent graphics commands also work at this
|
||||
brightness level). If there's a significant step up in brightness,
|
||||
the limited number of steps (quantization) in the old data will be
|
||||
quite visible in the re-scaled version. For a non-destructive
|
||||
change, you'll need to re-render the full strip data. C'est la vie.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::setBrightness(uint8_t b) {
|
||||
// Stored brightness value is different than what's passed.
|
||||
// This simplifies the actual scaling math later, allowing a fast
|
||||
// 8x8-bit multiply and taking the MSB. 'brightness' is a uint8_t,
|
||||
// adding 1 here may (intentionally) roll over...so 0 = max brightness
|
||||
// (color values are interpreted literally; no scaling), 1 = min
|
||||
// brightness (off), 255 = just below max brightness.
|
||||
uint8_t newBrightness = b + 1;
|
||||
if(newBrightness != brightness) { // Compare against prior value
|
||||
// Brightness has changed -- re-scale existing data in RAM
|
||||
uint8_t c,
|
||||
*ptr = pixels,
|
||||
oldBrightness = brightness - 1; // De-wrap old brightness value
|
||||
uint16_t scale;
|
||||
if(oldBrightness == 0) scale = 0; // Avoid /0
|
||||
else if(b == 255) scale = 65535 / oldBrightness;
|
||||
else scale = (((uint16_t)newBrightness << 8) - 1) / oldBrightness;
|
||||
for(uint16_t i=0; i<numBytes; i++) {
|
||||
c = *ptr;
|
||||
*ptr++ = (c * scale) >> 8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
brightness = newBrightness;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get the global brightness value
|
||||
@return the global brightness
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::getBrightness(void) const {
|
||||
return brightness - 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief set all neopixel data to 'off' in internal memory.
|
||||
@note this does not automatically update pixels. Update with show() after calling clear()
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::clear() {
|
||||
memset(pixels, 0, numBytes);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This bizarre construct isn't Arduino code in the conventional sense.
|
||||
// It exploits features of GCC's preprocessor to generate a PROGMEM
|
||||
// table (in flash memory) holding an 8-bit unsigned sine wave (0-255).
|
||||
static const int _SBASE_ = __COUNTER__ + 1; // Index of 1st __COUNTER__ below
|
||||
#define _S1_ (sin((__COUNTER__ - _SBASE_) / 128.0 * M_PI) + 1.0) * 127.5 + 0.5,
|
||||
#define _S2_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ _S1_ // Expands to 8 items
|
||||
#define _S3_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ _S2_ // Expands to 64 items
|
||||
static const uint8_t PROGMEM _sineTable[] = { _S3_ _S3_ _S3_ _S3_ }; // 256
|
||||
|
||||
// Similar to above, but for an 8-bit gamma-correction table.
|
||||
#define _GAMMA_ 2.6
|
||||
static const int _GBASE_ = __COUNTER__ + 1; // Index of 1st __COUNTER__ below
|
||||
#define _G1_ pow((__COUNTER__ - _GBASE_) / 255.0, _GAMMA_) * 255.0 + 0.5,
|
||||
#define _G2_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ _G1_ // Expands to 8 items
|
||||
#define _G3_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ _G2_ // Expands to 64 items
|
||||
static const uint8_t PROGMEM _gammaTable[] = { _G3_ _G3_ _G3_ _G3_ }; // 256
|
||||
|
||||
/*! @brief Get a sinusoidal value from a sine table
|
||||
@param x a 0 to 255 value corresponding to an index to the sine table
|
||||
@returns An 8-bit sinusoidal value back */
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::sine8(uint8_t x) const {
|
||||
return pgm_read_byte(&_sineTable[x]); // 0-255 in, 0-255 out
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*! @brief Get a gamma-corrected value from a gamma table
|
||||
@param x a 0 to 255 value corresponding to an index to the gamma table
|
||||
@returns An 8-bit gamma-corrected value back */
|
||||
uint8_t Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel::gamma8(uint8_t x) const {
|
||||
return pgm_read_byte(&_gammaTable[x]); // 0-255 in, 0-255 out
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
|
||||
/*--------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
This file is part of the Adafruit NeoPixel library.
|
||||
|
||||
NeoPixel is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
|
||||
published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of
|
||||
the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
NeoPixel is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License along with NeoPixel. If not, see
|
||||
<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_NEOPIXEL_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_NEOPIXEL_H
|
||||
|
||||
#if (ARDUINO >= 100)
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include <WProgram.h>
|
||||
#include <pins_arduino.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// The order of primary colors in the NeoPixel data stream can vary
|
||||
// among device types, manufacturers and even different revisions of
|
||||
// the same item. The third parameter to the Adafruit_NeoPixel
|
||||
// constructor encodes the per-pixel byte offsets of the red, green
|
||||
// and blue primaries (plus white, if present) in the data stream --
|
||||
// the following #defines provide an easier-to-use named version for
|
||||
// each permutation. e.g. NEO_GRB indicates a NeoPixel-compatible
|
||||
// device expecting three bytes per pixel, with the first byte
|
||||
// containing the green value, second containing red and third
|
||||
// containing blue. The in-memory representation of a chain of
|
||||
// NeoPixels is the same as the data-stream order; no re-ordering of
|
||||
// bytes is required when issuing data to the chain.
|
||||
|
||||
// Bits 5,4 of this value are the offset (0-3) from the first byte of
|
||||
// a pixel to the location of the red color byte. Bits 3,2 are the
|
||||
// green offset and 1,0 are the blue offset. If it is an RGBW-type
|
||||
// device (supporting a white primary in addition to R,G,B), bits 7,6
|
||||
// are the offset to the white byte...otherwise, bits 7,6 are set to
|
||||
// the same value as 5,4 (red) to indicate an RGB (not RGBW) device.
|
||||
// i.e. binary representation:
|
||||
// 0bWWRRGGBB for RGBW devices
|
||||
// 0bRRRRGGBB for RGB
|
||||
|
||||
// RGB NeoPixel permutations; white and red offsets are always same
|
||||
// Offset: W R G B
|
||||
#define NEO_RGB ((0 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_RBG ((0 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
#define NEO_GRB ((1 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_GBR ((2 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
#define NEO_BRG ((1 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BGR ((2 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBW NeoPixel permutations; all 4 offsets are distinct
|
||||
// Offset: W R G B
|
||||
#define NEO_WRGB ((0 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_WRBG ((0 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_WGRB ((0 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_WGBR ((0 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_WBRG ((0 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
#define NEO_WBGR ((0 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
|
||||
#define NEO_RWGB ((1 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_RWBG ((1 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_RGWB ((2 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_RGBW ((3 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_RBWG ((2 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
#define NEO_RBGW ((3 << 6) | (0 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
|
||||
#define NEO_GWRB ((1 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_GWBR ((1 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_GRWB ((2 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (3))
|
||||
#define NEO_GRBW ((3 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (2))
|
||||
#define NEO_GBWR ((2 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
#define NEO_GBRW ((3 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (0 << 2) | (1))
|
||||
|
||||
#define NEO_BWRG ((1 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BWGR ((1 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BRWG ((2 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (3 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BRGW ((3 << 6) | (1 << 4) | (2 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BGWR ((2 << 6) | (3 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
#define NEO_BGRW ((3 << 6) | (2 << 4) | (1 << 2) | (0))
|
||||
|
||||
// Add NEO_KHZ400 to the color order value to indicate a 400 KHz
|
||||
// device. All but the earliest v1 NeoPixels expect an 800 KHz data
|
||||
// stream, this is the default if unspecified.
|
||||
|
||||
#define NEO_KHZ800 0x0000 // 800 KHz datastream
|
||||
#define NEO_KHZ400 0x0100 // 400 KHz datastream
|
||||
|
||||
typedef uint16_t neoPixelType;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Class that stores state and functions for neopixels on CircuitPlayground boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel {
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
||||
// Constructor: number of LEDs, pin number, LED type
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel(uint16_t n, uint8_t p=17, neoPixelType t=NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel(void);
|
||||
~Adafruit_CPlay_NeoPixel();
|
||||
|
||||
void begin(void),
|
||||
show(void),
|
||||
setPin(uint8_t p),
|
||||
setPixelColor(uint16_t n, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b),
|
||||
setPixelColor(uint16_t n, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b, uint8_t w),
|
||||
setPixelColor(uint16_t n, uint32_t c),
|
||||
setBrightness(uint8_t),
|
||||
clear(),
|
||||
updateLength(uint16_t n),
|
||||
updateType(neoPixelType t);
|
||||
uint8_t
|
||||
*getPixels(void) const,
|
||||
getBrightness(void) const,
|
||||
sine8(uint8_t) const,
|
||||
gamma8(uint8_t) const;
|
||||
uint16_t
|
||||
numPixels(void) const;
|
||||
static uint32_t
|
||||
Color(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b),
|
||||
Color(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b, uint8_t w);
|
||||
uint32_t
|
||||
getPixelColor(uint16_t n) const;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief check if enough time has elapsed and the pixels are ready to refresh.
|
||||
@return true if ready to show, false otherwise.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
inline bool
|
||||
canShow(void) { return (micros() - endTime) >= 50L; }
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
boolean
|
||||
#ifdef NEO_KHZ400 // If 400 KHz NeoPixel support enabled...
|
||||
is800KHz, ///< ...true if 800 KHz pixels
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
begun; ///< true if begin() previously called
|
||||
uint16_t
|
||||
numLEDs, ///< Number of RGB LEDs in strip
|
||||
numBytes; ///< Size of 'pixels' buffer below (3 or 4 bytes/pixel)
|
||||
int8_t
|
||||
pin; ///< Output pin number (-1 if not yet set)
|
||||
uint8_t
|
||||
brightness,
|
||||
*pixels, ///< Holds LED color values (3 or 4 bytes each)
|
||||
rOffset, ///< Index of red byte within each 3- or 4-byte pixel
|
||||
gOffset, ///< Index of green byte
|
||||
bOffset, ///< Index of blue byte
|
||||
wOffset; ///< Index of white byte (same as rOffset if no white)
|
||||
uint32_t
|
||||
endTime; ///< Latch timing reference
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
volatile uint8_t
|
||||
*port; ///< Output PORT register
|
||||
uint8_t
|
||||
pinMask; ///< Output PORT bitmask
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_NEOPIXEL_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software< /span>
|
||||
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
* limitations under the License.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Update by K. Townsend (Adafruit Industries) for lighter typedefs, and
|
||||
* extended sensor support to include color, voltage and current */
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _ADAFRUIT_SENSOR_H
|
||||
#define _ADAFRUIT_SENSOR_H
|
||||
|
||||
#if ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
#include "Print.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Intentionally modeled after sensors.h in the Android API:
|
||||
* https://github.com/android/platform_hardware_libhardware/blob/master/include/hardware/sensors.h */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Constants */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_GRAVITY_EARTH (9.80665F) ///< Earth's gravity in m/s^2 */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_GRAVITY_MOON (1.6F) ///< The moon's gravity in m/s^2 */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_GRAVITY_SUN (275.0F) ///< The sun's gravity in m/s^2 */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_GRAVITY_STANDARD (SENSORS_GRAVITY_EARTH)
|
||||
#define SENSORS_MAGFIELD_EARTH_MAX (60.0F) ///< Maximum magnetic field on Earth's surface */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_MAGFIELD_EARTH_MIN (30.0F) ///< Minimum magnetic field on Earth's surface */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_PRESSURE_SEALEVELHPA (1013.25F) ///< Average sea level pressure is 1013.25 hPa */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_DPS_TO_RADS (0.017453293F) ///< Degrees/s to rad/s multiplier */
|
||||
#define SENSORS_GAUSS_TO_MICROTESLA (100) ///< Gauss to micro-Tesla multiplier */
|
||||
|
||||
/** Sensor types */
|
||||
typedef enum
|
||||
{
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER = (1), ///< Gravity + linear acceleration */
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD = (2),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_ORIENTATION = (3),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_GYROSCOPE = (4),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT = (5),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_PRESSURE = (6),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_PROXIMITY = (8),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_GRAVITY = (9),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION = (10), ///< Acceleration not including gravity */
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR = (11),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_RELATIVE_HUMIDITY = (12),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE = (13),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_OBJECT_TEMPERATURE = (14),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_VOLTAGE = (15),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_CURRENT = (16),
|
||||
SENSOR_TYPE_COLOR = (17)
|
||||
} sensors_type_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/** struct sensors_vec_s is used to return a vector in a common format. */
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
union {
|
||||
float v[3]; ///< array to store xyz G data
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
float x; ///< x-axis G data
|
||||
float y; ///< y-axis G data
|
||||
float z; ///< z-axis G data
|
||||
}; ///< axis data
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
float roll; ///< Rotation around the longitudinal axis (the plane body, 'X axis'). Roll is positive and increasing when moving downward. -90<39><=roll<=90<39> */
|
||||
float pitch; ///< Rotation around the lateral axis (the wing span, 'Y axis'). Pitch is positive and increasing when moving upwards. -180<38><=pitch<=180<38>) */
|
||||
float heading; ///< Angle between the longitudinal axis (the plane body) and magnetic north, measured clockwise when viewing from the top of the device. 0-359<35> */
|
||||
}; ///< Orientation sensors */
|
||||
}; ///< union of orientation data
|
||||
int8_t status; ///< sensor status
|
||||
uint8_t reserved[3]; ///< reserved
|
||||
} sensors_vec_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/** struct sensors_color_s is used to return color data in a common format. */
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
union {
|
||||
float c[3]; ///< array to hold floating point RGB color
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
float r; ///< Red component */
|
||||
float g; ///< Green component */
|
||||
float b; ///< Blue component */
|
||||
}; ///< RGB color space
|
||||
}; ///< union of RGB color space data
|
||||
uint32_t rgba; ///< 24-bit RGBA value */
|
||||
} sensors_color_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sensor event (36 bytes) */
|
||||
/** struct sensor_event_s is used to provide a single sensor event in a common format. */
|
||||
typedef struct
|
||||
{
|
||||
int32_t version; ///< must be sizeof(struct sensors_event_t) */
|
||||
int32_t sensor_id; ///< unique sensor identifier */
|
||||
int32_t type; ///< sensor type */
|
||||
int32_t reserved0; ///< reserved */
|
||||
int32_t timestamp; ///< time is in milliseconds */
|
||||
union
|
||||
{
|
||||
float data[4]; ///< array for floating point general data
|
||||
sensors_vec_t acceleration; ///< acceleration values are in meter per second per second (m/s^2) */
|
||||
sensors_vec_t magnetic; ///< magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT) */
|
||||
sensors_vec_t orientation; ///< orientation values are in degrees */
|
||||
sensors_vec_t gyro; ///< gyroscope values are in rad/s */
|
||||
float temperature; ///< temperature is in degrees centigrade (Celsius) */
|
||||
float distance; ///< distance in centimeters */
|
||||
float light; ///< light in SI lux units */
|
||||
float pressure; ///< pressure in hectopascal (hPa) */
|
||||
float relative_humidity; ///< relative humidity in percent */
|
||||
float current; ///< current in milliamps (mA) */
|
||||
float voltage; ///< voltage in volts (V) */
|
||||
sensors_color_t color; ///< color in RGB component values */
|
||||
}; ///< union of sensor event data
|
||||
} sensors_event_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sensor details (40 bytes) */
|
||||
/** struct sensor_s is used to describe basic information about a specific sensor. */
|
||||
typedef struct
|
||||
{
|
||||
char name[12]; ///< sensor name */
|
||||
int32_t version; ///< version of the hardware + driver */
|
||||
int32_t sensor_id; ///< unique sensor identifier */
|
||||
int32_t type; ///< this sensor's type (ex. SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT) */
|
||||
float max_value; ///< maximum value of this sensor's value in SI units */
|
||||
float min_value; ///< minimum value of this sensor's value in SI units */
|
||||
float resolution; ///< smallest difference between two values reported by this sensor */
|
||||
int32_t min_delay; ///< min delay in microseconds between events. zero = not a constant rate */
|
||||
} sensor_t;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sensor API class for CircuitPlayground board
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class Adafruit_Sensor {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// Constructor(s)
|
||||
Adafruit_Sensor() {}
|
||||
virtual ~Adafruit_Sensor() {}
|
||||
|
||||
// These must be defined by the subclass
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief enable or disable auto-ranging for the sensor
|
||||
@param enabled pass true to enable auto-ranging, false to disable
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
virtual void enableAutoRange(bool enabled) {};
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief enable auto-ranging for the sensor
|
||||
@return true on success, false on failure
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
virtual bool getEvent(sensors_event_t*) = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get information on the sensor
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
virtual void getSensor(sensor_t*) = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool _autoRange; ///< state of auto-ranging for this sensor. True if enabled, false if disabled
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,169 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Circuit Playground speaker library
|
||||
// by Phil Burgess / Paint Your Dragon.
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets up Circuit Playground speaker for PWM audio output: enables 48 KHz
|
||||
high-speed PWM mode, configures Timer/Counter 4, sets PWM duty cycle to
|
||||
50% (speaker idle position).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::begin(void) {
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
pinMode(5, OUTPUT); // Enable output
|
||||
#else
|
||||
pinMode(CPLAY_SPEAKER_SHUTDOWN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(CPLAY_SPEAKER_SHUTDOWN, HIGH);
|
||||
// PWM/timer not needed on CPlay Express, has true analog out.
|
||||
// Set analogWrite resolution to 8 bits to match AVR calls.
|
||||
analogWriteResolution(8);
|
||||
pinMode(A0, OUTPUT); // Enable output
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief enable or disable the speaker. This function only works on 'Express' boards.
|
||||
@param e pass true to enable, false to disable
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::enable(boolean e) {
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
#else // circuit playground express has nicer amp w/shutdown
|
||||
digitalWrite(CPLAY_SPEAKER_SHUTDOWN, e);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Turns off PWM output to the speaker.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::end(void) {
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
TCCR4A = 0; // PWMA off
|
||||
pinMode(5, INPUT);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
pinMode(A0, INPUT);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
started = false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Sets speaker position, enables PWM output if needed.
|
||||
@param value the value to set (0-255; 127=idle)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::set(uint8_t value) {
|
||||
if(!started) begin();
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
TCCR4A = value;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, value);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Plays digitized 8-bit audio (optionally 10 bits on Express board) from
|
||||
a PROGMEM (flash memory) buffer. Maybe 1-3 seconds tops depending on
|
||||
sampling rate (e.g. 8000 Hz = 8 Kbytes/second). Max ~20K space avail on
|
||||
Circuit Playground, lots more on Circuit Playground Express.
|
||||
This function currently "blocks" -- it will not play sounds in the
|
||||
background while other code runs.
|
||||
@param data pointer to the audio data to play
|
||||
@param len the length of the data in samples
|
||||
@param sampleRate the sample rate of the data in samples per second
|
||||
@param tenBit Optional flag if true 10-bit mode is enabled. AVR ONLY
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::playSound(
|
||||
const uint8_t *data, uint32_t len, uint16_t sampleRate, boolean tenBit) {
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t i;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!started) {
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
// Set up Timer4 for fast PWM on !OC4A
|
||||
PLLFRQ = (PLLFRQ & 0xCF) | 0x30; // Route PLL to async clk
|
||||
TCCR4A = _BV(COM4A0) | _BV(PWM4A); // Clear on match, PWMA on
|
||||
TCCR4B = _BV(PWM4X) |_BV(CS40); // PWM invert, 1:1 prescale
|
||||
TCCR4D = 0; // Fast PWM mode
|
||||
TCCR4E = 0; // Not enhanced mode
|
||||
TC4H = 0; // Not 10-bit mode
|
||||
DT4 = 0; // No dead time
|
||||
OCR4C = 255; // TOP
|
||||
OCR4A = 127; // 50% duty (idle position) to start
|
||||
started = true;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
uint16_t interval = 1000000L / sampleRate;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
uint32_t r2 = sampleRate / 2;
|
||||
uint32_t startTime = micros();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if(tenBit) { // 10-bit audio samples?
|
||||
uint8_t loIdx = 4;
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
// Because it uses 8-bit PWM for output, the AVR code must filter
|
||||
// 10-bit data down to 8 bits. This is ONLY here for compatibility
|
||||
// with sketches with 10-bit samples. If targeting a project for AVR,
|
||||
// it's best to produce and use optimized 8-bit audio, else it's just
|
||||
// wasted space! Timer/Counter 4 DOES offer a 10-bit mode, but it's
|
||||
// not used in this library, just not worth it in the limited flash
|
||||
// space of the 32U4 chip.
|
||||
uint16_t idx = 0;
|
||||
uint8_t hiBits;
|
||||
for(i=0; i<len; i++) {
|
||||
if(++loIdx >= 4) {
|
||||
hiBits = pgm_read_byte(&data[idx++]);
|
||||
loIdx = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
OCR4A = ((hiBits & 0xC0) | (pgm_read_byte(&data[idx++]) >> 2));
|
||||
hiBits <<= 2; // Do this after write, because of masking op above
|
||||
delayMicroseconds(interval);
|
||||
}
|
||||
OCR4A = 127;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
// Circuit Playground Express -- use 10-bit analogWrite()
|
||||
uint32_t idx = 0;
|
||||
uint16_t hiBits;
|
||||
analogWriteResolution(10);
|
||||
for(i=0; i<len; i++) {
|
||||
if(++loIdx >= 4) {
|
||||
hiBits = (uint16_t)pgm_read_byte(&data[idx++]);
|
||||
loIdx = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
hiBits <<= 2; // Do this before write, because of masking op below
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, (hiBits & 0x300) | pgm_read_byte(&data[idx++]));
|
||||
while(((micros()-startTime+50)/100) < ((i*10000UL+r2)/sampleRate));
|
||||
}
|
||||
analogWriteResolution(8); // Return to 8 bits for set() compatibility
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, 127);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
} else { // 8-bit audio samples
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
for(i=0; i<len; i++) {
|
||||
OCR4A = pgm_read_byte(&data[i]);
|
||||
delayMicroseconds(interval);
|
||||
}
|
||||
OCR4A = 127;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
for(i=0; i<len; i++) {
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, pgm_read_byte(&data[i]));
|
||||
while(((micros()-startTime+50)/100) < ((i*10000UL+r2)/sampleRate));
|
||||
}
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, 127);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Circuit Playground speaker library
|
||||
// by Phil Burgess / Paint Your Dragon.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_SPEAKER_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_SPEAKER_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
#else // circuit playground express has nicer amp w/shutdown
|
||||
#define CPLAY_SPEAKER_SHUTDOWN 11 ///< shutdown pin (Express boards only)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Class that stores state and functions for the speaker on CircuitPlayground boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker(void) { started = false; };
|
||||
void begin(void),
|
||||
end(void),
|
||||
set(uint8_t value),
|
||||
playSound(const uint8_t *data, uint32_t length, uint16_t sampleRate, boolean tenBit=false),
|
||||
say(const uint8_t *addr);
|
||||
|
||||
void enable(boolean e);
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief disable the speaker.
|
||||
@note this function only has an effect on 'Express' boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void off(void) { enable(false); };
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief enable the speaker.
|
||||
@note this function only has an effect on 'Express' boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void on(void) { enable(true); };
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
boolean started;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // ADAFRUIT_CPLAY_SPEAKER_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,381 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Arduino Zero / Feather M0 I2S audio library.
|
||||
// Author: Tony DiCola & Limor "ladyada" Fried
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2016 Adafruit Industries
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
// copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
// SOFTWARE.
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_ZeroPDM.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
|
||||
// Define macros for debug output that optimize out when debug mode is disabled.
|
||||
#ifdef DEBUG
|
||||
#define DEBUG_PRINT(...) DEBUG_PRINTER.print(__VA_ARGS__)
|
||||
#define DEBUG_PRINTLN(...) DEBUG_PRINTER.println(__VA_ARGS__)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define DEBUG_PRINT(...)
|
||||
#define DEBUG_PRINTLN(...)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Adafruit_ZeroPDM::Adafruit_ZeroPDM(int clockpin, int datapin, uint8_t gclk):
|
||||
_gclk(gclk), _clk(clockpin), _data(datapin) {
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool Adafruit_ZeroPDM::begin(void) {
|
||||
// check the pins are valid!
|
||||
_clk_pin = _clk_mux = _data_pin = _data_mux = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Clock pin, can only be one of 3 options
|
||||
uint32_t clockport = g_APinDescription[_clk].ulPort;
|
||||
uint32_t clockpin = g_APinDescription[_clk].ulPin;
|
||||
if ((clockport == 0) && (clockpin == 10)) {
|
||||
// PA10
|
||||
_i2sclock = I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_0;
|
||||
_clk_pin = PIN_PA10G_I2S_SCK0;
|
||||
_clk_mux = MUX_PA10G_I2S_SCK0;
|
||||
} else if ((clockport == 1) && (clockpin == 10)) {
|
||||
// PB11
|
||||
_i2sclock = I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_1;
|
||||
_clk_pin = PIN_PB11G_I2S_SCK1;
|
||||
_clk_mux = MUX_PB11G_I2S_SCK1;
|
||||
} else if ((clockport == 0) && (clockpin == 20)) {
|
||||
// PA20
|
||||
_i2sclock = I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_0;
|
||||
_clk_pin = PIN_PA20G_I2S_SCK0;
|
||||
_clk_mux = MUX_PA20G_I2S_SCK0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
DEBUG_PRINTLN("Clock isnt on a valid pin");
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Data pin, can only be one of 3 options
|
||||
uint32_t datapin = g_APinDescription[_data].ulPin;
|
||||
uint32_t dataport = g_APinDescription[_data].ulPort;
|
||||
if ((dataport == 0) && (datapin == 7)) {
|
||||
// PA07
|
||||
_i2sserializer = I2S_SERIALIZER_0;
|
||||
_data_pin = PIN_PA07G_I2S_SD0;
|
||||
_data_mux = MUX_PA07G_I2S_SD0;
|
||||
} else if ((dataport == 0) && (datapin == 8)) {
|
||||
// PA08
|
||||
_i2sserializer = I2S_SERIALIZER_1;
|
||||
_data_pin = PIN_PA08G_I2S_SD1;
|
||||
_data_mux = MUX_PA08G_I2S_SD1;
|
||||
} else if ((dataport == 0) && (datapin == 19)) {
|
||||
// PA19
|
||||
_i2sserializer = I2S_SERIALIZER_0;
|
||||
_data_pin = PIN_PA19G_I2S_SD0;
|
||||
_data_mux = MUX_PA19G_I2S_SD0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
DEBUG_PRINTLN("Data isnt on a valid pin");
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize I2S module from the ASF.
|
||||
// replace "status_code res = i2s_init(&_i2s_instance, I2S);
|
||||
// if (res != STATUS_OK) {
|
||||
// DEBUG_PRINT("i2s_init failed with result: "); DEBUG_PRINTLN(res);
|
||||
// return false;
|
||||
// }" with:
|
||||
|
||||
/* Enable the user interface clock in the PM */
|
||||
//system_apb_clock_set_mask(SYSTEM_CLOCK_APB_APBC, PM_APBCMASK_I2S);
|
||||
PM->APBCMASK.reg |= PM_APBCMASK_I2S;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Status check */
|
||||
uint32_t ctrla = I2S->CTRLA.reg;
|
||||
if (ctrla & I2S_CTRLA_ENABLE) {
|
||||
if (ctrla & (I2S_CTRLA_SEREN1 |
|
||||
I2S_CTRLA_SEREN0 | I2S_CTRLA_CKEN1 | I2S_CTRLA_CKEN0)) {
|
||||
//return STATUS_BUSY;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//return STATUS_ERR_DENIED;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initialize module */
|
||||
_hw = I2S;
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void Adafruit_ZeroPDM::end(void) {
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & I2S_SYNCBUSY_ENABLE); // Sync wait
|
||||
_hw->CTRLA.reg &= ~I2S_SYNCBUSY_ENABLE;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool Adafruit_ZeroPDM::configure(uint32_t sampleRateHz, boolean stereo) {
|
||||
// Convert bit per sample int into explicit ASF values.
|
||||
|
||||
// Disable I2S while it is being reconfigured to prevent unexpected output.
|
||||
end();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************* Set the GCLK generator config and enable it. *************/
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Cache new register configurations to minimize sync requirements. */
|
||||
uint32_t new_genctrl_config = (_gclk << GCLK_GENCTRL_ID_Pos);
|
||||
uint32_t new_gendiv_config = (_gclk << GCLK_GENDIV_ID_Pos);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Select the requested source clock for the generator */
|
||||
// Set the clock generator to use the 48mhz main CPU clock and divide it down
|
||||
// to the SCK frequency.
|
||||
new_genctrl_config |= GCLK_SOURCE_DFLL48M << GCLK_GENCTRL_SRC_Pos;
|
||||
uint32_t division_factor = F_CPU / (sampleRateHz*16); // 16 clocks for 16 stereo bits
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set division factor */
|
||||
if (division_factor > 1) {
|
||||
/* Check if division is a power of two */
|
||||
if (((division_factor & (division_factor - 1)) == 0)) {
|
||||
/* Determine the index of the highest bit set to get the
|
||||
* division factor that must be loaded into the division
|
||||
* register */
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t div2_count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t mask;
|
||||
for (mask = (1UL << 1); mask < division_factor;
|
||||
mask <<= 1) {
|
||||
div2_count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set binary divider power of 2 division factor */
|
||||
new_gendiv_config |= div2_count << GCLK_GENDIV_DIV_Pos;
|
||||
new_genctrl_config |= GCLK_GENCTRL_DIVSEL;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
/* Set integer division factor */
|
||||
|
||||
new_gendiv_config |=
|
||||
(division_factor) << GCLK_GENDIV_DIV_Pos;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Enable non-binary division with increased duty cycle accuracy */
|
||||
new_genctrl_config |= GCLK_GENCTRL_IDC;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
noInterrupts(); // cpu_irq_enter_critical();
|
||||
|
||||
while (GCLK->STATUS.reg & GCLK_STATUS_SYNCBUSY); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->GENDIV.reg) = _gclk; /* Select the correct generator */
|
||||
|
||||
while (GCLK->STATUS.reg & GCLK_STATUS_SYNCBUSY); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
GCLK->GENDIV.reg = new_gendiv_config; /* Write the new generator configuration */
|
||||
|
||||
while (GCLK->STATUS.reg & GCLK_STATUS_SYNCBUSY); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
GCLK->GENCTRL.reg = new_genctrl_config | (GCLK->GENCTRL.reg & GCLK_GENCTRL_GENEN);
|
||||
|
||||
// Replace "system_gclk_gen_enable(_gclk);" with:
|
||||
|
||||
while (GCLK->STATUS.reg & GCLK_STATUS_SYNCBUSY); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->GENCTRL.reg) = _gclk; /* Select the requested generator */
|
||||
|
||||
while (GCLK->STATUS.reg & GCLK_STATUS_SYNCBUSY); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
GCLK->GENCTRL.reg |= GCLK_GENCTRL_GENEN; /* Enable generator */
|
||||
|
||||
interrupts(); // cpu_irq_leave_critical();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************* Configure I2S clock *************/
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Status check */
|
||||
/* Busy ? */
|
||||
if (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & (I2S_SYNCBUSY_CKEN0 << _i2sclock)) {
|
||||
return false; //return STATUS_BUSY;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Already enabled ? */
|
||||
if (_hw->CTRLA.reg & (I2S_CTRLA_CKEN0 << _i2sclock)) {
|
||||
|
||||
return false; //return STATUS_ERR_DENIED;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/***************************** Initialize Clock Unit *************/
|
||||
uint32_t clkctrl =
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_MCKOUTINV | // mck out not inverted
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_SCKOUTINV | // sck out not inverted
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_FSOUTINV | // fs not inverted
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_MCKEN | // Disable MCK output
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_MCKSEL | // Disable MCK output
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_SCKSEL | // SCK source is GCLK
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_FSINV | // do not invert frame sync
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_FSSEL | // Configure FS generation from SCK clock.
|
||||
// I2S_CLKCTRL_BITDELAY | // No bit delay (PDM)
|
||||
0;
|
||||
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_MCKOUTDIV(0);
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_MCKDIV(0);
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_NBSLOTS(1); // STEREO is '1' (subtract one from #)
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_FSWIDTH(I2S_FRAME_SYNC_WIDTH_SLOT); // Frame Sync (FS) Pulse is 1 Slot width
|
||||
if (stereo) {
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_SLOTSIZE(I2S_SLOT_SIZE_16_BIT);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
clkctrl |= I2S_CLKCTRL_SLOTSIZE(I2S_SLOT_SIZE_32_BIT);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write clock unit configurations */
|
||||
_hw->CLKCTRL[_i2sclock].reg = clkctrl;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Select general clock source */
|
||||
const uint8_t i2s_gclk_ids[2] = {I2S_GCLK_ID_0, I2S_GCLK_ID_1};
|
||||
|
||||
/* Cache the new config to reduce sync requirements */
|
||||
uint32_t new_clkctrl_config = (i2s_gclk_ids[_i2sclock] << GCLK_CLKCTRL_ID_Pos);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Select the desired generic clock generator */
|
||||
new_clkctrl_config |= _gclk << GCLK_CLKCTRL_GEN_Pos;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Disable generic clock channel */
|
||||
noInterrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
/* Select the requested generator channel */
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg) = i2s_gclk_ids[_i2sclock];
|
||||
|
||||
/* Switch to known-working source so that the channel can be disabled */
|
||||
uint32_t prev_gen_id = GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN;
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Disable the generic clock */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg &= ~GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN;
|
||||
while (GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg & GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN); /* Wait for clock to become disabled */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Restore previous configured clock generator */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.bit.GEN = prev_gen_id;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write the new configuration */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg = new_clkctrl_config;
|
||||
|
||||
// enable it
|
||||
*((uint8_t*)&GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg) = i2s_gclk_ids[_i2sclock]; /* Select the requested generator channel */
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg |= GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN; /* Enable the generic clock */
|
||||
|
||||
interrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initialize pins */
|
||||
pinPeripheral(_clk, (EPioType)_clk_mux);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/***************************** Configure I2S serializer *************/
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Status check */
|
||||
/* Busy ? */
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & ((I2S_SYNCBUSY_SEREN0 | I2S_SYNCBUSY_DATA0) << _i2sserializer)) {
|
||||
//return STATUS_BUSY;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Already enabled ? */
|
||||
if (_hw->CTRLA.reg & (I2S_CTRLA_CKEN0 << _i2sserializer)) {
|
||||
// return STATUS_ERR_DENIED;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initialize Serializer */
|
||||
uint32_t serctrl =
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_RXLOOP | // Dont use loopback mode
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_DMA | // Single DMA channel for all I2S channels
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_MONO | // Dont use MONO mode
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS7 | // Dont have any slot disabling
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS6 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS5 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS4 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS3 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS2 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS1 |
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTDIS0 |
|
||||
I2S_SERCTRL_BITREV | // Do not transfer LSB first (MSB first!)
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_WORDADJ | // Data NOT left in word
|
||||
I2S_SERCTRL_SLOTADJ | // Data is left in slot
|
||||
// I2S_SERCTRL_TXSAME | // Pad 0 on underrun
|
||||
0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Configure clock unit to use with serializer, and set serializer as an output.
|
||||
if (_i2sclock < 2) {
|
||||
serctrl |= (_i2sclock ? I2S_SERCTRL_CLKSEL : 0);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return false; //return STATUS_ERR_INVALID_ARG;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (stereo) {
|
||||
serctrl |= I2S_SERCTRL_SERMODE(I2S_SERIALIZER_PDM2); //Serializer is used to receive PDM data on each clock edge
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
serctrl |= I2S_SERCTRL_SERMODE(I2S_SERIALIZER_RECEIVE); // act like I2S
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Configure serializer data size.
|
||||
serctrl |= I2S_SERCTRL_DATASIZE(I2S_DATA_SIZE_32BIT); // anything other than 32 bits is ridiculous to manage, force this to be 32
|
||||
|
||||
serctrl |= I2S_SERCTRL_TXDEFAULT(I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_0) | /** Output default value is 0 */
|
||||
I2S_SERCTRL_EXTEND(I2S_DATA_PADDING_0); /** Padding 0 in case of under-run */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Write Serializer configuration */
|
||||
_hw->SERCTRL[_i2sserializer].reg = serctrl;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initialize pins */
|
||||
// Enable SD pin. See Adafruit_ZeroI2S.h for default pin value.
|
||||
pinPeripheral(_data, (EPioType)_data_mux);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/***************************** Enable everything configured above *************/
|
||||
|
||||
// Replace "i2s_enable(&_i2s_instance);" with:
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & I2S_SYNCBUSY_ENABLE); // Sync wait
|
||||
_hw->CTRLA.reg |= I2S_SYNCBUSY_ENABLE;
|
||||
|
||||
// Replace "i2s_clock_unit_enable(&_i2s_instance, _i2sclock);" with:
|
||||
uint32_t cken_bit = I2S_CTRLA_CKEN0 << _i2sclock;
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & cken_bit); // Sync wait
|
||||
_hw->CTRLA.reg |= cken_bit;
|
||||
|
||||
// Replace "i2s_serializer_enable(&_i2s_instance, _i2sserializer);" with:
|
||||
uint32_t seren_bit = I2S_CTRLA_SEREN0 << _i2sserializer;
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & seren_bit); // Sync wait
|
||||
_hw->CTRLA.reg |= seren_bit;
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint32_t Adafruit_ZeroPDM::read(void) {
|
||||
// Read the sample from the I2S data register.
|
||||
// This will wait for the I2S hardware to be ready to send the byte.
|
||||
//return i2s_serializer_read_wait(&_i2s_instance, _i2sserializer);
|
||||
|
||||
// replace i2s_serializer_read_wait with deASF'd code:
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint32_t sync_bit, ready_bit;
|
||||
uint32_t data;
|
||||
ready_bit = I2S_INTFLAG_RXRDY0 << _i2sserializer;
|
||||
while (!(_hw->INTFLAG.reg & ready_bit)) {
|
||||
/* Wait until ready to transmit */
|
||||
}
|
||||
sync_bit = I2S_SYNCBUSY_DATA0 << _i2sserializer;
|
||||
while (_hw->SYNCBUSY.reg & sync_bit) {
|
||||
/* Wait sync */
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Read data */
|
||||
data = _hw->DATA[_i2sserializer].reg;
|
||||
_hw->INTFLAG.reg = ready_bit;
|
||||
return data;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
|
||||
// Adafruit Arduino Zero / Feather M0 PDM mic library.
|
||||
// Author: Tony DiCola & Limor "Ladyada" Fried
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2016 Adafruit Industries
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
// copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
// SOFTWARE.
|
||||
#ifndef ADAFRUIT_ZEROPDM_H
|
||||
#define ADAFRUIT_ZEROPDM_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#include "wiring_private.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_SAMD)
|
||||
|
||||
// Uncomment to enable debug message output.
|
||||
#define DEBUG
|
||||
|
||||
// Define where debug output is printed (the native USB port on the Zero).
|
||||
#define DEBUG_PRINTER Serial
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Adafruit_ZeroPDM {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// Create a new instance of an I2S audio transmitter.
|
||||
// Can specify the pins to use and the generic clock ID to use for driving the I2S
|
||||
// hardware (default is GCLK 3).
|
||||
Adafruit_ZeroPDM(int clockpin, int datapin, uint8_t gclk = 3);
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize the I2S audio receiver.
|
||||
bool begin();
|
||||
void end();
|
||||
|
||||
// Configure the transmitter with the sample rate (in hertz
|
||||
bool configure(uint32_t sampleRateHz, boolean stereo);
|
||||
|
||||
// Read a single sample from the I2S subsystem. Will wait until the I2S
|
||||
// hardware is ready to receive the sample.
|
||||
uint32_t read(void);
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t getSerializer(void) { return _i2sserializer; };
|
||||
bool read(uint32_t *buffer, int bufsiz);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int _clk, _data;
|
||||
uint32_t _clk_pin, _clk_mux, _data_pin, _data_mux;
|
||||
uint8_t _i2sserializer;
|
||||
uint8_t _i2sclock;
|
||||
uint8_t _gclk;
|
||||
|
||||
I2s *_hw;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef I2S_H_INCLUDED
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Master Clock (MCK) source selection
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_master_clock_source {
|
||||
/** Master Clock (MCK) is from general clock */
|
||||
I2S_MASTER_CLOCK_SOURCE_GCLK,
|
||||
/** Master Clock (MCK) is from MCK input pin */
|
||||
I2S_MASTER_CLOCK_SOURCE_MCKPIN
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Serial Clock (SCK) source selection
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_serial_clock_source {
|
||||
/** Serial Clock (SCK) is divided from Master Clock */
|
||||
I2S_SERIAL_CLOCK_SOURCE_MCKDIV,
|
||||
/** Serial Clock (SCK) is input from SCK input pin */
|
||||
I2S_SERIAL_CLOCK_SOURCE_SCKPIN
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Data delay from Frame Sync (FS)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_data_delay {
|
||||
/** Left Justified (no delay) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_DELAY_0,
|
||||
/** I2S data delay (1-bit delay) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_DELAY_1,
|
||||
/** Left Justified (no delay) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_DELAY_LEFT_JUSTIFIED = I2S_DATA_DELAY_0,
|
||||
/** I2S data delay (1-bit delay) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_DELAY_I2S = I2S_DATA_DELAY_1
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Frame Sync (FS) source
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_frame_sync_source {
|
||||
/** Frame Sync (FS) is divided from I2S Serial Clock */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_SOURCE_SCKDIV,
|
||||
/** Frame Sync (FS) is input from FS input pin */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_SOURCE_FSPIN
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Frame Sync (FS) output pulse width
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_frame_sync_width {
|
||||
/** Frame Sync (FS) Pulse is 1 Slot width */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_WIDTH_SLOT,
|
||||
/** Frame Sync (FS) Pulse is half a Frame width */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_WIDTH_HALF_FRAME,
|
||||
/** Frame Sync (FS) Pulse is 1 Bit width */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_WIDTH_BIT,
|
||||
/** 1-bit wide Frame Sync (FS) per Data sample, only used when Data transfer
|
||||
* is requested */
|
||||
I2S_FRAME_SYNC_WIDTH_BURST
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Time Slot Size in number of I2S serial clocks (bits)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_slot_size {
|
||||
/** 8-bit slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_SIZE_8_BIT,
|
||||
/** 16-bit slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_SIZE_16_BIT,
|
||||
/** 24-bit slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_SIZE_24_BIT,
|
||||
/** 32-bit slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_SIZE_32_BIT
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* DMA channels usage for I2S
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_dma_usage {
|
||||
/** Single DMA channel for all I2S channels */
|
||||
I2S_DMA_USE_SINGLE_CHANNEL_FOR_ALL,
|
||||
/** One DMA channel per data channel */
|
||||
I2S_DMA_USE_ONE_CHANNEL_PER_DATA_CHANNEL
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data format, to extend mono data to 2 channels
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_data_format {
|
||||
/** Normal mode, keep data to its right channel */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_FORMAT_STEREO,
|
||||
/** Assume input is mono data for left channel, the data is duplicated to
|
||||
* right channel */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_FORMAT_MONO
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data bit order
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_bit_order {
|
||||
/** Transfer Data Most Significant Bit first (Default for I2S protocol) */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_ORDER_MSB_FIRST,
|
||||
/** Transfer Data Least Significant Bit first */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_ORDER_LSB_FIRST
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data bit padding
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_bit_padding {
|
||||
/** Padding with 0 */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_PADDING_0,
|
||||
/** Padding with 1 */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_PADDING_1,
|
||||
/** Padding with MSBit */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_PADDING_MSB,
|
||||
/** Padding with LSBit */
|
||||
I2S_BIT_PADDING_LSB,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data word adjust
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_data_adjust {
|
||||
/** Data is right adjusted in word */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_ADJUST_RIGHT,
|
||||
/** Data is left adjusted in word */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_ADJUST_LEFT
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data word size
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_data_size {
|
||||
/** 32-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_32BIT,
|
||||
/** 24-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_24BIT,
|
||||
/** 20-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_20BIT,
|
||||
/** 18-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_18BIT,
|
||||
/** 16-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_16BIT,
|
||||
/** 16-bit compact stereo */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_16BIT_COMPACT,
|
||||
/** 8-bit */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_8BIT,
|
||||
/** 8-bit compact stereo */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_SIZE_8BIT_COMPACT
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data slot adjust
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_slot_adjust {
|
||||
/** Data is right adjusted in slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_ADJUST_RIGHT,
|
||||
/** Data is left adjusted in slot */
|
||||
I2S_SLOT_ADJUST_LEFT
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S data padding
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_data_padding {
|
||||
/** Padding 0 in case of under-run */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_PADDING_0,
|
||||
/** Padding last data in case of under-run */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME_AS_LAST,
|
||||
/** Padding last data in case of under-run
|
||||
* (abbr. \c I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME_AS_LAST) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_PADDING_LAST = I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME_AS_LAST,
|
||||
/** Padding last data in case of under-run
|
||||
* (abbr. \c I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME_AS_LAST) */
|
||||
I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME = I2S_DATA_PADDING_SAME_AS_LAST
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S line default value when slot disabled
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_line_default_state {
|
||||
/** Output default value is 0 */
|
||||
I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_0,
|
||||
/** Output default value is 1 */
|
||||
I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_1,
|
||||
/** Output default value is high impedance */
|
||||
I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_HIGH_IMPEDANCE = 3,
|
||||
/** Output default value is high impedance
|
||||
* (abbr. \c I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_HIGH_IMPEDANCE) */
|
||||
I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_HIZ = I2S_LINE_DEFAULT_HIGH_IMPEDANCE
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S Serializer mode
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_serializer_mode {
|
||||
/** Serializer is used to receive data */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_RECEIVE,
|
||||
/** Serializer is used to transmit data */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_TRANSMIT,
|
||||
/** Serializer is used to receive PDM data on each clock edge */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_PDM2
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S clock unit selection
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_clock_unit {
|
||||
/** Clock Unit channel 0 */
|
||||
I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_0,
|
||||
/** Clock Unit channel 1 */
|
||||
I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_1,
|
||||
/** Number of Clock Unit channels */
|
||||
I2S_CLOCK_UNIT_N
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* I2S Serializer selection
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enum i2s_serializer {
|
||||
/** Serializer channel 0 */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_0,
|
||||
/** Serializer channel 1 */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_1,
|
||||
/** Number of Serializer channels */
|
||||
I2S_SERIALIZER_N
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,824 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Boards.h - Hardware Abstraction Layer for Firmata library
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2006-2008 Hans-Christoph Steiner. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2009-2016 Jeff Hoefs. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
See file LICENSE.txt for further informations on licensing terms.
|
||||
|
||||
Last updated April 10th, 2016
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef Firmata_Boards_h
|
||||
#define Firmata_Boards_h
|
||||
|
||||
#include <inttypes.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO) && ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h" // for digitalRead, digitalWrite, etc
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Normally Servo.h must be included before Firmata.h (which then includes
|
||||
// this file). If Servo.h wasn't included, this allows the code to still
|
||||
// compile, but without support for any Servos. Hopefully that's what the
|
||||
// user intended by not including Servo.h
|
||||
#ifndef MAX_SERVOS
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Firmata Hardware Abstraction Layer
|
||||
|
||||
Firmata is built on top of the hardware abstraction functions of Arduino,
|
||||
specifically digitalWrite, digitalRead, analogWrite, analogRead, and
|
||||
pinMode. While these functions offer simple integer pin numbers, Firmata
|
||||
needs more information than is provided by Arduino. This file provides
|
||||
all other hardware specific details. To make Firmata support a new board,
|
||||
only this file should require editing.
|
||||
|
||||
The key concept is every "pin" implemented by Firmata may be mapped to
|
||||
any pin as implemented by Arduino. Usually a simple 1-to-1 mapping is
|
||||
best, but such mapping should not be assumed. This hardware abstraction
|
||||
layer allows Firmata to implement any number of pins which map onto the
|
||||
Arduino implemented pins in almost any arbitrary way.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
General Constants:
|
||||
|
||||
These constants provide basic information Firmata requires.
|
||||
|
||||
TOTAL_PINS: The total number of pins Firmata implemented by Firmata.
|
||||
Usually this will match the number of pins the Arduino functions
|
||||
implement, including any pins pins capable of analog or digital.
|
||||
However, Firmata may implement any number of pins. For example,
|
||||
on Arduino Mini with 8 analog inputs, 6 of these may be used
|
||||
for digital functions, and 2 are analog only. On such boards,
|
||||
Firmata can implement more pins than Arduino's pinMode()
|
||||
function, in order to accommodate those special pins. The
|
||||
Firmata protocol supports a maximum of 128 pins, so this
|
||||
constant must not exceed 128.
|
||||
|
||||
TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS: The total number of analog input pins implemented.
|
||||
The Firmata protocol allows up to 16 analog inputs, accessed
|
||||
using offsets 0 to 15. Because Firmata presents the analog
|
||||
inputs using different offsets than the actual pin numbers
|
||||
(a legacy of Arduino's analogRead function, and the way the
|
||||
analog input capable pins are physically labeled on all
|
||||
Arduino boards), the total number of analog input signals
|
||||
must be specified. 16 is the maximum.
|
||||
|
||||
VERSION_BLINK_PIN: When Firmata starts up, it will blink the version
|
||||
number. This constant is the Arduino pin number where a
|
||||
LED is connected.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Pin Mapping Macros:
|
||||
|
||||
These macros provide the mapping between pins as implemented by
|
||||
Firmata protocol and the actual pin numbers used by the Arduino
|
||||
functions. Even though such mappings are often simple, pin
|
||||
numbers received by Firmata protocol should always be used as
|
||||
input to these macros, and the result of the macro should be
|
||||
used with with any Arduino function.
|
||||
|
||||
When Firmata is extended to support a new pin mode or feature,
|
||||
a pair of macros should be added and used for all hardware
|
||||
access. For simple 1:1 mapping, these macros add no actual
|
||||
overhead, yet their consistent use allows source code which
|
||||
uses them consistently to be easily adapted to all other boards
|
||||
with different requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
IS_PIN_XXXX(pin): The IS_PIN macros resolve to true or non-zero
|
||||
if a pin as implemented by Firmata corresponds to a pin
|
||||
that actually implements the named feature.
|
||||
|
||||
PIN_TO_XXXX(pin): The PIN_TO macros translate pin numbers as
|
||||
implemented by Firmata to the pin numbers needed as inputs
|
||||
to the Arduino functions. The corresponding IS_PIN macro
|
||||
should always be tested before using a PIN_TO macro, so
|
||||
these macros only need to handle valid Firmata pin
|
||||
numbers for the named feature.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Port Access Inline Funtions:
|
||||
|
||||
For efficiency, Firmata protocol provides access to digital
|
||||
input and output pins grouped by 8 bit ports. When these
|
||||
groups of 8 correspond to actual 8 bit ports as implemented
|
||||
by the hardware, these inline functions can provide high
|
||||
speed direct port access. Otherwise, a default implementation
|
||||
using 8 calls to digitalWrite or digitalRead is used.
|
||||
|
||||
When porting Firmata to a new board, it is recommended to
|
||||
use the default functions first and focus only on the constants
|
||||
and macros above. When those are working, if optimized port
|
||||
access is desired, these inline functions may be extended.
|
||||
The recommended approach defines a symbol indicating which
|
||||
optimization to use, and then conditional complication is
|
||||
used within these functions.
|
||||
|
||||
readPort(port, bitmask): Read an 8 bit port, returning the value.
|
||||
port: The port number, Firmata pins port*8 to port*8+7
|
||||
bitmask: The actual pins to read, indicated by 1 bits.
|
||||
|
||||
writePort(port, value, bitmask): Write an 8 bit port.
|
||||
port: The port number, Firmata pins port*8 to port*8+7
|
||||
value: The 8 bit value to write
|
||||
bitmask: The actual pins to write, indicated by 1 bits.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*==============================================================================
|
||||
* Board Specific Configuration
|
||||
*============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef digitalPinHasPWM
|
||||
#define digitalPinHasPWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino Duemilanove, Diecimila, and NG
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega168__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega328P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega328__)
|
||||
#if defined(NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS) && NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS == 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 20 // 14 digital + 6 analog
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 8
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 22 // 14 digital + 8 analog
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) < 14 + TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) - 2 < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 18 || (p) == 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
#define ARDUINO_PINOUT_OPTIMIZE 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Wiring (and board)
|
||||
#elif defined(WIRING)
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN WLED
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= FIRST_ANALOG_PIN && (p) < (FIRST_ANALOG_PIN+TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SDA || (p) == SCL)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - FIRST_ANALOG_PIN)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// old Arduinos
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega8__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 20 // 14 digital + 6 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) - 2 < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 18 || (p) == 19)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
#define ARDUINO_PINOUT_OPTIMIZE 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino Mega
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 16
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 70 // 54 digital + 16 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 19
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 18
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_RX 17
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_TX 16
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_RX 15
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_TX 14
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 54 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) - 2 < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 20 || (p) == 21)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) > 13 && (p) < 20)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 54)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino DUE
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAM3X8E__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 12
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 66 // 54 digital + 12 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 19
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 18
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_RX 17
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_TX 16
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_RX 15
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_TX 14
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 54 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) - 2 < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 20 || (p) == 21) // 70 71
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) > 13 && (p) < 20)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 54)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino/Genuino MKR1000
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_SAMD_MKR1000)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 7
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 22 // 8 digital + 3 spi + 2 i2c + 2 uart + 7 analog
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) (((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 21) && !IS_PIN_SERIAL(p))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 15 && (p) < 15 + TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) < MAX_SERVOS) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 11 || (p) == 12) // SDA = 11, SCL = 12
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == PIN_SERIAL1_RX || (p) == PIN_SERIAL1_TX) //defined in variant.h RX = 13, TX = 14
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 15)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino Zero
|
||||
// Note this will work with an Arduino Zero Pro, but not with an Arduino M0 Pro
|
||||
// Arduino M0 Pro does not properly map pins to the board labeled pin numbers
|
||||
#elif defined(_VARIANT_ARDUINO_ZERO_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 25 // 14 digital + 6 analog + 2 i2c + 3 spi
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PORTS 3 // set when TOTAL_PINS > num digitial I/O pins
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN LED_BUILTIN
|
||||
//#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0 // already defined in zero core variant.h
|
||||
//#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1 // already defined in zero core variant.h
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) < 14 + TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) < MAX_SERVOS) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 20 || (p) == 21) // SDA = 20, SCL = 21
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK) // SS = A2
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino 101
|
||||
#elif defined(_VARIANT_ARDUINO_101_X_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 15 digital (including ATN pin) + 6 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN LED_BUILTIN
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 20)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) < 14 + TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p) // 3, 5, 6, 9
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) < MAX_SERVOS) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SDA || (p) == SCL) // SDA = 18, SCL = 19
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Teensy 1.0
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_AT90USB162__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 0
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 21 // 21 digital + no analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 6
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 2
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 3
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) (0)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) (0)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 2 || (p) == 3)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (0)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Teensy 2.0
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) && defined(CORE_TEENSY)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 12
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 25 // 11 digital + 12 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 11
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 7
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 8
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 11 && (p) <= 22)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 5 || (p) == 6)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 7 || (p) == 8)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (((p) < 22) ? 21 - (p) : 11)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Teensy 3.0, 3.1 and 3.2
|
||||
#elif defined(__MK20DX128__) || defined(__MK20DX256__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 14
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 38 // 24 digital + 10 analog-digital + 4 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_RX 9
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_TX 10
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_RX 7
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_TX 8
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 33)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) (((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 23) || ((p) >= 34 && (p) <= 38))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 18 || (p) == 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) (((p) > 6 && (p) < 11) || ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (((p) <= 23) ? (p) - 14 : (p) - 24)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Teensy-LC
|
||||
#elif defined(__MKL26Z64__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 13
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 27 // 27 digital + 13 analog-digital
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_RX 9
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL2_TX 10
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_RX 7
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL3_TX 8
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 26)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 18 || (p) == 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) (((p) > 6 && (p) < 11) || ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Teensy++ 1.0 and 2.0
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_AT90USB646__) || defined(__AVR_AT90USB1286__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 8
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 46 // 38 digital + 8 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 6
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 2
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 3
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 38 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 2 || (p) == 3)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 38)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Leonardo
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 12
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 30 // 14 digital + 12 analog + 4 SPI (D14-D17 on ISP header)
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 18 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) ((p) == 3 || (p) == 5 || (p) == 6 || (p) == 9 || (p) == 10 || (p) == 11 || (p) == 13)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 2 || (p) == 3)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (p) - 18
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Intel Galileo Board (gen 1 and 2) and Intel Edison
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_LINUX)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 20 // 14 digital + 6 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) - 2 < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SDA || (p) == SCL)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// RedBearLab BLE Nano with factory switch settings (S1 - S10)
|
||||
#elif defined(BLE_NANO)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 15 // 9 digital + 3 analog
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 14)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) == 8 || (p) == 9 || (p) == 10 || (p) == 11 || (p) == 12 || (p) == 14) //A0~A5
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) ((p) == 3 || (p) == 5 || (p) == 6)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 7)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SDA || (p) == SCL)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == CS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 8)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Sanguino
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega644__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 8
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 32 // 24 digital + 8 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 0
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 24 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 16 || (p) == 17)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 24)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Illuminato
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega645__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 42 // 36 digital + 6 analog
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 13
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 36 && (p) < TOTAL_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 4 || (p) == 5)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 36)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT FubarinoSD
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_FUBARINO_SD_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS // 15
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 45, All pins can be digital
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) 1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 30 && (p) <= 44)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 1 || (p) == 2)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (14 - (p - 30))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT FubarinoMini
|
||||
// Note, FubarinoMini analog pin 20 will not function in Firmata as analog input due to limitation in analog mapping
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_FUBARINO_MINI_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 14 // We have to fake this because of the poor analog pin mapping planning in FubarinoMini
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 33
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) != 14 && (p) != 15 && (p) != 31 && (p) != 32)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) == 0 || ((p) >= 3 && (p) <= 13))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 25 || (p) == 26)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT UNO32
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_UNO_) && defined(__PIC32) // NOTE: no _BOARD_UNO32_ to use
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS // 12
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 47 All pins can be digital
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // All pins can be servo with SoftPWMservo
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 25)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 45 || (p) == 46)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT DP32
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_DP32_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 15 // Really only has 9, but have to override because of mistake in variant file
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 19
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // All pins can be servo with SoftPWMservo
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) (((p) != 1) && ((p) != 4) && ((p) != 5) && ((p) != 15) && ((p) != 16))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 6 && (p) <= 14)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 2 || (p) == 3)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT uC32
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_UC32_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS // 12
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 47 All pins can be digital
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // All pins can be servo with SoftPWMservo
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 25)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 45 || (p) == 46)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT WF32
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_WF32_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 49) // Accounts for SD and WiFi dedicated pins
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 25)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 34 || (p) == 35)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT WiFire
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_WIFIRE_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS // 14
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 71
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2 && (p) <= 47) // Accounts for SD and WiFi dedicated pins
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 25)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 34 || (p) == 35)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) <= 25 ? ((p) - 14) : (p) - 36)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT MAX32
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_MEGA_) && defined(__PIC32) // NOTE: no _BOARD_MAX32_ to use
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_PINS // 16
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 87
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 2)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 54 && (p) <= 69)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 34 || (p) == 35)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 54)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Pic32 chipKIT Pi
|
||||
#elif defined(_BOARD_CHIPKIT_PI_)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 16
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 19
|
||||
#define MAX_SERVOS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN PIN_LED1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) (((p) >= 2) && ((p) <= 3) || (((p) >= 8) && ((p) <= 13)) || (((p) >= 14) && ((p) <= 17)))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) <= 17)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 16 || (p) == 17)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) <= 15 ? (p) - 14 : (p) - 12)
|
||||
//#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) (((p) <= 16) ? ((p) - 14) : ((p) - 16))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
|
||||
// Pinoccio Scout
|
||||
// Note: digital pins 9-16 are usable but not labeled on the board numerically.
|
||||
// SS=9, MOSI=10, MISO=11, SCK=12, RX1=13, TX1=14, SCL=15, SDA=16
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_PINOCCIO)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 8
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS NUM_DIGITAL_PINS // 32
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN 23
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 13
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 14
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) (((p) >= 2) && ((p) <= 16)) || (((p) >= 24) && ((p) <= 31))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 24 && (p) <= 31)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SCL || (p) == SDA)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 13 || (p) == 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 24)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) ((p) - 2)
|
||||
|
||||
// ESP8266
|
||||
// note: boot mode GPIOs 0, 2 and 15 can be used as outputs, GPIOs 6-11 are in use for flash IO
|
||||
#elif defined(ESP8266)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS A0 + NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL_RX 3
|
||||
#define PIN_SERIAL_TX 1
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) (((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 5) || ((p) >= 12 && (p) < A0))
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= A0 && (p) < A0 + NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) < MAX_SERVOS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == SDA || (p) == SCL)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_INTERRUPT(p) (digitalPinToInterrupt(p) > NOT_AN_INTERRUPT)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == PIN_SERIAL_RX || (p) == PIN_SERIAL_TX)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - A0)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_SERVO(p) (p)
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_PWM_RESOLUTION 10
|
||||
|
||||
// Circuit Playground Express
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
#define TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS 6
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PINS 25 // 14 digital + 6 analog + 2 i2c + 3 spi
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PORTS 3 // set when TOTAL_PINS > num digitial I/O pins
|
||||
#define VERSION_BLINK_PIN LED_BUILTIN
|
||||
//#define PIN_SERIAL1_RX 0 // already defined in zero core variant.h
|
||||
//#define PIN_SERIAL1_TX 1 // already defined in zero core variant.h
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) ((p) >= 0 && (p) <= 19)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_ANALOG(p) ((p) >= 14 && (p) < 14 + TOTAL_ANALOG_PINS)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_PWM(p) digitalPinHasPWM(p)
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERVO(p) (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(p) && (p) < MAX_SERVOS) // deprecated since v2.4
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_I2C(p) ((p) == 20 || (p) == 21) // SDA = 20, SCL = 21
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) ((p) == SS || (p) == MOSI || (p) == MISO || (p) == SCK) // SS = A2
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) ((p) == 0 || (p) == 1)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p) (p)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_ANALOG(p) ((p) - 14)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_PWM(p) PIN_TO_DIGITAL(p)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// anything else
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Please edit CP_Boards.h with a hardware abstraction for this board"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// as long this is not defined for all boards:
|
||||
#ifndef IS_PIN_SPI
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SPI(p) 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IS_PIN_SERIAL
|
||||
#define IS_PIN_SERIAL(p) 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef DEFAULT_PWM_RESOLUTION
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_PWM_RESOLUTION 8
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/*==============================================================================
|
||||
* readPort() - Read an 8 bit port
|
||||
*============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
static inline unsigned char readPort(byte, byte) __attribute__((always_inline, unused));
|
||||
static inline unsigned char readPort(byte port, byte bitmask)
|
||||
{
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_PINOUT_OPTIMIZE)
|
||||
if (port == 0) return (PIND & 0xFC) & bitmask; // ignore Rx/Tx 0/1
|
||||
if (port == 1) return ((PINB & 0x3F) | ((PINC & 0x03) << 6)) & bitmask;
|
||||
if (port == 2) return ((PINC & 0x3C) >> 2) & bitmask;
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
unsigned char out = 0, pin = port * 8;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 0) && (bitmask & 0x01) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 0))) out |= 0x01;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 1) && (bitmask & 0x02) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 1))) out |= 0x02;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 2) && (bitmask & 0x04) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 2))) out |= 0x04;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 3) && (bitmask & 0x08) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 3))) out |= 0x08;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 4) && (bitmask & 0x10) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 4))) out |= 0x10;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 5) && (bitmask & 0x20) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 5))) out |= 0x20;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 6) && (bitmask & 0x40) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 6))) out |= 0x40;
|
||||
if (IS_PIN_DIGITAL(pin + 7) && (bitmask & 0x80) && digitalRead(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 7))) out |= 0x80;
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*==============================================================================
|
||||
* writePort() - Write an 8 bit port, only touch pins specified by a bitmask
|
||||
*============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
static inline unsigned char writePort(byte, byte, byte) __attribute__((always_inline, unused));
|
||||
static inline unsigned char writePort(byte port, byte value, byte bitmask)
|
||||
{
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_PINOUT_OPTIMIZE)
|
||||
if (port == 0) {
|
||||
bitmask = bitmask & 0xFC; // do not touch Tx & Rx pins
|
||||
byte valD = value & bitmask;
|
||||
byte maskD = ~bitmask;
|
||||
cli();
|
||||
PORTD = (PORTD & maskD) | valD;
|
||||
sei();
|
||||
} else if (port == 1) {
|
||||
byte valB = (value & bitmask) & 0x3F;
|
||||
byte valC = (value & bitmask) >> 6;
|
||||
byte maskB = ~(bitmask & 0x3F);
|
||||
byte maskC = ~((bitmask & 0xC0) >> 6);
|
||||
cli();
|
||||
PORTB = (PORTB & maskB) | valB;
|
||||
PORTC = (PORTC & maskC) | valC;
|
||||
sei();
|
||||
} else if (port == 2) {
|
||||
bitmask = bitmask & 0x0F;
|
||||
byte valC = (value & bitmask) << 2;
|
||||
byte maskC = ~(bitmask << 2);
|
||||
cli();
|
||||
PORTC = (PORTC & maskC) | valC;
|
||||
sei();
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
byte pin = port * 8;
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x01)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 0), (value & 0x01));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x02)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 1), (value & 0x02));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x04)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 2), (value & 0x04));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x08)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 3), (value & 0x08));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x10)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 4), (value & 0x10));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x20)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 5), (value & 0x20));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x40)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 6), (value & 0x40));
|
||||
if ((bitmask & 0x80)) digitalWrite(PIN_TO_DIGITAL(pin + 7), (value & 0x80));
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef TOTAL_PORTS
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PORTS ((TOTAL_PINS + 7) / 8)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* Firmata_Boards_h */
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,668 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Firmata.cpp - Firmata library v2.5.3 - 2016-06-18
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2006-2008 Hans-Christoph Steiner. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2009-2016 Jeff Hoefs. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
See file LICENSE.txt for further informations on licensing terms.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
//* Includes
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
#include "CP_Firmata.h"
|
||||
#include "HardwareSerial.h"
|
||||
|
||||
extern "C" {
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
//* Support Functions
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Split a 16-bit byte into two 7-bit values and write each value.
|
||||
* @param value The 16-bit value to be split and written separately.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendValueAsTwo7bitBytes(int value)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(value & 0x7F); // LSB
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(value >> 7 & 0x7F); // MSB
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A helper method to write the beginning of a Sysex message transmission.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::startSysex(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(START_SYSEX);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A helper method to write the end of a Sysex message transmission.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::endSysex(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(END_SYSEX);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
//* Constructors
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The Firmata class.
|
||||
* An instance named "Firmata" is created automatically for the user.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
FirmataClass::FirmataClass()
|
||||
{
|
||||
firmwareVersionCount = 0;
|
||||
firmwareVersionVector = 0;
|
||||
systemReset();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
//* Public Methods
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Initialize the default Serial transport at the default baud of 57600.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::begin(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
begin(57600);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Initialize the default Serial transport and override the default baud.
|
||||
* Sends the protocol version to the host application followed by the firmware version and name.
|
||||
* blinkVersion is also called. To skip the call to blinkVersion, call Firmata.disableBlinkVersion()
|
||||
* before calling Firmata.begin(baud).
|
||||
* @param speed The baud to use. 57600 baud is the default value.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::begin(long speed)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(speed);
|
||||
FirmataStream = &Serial;
|
||||
blinkVersion();
|
||||
printVersion(); // send the protocol version
|
||||
printFirmwareVersion(); // send the firmware name and version
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Reassign the Firmata stream transport.
|
||||
* @param s A reference to the Stream transport object. This can be any type of
|
||||
* transport that implements the Stream interface. Some examples include Ethernet, WiFi
|
||||
* and other UARTs on the board (Serial1, Serial2, etc).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::begin(Stream &s)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream = &s;
|
||||
// do not call blinkVersion() here because some hardware such as the
|
||||
// Ethernet shield use pin 13
|
||||
printVersion();
|
||||
printFirmwareVersion();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send the Firmata protocol version to the Firmata host application.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::printVersion(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(REPORT_VERSION);
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MAJOR_VERSION);
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MINOR_VERSION);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Blink the Firmata protocol version to the onboard LEDs (if the board has an onboard LED).
|
||||
* If VERSION_BLINK_PIN is not defined in Boards.h for a particular board, then this method
|
||||
* does nothing.
|
||||
* The first series of flashes indicates the firmware major version (2 flashes = 2).
|
||||
* The second series of flashes indicates the firmware minor version (5 flashes = 5).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::blinkVersion(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
#if defined(VERSION_BLINK_PIN)
|
||||
if (blinkVersionDisabled) return;
|
||||
// flash the pin with the protocol version
|
||||
pinMode(VERSION_BLINK_PIN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
strobeBlinkPin(VERSION_BLINK_PIN, FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MAJOR_VERSION, 40, 210);
|
||||
delay(250);
|
||||
strobeBlinkPin(VERSION_BLINK_PIN, FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MINOR_VERSION, 40, 210);
|
||||
delay(125);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Provides a means to disable the version blink sequence on the onboard LED, trimming startup
|
||||
* time by a couple of seconds.
|
||||
* Call this before Firmata.begin(). It only applies when using the default Serial transport.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::disableBlinkVersion()
|
||||
{
|
||||
blinkVersionDisabled = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Sends the firmware name and version to the Firmata host application. The major and minor version
|
||||
* numbers are the first 2 bytes in the message. The following bytes are the characters of the
|
||||
* firmware name.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::printFirmwareVersion(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
byte i;
|
||||
|
||||
if (firmwareVersionCount) { // make sure that the name has been set before reporting
|
||||
startSysex();
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(REPORT_FIRMWARE);
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(firmwareVersionVector[0]); // major version number
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(firmwareVersionVector[1]); // minor version number
|
||||
for (i = 2; i < firmwareVersionCount; ++i) {
|
||||
sendValueAsTwo7bitBytes(firmwareVersionVector[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
endSysex();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Sets the name and version of the firmware. This is not the same version as the Firmata protocol
|
||||
* (although at times the firmware version and protocol version may be the same number).
|
||||
* @param name A pointer to the name char array
|
||||
* @param major The major version number
|
||||
* @param minor The minor version number
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::setFirmwareNameAndVersion(const char *name, byte major, byte minor)
|
||||
{
|
||||
const char *firmwareName;
|
||||
const char *extension;
|
||||
|
||||
// parse out ".cpp" and "applet/" that comes from using __FILE__
|
||||
extension = strstr(name, ".cpp");
|
||||
firmwareName = strrchr(name, '/');
|
||||
|
||||
if (!firmwareName) {
|
||||
// windows
|
||||
firmwareName = strrchr(name, '\\');
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!firmwareName) {
|
||||
// user passed firmware name
|
||||
firmwareName = name;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
firmwareName ++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!extension) {
|
||||
firmwareVersionCount = strlen(firmwareName) + 2;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
firmwareVersionCount = extension - firmwareName + 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// in case anyone calls setFirmwareNameAndVersion more than once
|
||||
free(firmwareVersionVector);
|
||||
|
||||
firmwareVersionVector = (byte *) malloc(firmwareVersionCount + 1);
|
||||
firmwareVersionVector[firmwareVersionCount] = 0;
|
||||
firmwareVersionVector[0] = major;
|
||||
firmwareVersionVector[1] = minor;
|
||||
strncpy((char *)firmwareVersionVector + 2, firmwareName, firmwareVersionCount - 2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// Serial Receive Handling
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A wrapper for Stream::available()
|
||||
* @return The number of bytes remaining in the input stream buffer.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int FirmataClass::available(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return FirmataStream->available();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Process incoming sysex messages. Handles REPORT_FIRMWARE and STRING_DATA internally.
|
||||
* Calls callback function for STRING_DATA and all other sysex messages.
|
||||
* @private
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::processSysexMessage(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch (storedInputData[0]) { //first byte in buffer is command
|
||||
case REPORT_FIRMWARE:
|
||||
printFirmwareVersion();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STRING_DATA:
|
||||
if (currentStringCallback) {
|
||||
byte bufferLength = (sysexBytesRead - 1) / 2;
|
||||
byte i = 1;
|
||||
byte j = 0;
|
||||
while (j < bufferLength) {
|
||||
// The string length will only be at most half the size of the
|
||||
// stored input buffer so we can decode the string within the buffer.
|
||||
storedInputData[j] = storedInputData[i];
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
storedInputData[j] += (storedInputData[i] << 7);
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
j++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Make sure string is null terminated. This may be the case for data
|
||||
// coming from client libraries in languages that don't null terminate
|
||||
// strings.
|
||||
if (storedInputData[j - 1] != '\0') {
|
||||
storedInputData[j] = '\0';
|
||||
}
|
||||
(*currentStringCallback)((char *)&storedInputData[0]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if (currentSysexCallback)
|
||||
(*currentSysexCallback)(storedInputData[0], sysexBytesRead - 1, storedInputData + 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Read a single int from the input stream. If the value is not = -1, pass it on to parse(byte)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::processInput(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int inputData = FirmataStream->read(); // this is 'int' to handle -1 when no data
|
||||
if (inputData != -1) {
|
||||
parse(inputData);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Parse data from the input stream.
|
||||
* @param inputData A single byte to be added to the parser.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::parse(byte inputData)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int command;
|
||||
|
||||
if (parsingSysex) {
|
||||
if (inputData == END_SYSEX) {
|
||||
//stop sysex byte
|
||||
parsingSysex = false;
|
||||
//fire off handler function
|
||||
processSysexMessage();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//normal data byte - add to buffer
|
||||
storedInputData[sysexBytesRead] = inputData;
|
||||
sysexBytesRead++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ( (waitForData > 0) && (inputData < 128) ) {
|
||||
waitForData--;
|
||||
storedInputData[waitForData] = inputData;
|
||||
if ( (waitForData == 0) && executeMultiByteCommand ) { // got the whole message
|
||||
switch (executeMultiByteCommand) {
|
||||
case ANALOG_MESSAGE:
|
||||
if (currentAnalogCallback) {
|
||||
(*currentAnalogCallback)(multiByteChannel,
|
||||
(storedInputData[0] << 7)
|
||||
+ storedInputData[1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case DIGITAL_MESSAGE:
|
||||
if (currentDigitalCallback) {
|
||||
(*currentDigitalCallback)(multiByteChannel,
|
||||
(storedInputData[0] << 7)
|
||||
+ storedInputData[1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case SET_PIN_MODE:
|
||||
if (currentPinModeCallback)
|
||||
(*currentPinModeCallback)(storedInputData[1], storedInputData[0]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE:
|
||||
if (currentPinValueCallback)
|
||||
(*currentPinValueCallback)(storedInputData[1], storedInputData[0]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case REPORT_ANALOG:
|
||||
if (currentReportAnalogCallback)
|
||||
(*currentReportAnalogCallback)(multiByteChannel, storedInputData[0]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case REPORT_DIGITAL:
|
||||
if (currentReportDigitalCallback)
|
||||
(*currentReportDigitalCallback)(multiByteChannel, storedInputData[0]);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
executeMultiByteCommand = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// remove channel info from command byte if less than 0xF0
|
||||
if (inputData < 0xF0) {
|
||||
command = inputData & 0xF0;
|
||||
multiByteChannel = inputData & 0x0F;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
command = inputData;
|
||||
// commands in the 0xF* range don't use channel data
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch (command) {
|
||||
case ANALOG_MESSAGE:
|
||||
case DIGITAL_MESSAGE:
|
||||
case SET_PIN_MODE:
|
||||
case SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE:
|
||||
waitForData = 2; // two data bytes needed
|
||||
executeMultiByteCommand = command;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case REPORT_ANALOG:
|
||||
case REPORT_DIGITAL:
|
||||
waitForData = 1; // one data byte needed
|
||||
executeMultiByteCommand = command;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case START_SYSEX:
|
||||
parsingSysex = true;
|
||||
sysexBytesRead = 0;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case SYSTEM_RESET:
|
||||
systemReset();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case REPORT_VERSION:
|
||||
Firmata.printVersion();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @return Returns true if the parser is actively parsing data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
boolean FirmataClass::isParsingMessage(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return (waitForData > 0 || parsingSysex);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
// Output Stream Handling
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send an analog message to the Firmata host application. The range of pins is limited to [0..15]
|
||||
* when using the ANALOG_MESSAGE. The maximum value of the ANALOG_MESSAGE is limited to 14 bits
|
||||
* (16384). To increase the pin range or value, see the documentation for the EXTENDED_ANALOG
|
||||
* message.
|
||||
* @param pin The analog pin to send the value of (limited to pins 0 - 15).
|
||||
* @param value The value of the analog pin (0 - 1024 for 10-bit analog, 0 - 4096 for 12-bit, etc).
|
||||
* The maximum value is 14-bits (16384).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendAnalog(byte pin, int value)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// pin can only be 0-15, so chop higher bits
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(ANALOG_MESSAGE | (pin & 0xF));
|
||||
sendValueAsTwo7bitBytes(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* (intentionally left out asterix here)
|
||||
* STUB - NOT IMPLEMENTED
|
||||
* Send a single digital pin value to the Firmata host application.
|
||||
* @param pin The digital pin to send the value of.
|
||||
* @param value The value of the pin.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendDigital(byte pin, int value)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* TODO add single pin digital messages to the protocol, this needs to
|
||||
* track the last digital data sent so that it can be sure to change just
|
||||
* one bit in the packet. This is complicated by the fact that the
|
||||
* numbering of the pins will probably differ on Arduino, Wiring, and
|
||||
* other boards.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: the digital message should not be sent on the serial port every
|
||||
// time sendDigital() is called. Instead, it should add it to an int
|
||||
// which will be sent on a schedule. If a pin changes more than once
|
||||
// before the digital message is sent on the serial port, it should send a
|
||||
// digital message for each change.
|
||||
|
||||
// if(value == 0)
|
||||
// sendDigitalPortPair();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send an 8-bit port in a single digital message (protocol v2 and later).
|
||||
* Send 14-bits in a single digital message (protocol v1).
|
||||
* @param portNumber The port number to send. Note that this is not the same as a "port" on the
|
||||
* physical microcontroller. Ports are defined in order per every 8 pins in ascending order
|
||||
* of the Arduino digital pin numbering scheme. Port 0 = pins D0 - D7, port 1 = pins D8 - D15, etc.
|
||||
* @param portData The value of the port. The value of each pin in the port is represented by a bit.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendDigitalPort(byte portNumber, int portData)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(DIGITAL_MESSAGE | (portNumber & 0xF));
|
||||
FirmataStream->write((byte)portData % 128); // Tx bits 0-6 (protocol v1 and higher)
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(portData >> 7); // Tx bits 7-13 (bit 7 only for protocol v2 and higher)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send a sysex message where all values after the command byte are packet as 2 7-bit bytes
|
||||
* (this is not always the case so this function is not always used to send sysex messages).
|
||||
* @param command The sysex command byte.
|
||||
* @param bytec The number of data bytes in the message (excludes start, command and end bytes).
|
||||
* @param bytev A pointer to the array of data bytes to send in the message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendSysex(byte command, byte bytec, byte *bytev)
|
||||
{
|
||||
byte i;
|
||||
startSysex();
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(command);
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < bytec; i++) {
|
||||
sendValueAsTwo7bitBytes(bytev[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
endSysex();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send a string to the Firmata host application.
|
||||
* @param command Must be STRING_DATA
|
||||
* @param string A pointer to the char string
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendString(byte command, const char *string)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (command == STRING_DATA) {
|
||||
sendSysex(command, strlen(string), (byte *)string);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Send a string to the Firmata host application.
|
||||
* @param string A pointer to the char string
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::sendString(const char *string)
|
||||
{
|
||||
sendString(STRING_DATA, string);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A wrapper for Stream::available().
|
||||
* Write a single byte to the output stream.
|
||||
* @param c The byte to be written.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::write(byte c)
|
||||
{
|
||||
FirmataStream->write(c);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Attach a generic sysex callback function to a command (options are: ANALOG_MESSAGE,
|
||||
* DIGITAL_MESSAGE, REPORT_ANALOG, REPORT DIGITAL, SET_PIN_MODE and SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE).
|
||||
* @param command The ID of the command to attach a callback function to.
|
||||
* @param newFunction A reference to the callback function to attach.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::attach(byte command, callbackFunction newFunction)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch (command) {
|
||||
case ANALOG_MESSAGE: currentAnalogCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
case DIGITAL_MESSAGE: currentDigitalCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
case REPORT_ANALOG: currentReportAnalogCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
case REPORT_DIGITAL: currentReportDigitalCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
case SET_PIN_MODE: currentPinModeCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
case SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE: currentPinValueCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Attach a callback function for the SYSTEM_RESET command.
|
||||
* @param command Must be set to SYSTEM_RESET or it will be ignored.
|
||||
* @param newFunction A reference to the system reset callback function to attach.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::attach(byte command, systemResetCallbackFunction newFunction)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch (command) {
|
||||
case SYSTEM_RESET: currentSystemResetCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Attach a callback function for the STRING_DATA command.
|
||||
* @param command Must be set to STRING_DATA or it will be ignored.
|
||||
* @param newFunction A reference to the string callback function to attach.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::attach(byte command, stringCallbackFunction newFunction)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch (command) {
|
||||
case STRING_DATA: currentStringCallback = newFunction; break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Attach a generic sysex callback function to sysex command.
|
||||
* @param command The ID of the command to attach a callback function to.
|
||||
* @param newFunction A reference to the sysex callback function to attach.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::attach(byte command, sysexCallbackFunction newFunction)
|
||||
{
|
||||
currentSysexCallback = newFunction;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Detach a callback function for a specified command (such as SYSTEM_RESET, STRING_DATA,
|
||||
* ANALOG_MESSAGE, DIGITAL_MESSAGE, etc).
|
||||
* @param command The ID of the command to detatch the callback function from.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::detach(byte command)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch (command) {
|
||||
case SYSTEM_RESET: currentSystemResetCallback = NULL; break;
|
||||
case STRING_DATA: currentStringCallback = NULL; break;
|
||||
case START_SYSEX: currentSysexCallback = NULL; break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
attach(command, (callbackFunction)NULL);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param pin The pin to get the configuration of.
|
||||
* @return The configuration of the specified pin.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
byte FirmataClass::getPinMode(byte pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return pinConfig[pin];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Set the pin mode/configuration. The pin configuration (or mode) in Firmata represents the
|
||||
* current function of the pin. Examples are digital input or output, analog input, pwm, i2c,
|
||||
* serial (uart), etc.
|
||||
* @param pin The pin to configure.
|
||||
* @param config The configuration value for the specified pin.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::setPinMode(byte pin, byte config)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (pinConfig[pin] == PIN_MODE_IGNORE)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
pinConfig[pin] = config;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param pin The pin to get the state of.
|
||||
* @return The state of the specified pin.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int FirmataClass::getPinState(byte pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return pinState[pin];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Set the pin state. The pin state of an output pin is the pin value. The state of an
|
||||
* input pin is 0, unless the pin has it's internal pull up resistor enabled, then the value is 1.
|
||||
* @param pin The pin to set the state of
|
||||
* @param state Set the state of the specified pin
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::setPinState(byte pin, int state)
|
||||
{
|
||||
pinState[pin] = state;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sysex callbacks
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* this is too complicated for analogReceive, but maybe for Sysex?
|
||||
void FirmataClass::attachSysex(sysexFunction newFunction)
|
||||
{
|
||||
byte i;
|
||||
byte tmpCount = analogReceiveFunctionCount;
|
||||
analogReceiveFunction* tmpArray = analogReceiveFunctionArray;
|
||||
analogReceiveFunctionCount++;
|
||||
analogReceiveFunctionArray = (analogReceiveFunction*) calloc(analogReceiveFunctionCount, sizeof(analogReceiveFunction));
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < tmpCount; i++) {
|
||||
analogReceiveFunctionArray[i] = tmpArray[i];
|
||||
}
|
||||
analogReceiveFunctionArray[tmpCount] = newFunction;
|
||||
free(tmpArray);
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
//* Private Methods
|
||||
//******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Resets the system state upon a SYSTEM_RESET message from the host software.
|
||||
* @private
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::systemReset(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
byte i;
|
||||
|
||||
waitForData = 0; // this flag says the next serial input will be data
|
||||
executeMultiByteCommand = 0; // execute this after getting multi-byte data
|
||||
multiByteChannel = 0; // channel data for multiByteCommands
|
||||
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < MAX_DATA_BYTES; i++) {
|
||||
storedInputData[i] = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parsingSysex = false;
|
||||
sysexBytesRead = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (currentSystemResetCallback)
|
||||
(*currentSystemResetCallback)();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Flashing the pin for the version number
|
||||
* @private
|
||||
* @param pin The pin the LED is attached to.
|
||||
* @param count The number of times to flash the LED.
|
||||
* @param onInterval The number of milliseconds for the LED to be ON during each interval.
|
||||
* @param offInterval The number of milliseconds for the LED to be OFF during each interval.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void FirmataClass::strobeBlinkPin(byte pin, int count, int onInterval, int offInterval)
|
||||
{
|
||||
byte i;
|
||||
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
|
||||
delay(offInterval);
|
||||
digitalWrite(pin, HIGH);
|
||||
delay(onInterval);
|
||||
digitalWrite(pin, LOW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// make one instance for the user to use
|
||||
FirmataClass Firmata;
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Firmata.h - Firmata library v2.5.3 - 2016-06-18
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2006-2008 Hans-Christoph Steiner. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2009-2015 Jeff Hoefs. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
||||
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
||||
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
||||
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
See file LICENSE.txt for further informations on licensing terms.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef Firmata_h
|
||||
#define Firmata_h
|
||||
|
||||
#include "CP_Boards.h" /* Hardware Abstraction Layer + Wiring/Arduino */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Version numbers for the protocol. The protocol is still changing, so these
|
||||
* version numbers are important.
|
||||
* Query using the REPORT_VERSION message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MAJOR_VERSION 2 // for non-compatible changes
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MINOR_VERSION 5 // for backwards compatible changes
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_BUGFIX_VERSION 1 // for bugfix releases
|
||||
|
||||
/* Version numbers for the Firmata library.
|
||||
* The firmware version will not always equal the protocol version going forward.
|
||||
* Query using the REPORT_FIRMWARE message.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MAJOR_VERSION 2
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_MINOR_VERSION 5
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_FIRMWARE_BUGFIX_VERSION 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* DEPRECATED as of Firmata v2.5.1. As of 2.5.1 there are separate version numbers for
|
||||
* the protocol version and the firmware version.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_MAJOR_VERSION 2 // same as FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MAJOR_VERSION
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_MINOR_VERSION 5 // same as FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_MINOR_VERSION
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_BUGFIX_VERSION 1 // same as FIRMATA_PROTOCOL_BUGFIX_VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_DATA_BYTES 64 // max number of data bytes in incoming messages
|
||||
|
||||
// Arduino 101 also defines SET_PIN_MODE as a macro in scss_registers.h
|
||||
#ifdef SET_PIN_MODE
|
||||
#undef SET_PIN_MODE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// message command bytes (128-255/0x80-0xFF)
|
||||
#define DIGITAL_MESSAGE 0x90 // send data for a digital port (collection of 8 pins)
|
||||
#define ANALOG_MESSAGE 0xE0 // send data for an analog pin (or PWM)
|
||||
#define REPORT_ANALOG 0xC0 // enable analog input by pin #
|
||||
#define REPORT_DIGITAL 0xD0 // enable digital input by port pair
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define SET_PIN_MODE 0xF4 // set a pin to INPUT/OUTPUT/PWM/etc
|
||||
#define SET_DIGITAL_PIN_VALUE 0xF5 // set value of an individual digital pin
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define REPORT_VERSION 0xF9 // report protocol version
|
||||
#define SYSTEM_RESET 0xFF // reset from MIDI
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define START_SYSEX 0xF0 // start a MIDI Sysex message
|
||||
#define END_SYSEX 0xF7 // end a MIDI Sysex message
|
||||
|
||||
// extended command set using sysex (0-127/0x00-0x7F)
|
||||
/* 0x00-0x0F reserved for user-defined commands */
|
||||
#define SERIAL_MESSAGE 0x60 // communicate with serial devices, including other boards
|
||||
#define ENCODER_DATA 0x61 // reply with encoders current positions
|
||||
#define SERVO_CONFIG 0x70 // set max angle, minPulse, maxPulse, freq
|
||||
#define STRING_DATA 0x71 // a string message with 14-bits per char
|
||||
#define STEPPER_DATA 0x72 // control a stepper motor
|
||||
#define ONEWIRE_DATA 0x73 // send an OneWire read/write/reset/select/skip/search request
|
||||
#define SHIFT_DATA 0x75 // a bitstream to/from a shift register
|
||||
#define I2C_REQUEST 0x76 // send an I2C read/write request
|
||||
#define I2C_REPLY 0x77 // a reply to an I2C read request
|
||||
#define I2C_CONFIG 0x78 // config I2C settings such as delay times and power pins
|
||||
#define EXTENDED_ANALOG 0x6F // analog write (PWM, Servo, etc) to any pin
|
||||
#define PIN_STATE_QUERY 0x6D // ask for a pin's current mode and value
|
||||
#define PIN_STATE_RESPONSE 0x6E // reply with pin's current mode and value
|
||||
#define CAPABILITY_QUERY 0x6B // ask for supported modes and resolution of all pins
|
||||
#define CAPABILITY_RESPONSE 0x6C // reply with supported modes and resolution
|
||||
#define ANALOG_MAPPING_QUERY 0x69 // ask for mapping of analog to pin numbers
|
||||
#define ANALOG_MAPPING_RESPONSE 0x6A // reply with mapping info
|
||||
#define REPORT_FIRMWARE 0x79 // report name and version of the firmware
|
||||
#define SAMPLING_INTERVAL 0x7A // set the poll rate of the main loop
|
||||
#define SCHEDULER_DATA 0x7B // send a createtask/deletetask/addtotask/schedule/querytasks/querytask request to the scheduler
|
||||
#define SYSEX_NON_REALTIME 0x7E // MIDI Reserved for non-realtime messages
|
||||
#define SYSEX_REALTIME 0x7F // MIDI Reserved for realtime messages
|
||||
// these are DEPRECATED to make the naming more consistent
|
||||
#define FIRMATA_STRING 0x71 // same as STRING_DATA
|
||||
#define SYSEX_I2C_REQUEST 0x76 // same as I2C_REQUEST
|
||||
#define SYSEX_I2C_REPLY 0x77 // same as I2C_REPLY
|
||||
#define SYSEX_SAMPLING_INTERVAL 0x7A // same as SAMPLING_INTERVAL
|
||||
|
||||
// pin modes
|
||||
//#define INPUT 0x00 // defined in Arduino.h
|
||||
//#define OUTPUT 0x01 // defined in Arduino.h
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_ANALOG 0x02 // analog pin in analogInput mode
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_PWM 0x03 // digital pin in PWM output mode
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_SERVO 0x04 // digital pin in Servo output mode
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_SHIFT 0x05 // shiftIn/shiftOut mode
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_I2C 0x06 // pin included in I2C setup
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_ONEWIRE 0x07 // pin configured for 1-wire
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_STEPPER 0x08 // pin configured for stepper motor
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_ENCODER 0x09 // pin configured for rotary encoders
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_SERIAL 0x0A // pin configured for serial communication
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_PULLUP 0x0B // enable internal pull-up resistor for pin
|
||||
#define PIN_MODE_IGNORE 0x7F // pin configured to be ignored by digitalWrite and capabilityResponse
|
||||
#define TOTAL_PIN_MODES 13
|
||||
// DEPRECATED as of Firmata v2.5
|
||||
#define ANALOG 0x02 // same as PIN_MODE_ANALOG
|
||||
#define PWM 0x03 // same as PIN_MODE_PWM
|
||||
#define SERVO 0x04 // same as PIN_MODE_SERVO
|
||||
#define SHIFT 0x05 // same as PIN_MODE_SHIFT
|
||||
#define I2C 0x06 // same as PIN_MODE_I2C
|
||||
#define ONEWIRE 0x07 // same as PIN_MODE_ONEWIRE
|
||||
#define STEPPER 0x08 // same as PIN_MODE_STEPPER
|
||||
#define ENCODER 0x09 // same as PIN_MODE_ENCODER
|
||||
#define IGNORE 0x7F // same as PIN_MODE_IGNORE
|
||||
|
||||
extern "C" {
|
||||
// callback function types
|
||||
typedef void (*callbackFunction)(byte, int);
|
||||
typedef void (*systemResetCallbackFunction)(void);
|
||||
typedef void (*stringCallbackFunction)(char *);
|
||||
typedef void (*sysexCallbackFunction)(byte command, byte argc, byte *argv);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO make it a subclass of a generic Serial/Stream base class
|
||||
class FirmataClass
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FirmataClass();
|
||||
/* Arduino constructors */
|
||||
void begin();
|
||||
void begin(long);
|
||||
void begin(Stream &s);
|
||||
/* querying functions */
|
||||
void printVersion(void);
|
||||
void blinkVersion(void);
|
||||
void printFirmwareVersion(void);
|
||||
//void setFirmwareVersion(byte major, byte minor); // see macro below
|
||||
void setFirmwareNameAndVersion(const char *name, byte major, byte minor);
|
||||
void disableBlinkVersion();
|
||||
/* serial receive handling */
|
||||
int available(void);
|
||||
void processInput(void);
|
||||
void parse(unsigned char value);
|
||||
boolean isParsingMessage(void);
|
||||
/* serial send handling */
|
||||
void sendAnalog(byte pin, int value);
|
||||
void sendDigital(byte pin, int value); // TODO implement this
|
||||
void sendDigitalPort(byte portNumber, int portData);
|
||||
void sendString(const char *string);
|
||||
void sendString(byte command, const char *string);
|
||||
void sendSysex(byte command, byte bytec, byte *bytev);
|
||||
void write(byte c);
|
||||
/* attach & detach callback functions to messages */
|
||||
void attach(byte command, callbackFunction newFunction);
|
||||
void attach(byte command, systemResetCallbackFunction newFunction);
|
||||
void attach(byte command, stringCallbackFunction newFunction);
|
||||
void attach(byte command, sysexCallbackFunction newFunction);
|
||||
void detach(byte command);
|
||||
|
||||
/* access pin state and config */
|
||||
byte getPinMode(byte pin);
|
||||
void setPinMode(byte pin, byte config);
|
||||
/* access pin state */
|
||||
int getPinState(byte pin);
|
||||
void setPinState(byte pin, int state);
|
||||
|
||||
/* utility methods */
|
||||
void sendValueAsTwo7bitBytes(int value);
|
||||
void startSysex(void);
|
||||
void endSysex(void);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
Stream *FirmataStream;
|
||||
/* firmware name and version */
|
||||
byte firmwareVersionCount;
|
||||
byte *firmwareVersionVector;
|
||||
/* input message handling */
|
||||
byte waitForData; // this flag says the next serial input will be data
|
||||
byte executeMultiByteCommand; // execute this after getting multi-byte data
|
||||
byte multiByteChannel; // channel data for multiByteCommands
|
||||
byte storedInputData[MAX_DATA_BYTES]; // multi-byte data
|
||||
/* sysex */
|
||||
boolean parsingSysex;
|
||||
int sysexBytesRead;
|
||||
/* pin configuration */
|
||||
byte pinConfig[TOTAL_PINS];
|
||||
int pinState[TOTAL_PINS];
|
||||
|
||||
/* callback functions */
|
||||
callbackFunction currentAnalogCallback;
|
||||
callbackFunction currentDigitalCallback;
|
||||
callbackFunction currentReportAnalogCallback;
|
||||
callbackFunction currentReportDigitalCallback;
|
||||
callbackFunction currentPinModeCallback;
|
||||
callbackFunction currentPinValueCallback;
|
||||
systemResetCallbackFunction currentSystemResetCallback;
|
||||
stringCallbackFunction currentStringCallback;
|
||||
sysexCallbackFunction currentSysexCallback;
|
||||
|
||||
boolean blinkVersionDisabled;
|
||||
|
||||
/* private methods ------------------------------ */
|
||||
void processSysexMessage(void);
|
||||
void systemReset(void);
|
||||
void strobeBlinkPin(byte pin, int count, int onInterval, int offInterval);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
extern FirmataClass Firmata;
|
||||
|
||||
/*==============================================================================
|
||||
* MACROS
|
||||
*============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* shortcut for setFirmwareNameAndVersion() that uses __FILE__ to set the
|
||||
* firmware name. It needs to be a macro so that __FILE__ is included in the
|
||||
* firmware source file rather than the library source file.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define setFirmwareVersion(x, y) setFirmwareNameAndVersion(__FILE__, x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
#endif /* Firmata_h */
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,238 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
CapacitiveSense.h v.04 - Capacitive Sensing Library for 'duino / Wiring
|
||||
https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
http://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_CapacitiveSensor.html
|
||||
http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2009 Paul Bagder All right reserved.
|
||||
Version 05 by Paul Stoffregen - Support non-AVR board: Teensy 3.x, Arduino Due
|
||||
Version 04 by Paul Stoffregen - Arduino 1.0 compatibility, issue 146 fix
|
||||
vim: set ts=4:
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#if ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#include "pins_arduino.h"
|
||||
#include "WConstants.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "CPlay_CapacitiveSensor.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Function that handles the creation and setup of instances
|
||||
@param sendPin send pin for the sensor
|
||||
@param receivePin the receiving pin for the sensor
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::CPlay_CapacitiveSensor(uint8_t sendPin, uint8_t receivePin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// initialize this instance's variables
|
||||
// Serial.begin(9600); // for debugging
|
||||
error = 1;
|
||||
loopTimingFactor = 300; // determined empirically - a hack
|
||||
|
||||
CS_Timeout_Millis = (2000 * (float)loopTimingFactor * (float)F_CPU) / 16000000;
|
||||
CS_AutocaL_Millis = 20000;
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.print("timwOut = ");
|
||||
// Serial.println(CS_Timeout_Millis);
|
||||
// get pin mapping and port for send Pin - from PinMode function in core
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef NUM_DIGITAL_PINS
|
||||
if (sendPin >= NUM_DIGITAL_PINS) error = -1;
|
||||
if (receivePin >= NUM_DIGITAL_PINS) error = -2;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// sendpin to OUTPUT
|
||||
#ifdef ARDUINO_TEEONARDU_FLORA
|
||||
// terrible hack!
|
||||
DDRD |= _BV(5);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
pinMode(sendPin, OUTPUT);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
pinMode(receivePin, INPUT); // receivePin to INPUT
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef ARDUINO_TEEONARDU_FLORA
|
||||
// terrible hack!
|
||||
PORTD &= ~_BV(5);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
digitalWrite(sendPin, LOW);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
sBit = PIN_TO_BITMASK(sendPin); // get send pin's ports and bitmask
|
||||
sReg = PIN_TO_BASEREG(sendPin); // get pointer to output register
|
||||
|
||||
rBit = PIN_TO_BITMASK(receivePin); // get receive pin's ports and bitmask
|
||||
rReg = PIN_TO_BASEREG(receivePin);
|
||||
|
||||
// get pin mapping and port for receive Pin - from digital pin functions in Wiring.c
|
||||
leastTotal = 0x0FFFFFFFL; // input large value for autocalibrate begin
|
||||
lastCal = millis(); // set millis for start
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Public Methods //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
// Functions available in Wiring sketches, this library, and other libraries
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get a capacitive sensor reading
|
||||
@param samples number of samples to take
|
||||
@return the sensor reading
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
long CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::capacitiveSensor(uint8_t samples)
|
||||
{
|
||||
total = 0;
|
||||
if (samples == 0) return 0;
|
||||
if (error < 0) return -1; // bad pin
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < samples; i++) { // loop for samples parameter - simple lowpass filter
|
||||
if (SenseOneCycle() < 0) return -2; // variable over timeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// only calibrate if time is greater than CS_AutocaL_Millis and total is less than 10% of baseline
|
||||
// this is an attempt to keep from calibrating when the sensor is seeing a "touched" signal
|
||||
|
||||
if ( (millis() - lastCal > CS_AutocaL_Millis) && abs(total - leastTotal) < (int)(.10 * (float)leastTotal) ) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.println(); // debugging
|
||||
// Serial.println("auto-calibrate");
|
||||
// Serial.println();
|
||||
// delay(2000); */
|
||||
|
||||
leastTotal = 0x0FFFFFFFL; // reset for "autocalibrate"
|
||||
lastCal = millis();
|
||||
}
|
||||
/*else{ // debugging
|
||||
Serial.print(" total = ");
|
||||
Serial.print(total);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print(" leastTotal = ");
|
||||
Serial.println(leastTotal);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("total - leastTotal = ");
|
||||
x = total - leastTotal ;
|
||||
Serial.print(x);
|
||||
Serial.print(" .1 * leastTotal = ");
|
||||
x = (int)(.1 * (float)leastTotal);
|
||||
Serial.println(x);
|
||||
} */
|
||||
|
||||
// routine to subtract baseline (non-sensed capacitance) from sensor return
|
||||
if (total < leastTotal) leastTotal = total; // set floor value to subtract from sensed value
|
||||
return(total - leastTotal);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief get a raw sensor reading
|
||||
@param samples the number of samples to take
|
||||
@return -1 for error, -2 for timeout, other values are a raw sensor reading
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
long CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::capacitiveSensorRaw(uint8_t samples)
|
||||
{
|
||||
total = 0;
|
||||
if (samples == 0) return 0;
|
||||
if (error < 0) return -1; // bad pin - this appears not to work
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < samples; i++) { // loop for samples parameter - simple lowpass filter
|
||||
if (SenseOneCycle() < 0) return -2; // variable over timeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return total;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief reset the auto calibration
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::reset_CS_AutoCal(void){
|
||||
leastTotal = 0x0FFFFFFFL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief set the auto-calibration time
|
||||
@param autoCal_millis the desired calibration time in milliseconds
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(unsigned long autoCal_millis){
|
||||
CS_AutocaL_Millis = autoCal_millis;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief set the sensor timeout
|
||||
@param timeout_millis the number of milliseconds to set the timeout to
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::set_CS_Timeout_Millis(unsigned long timeout_millis){
|
||||
CS_Timeout_Millis = (timeout_millis * (float)loopTimingFactor * (float)F_CPU) / 16000000; // floats to deal with large numbers
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Private Methods /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
// Functions only available to other functions in this library
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief sense a single sicle
|
||||
@return the reading
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
int CPlay_CapacitiveSensor::SenseOneCycle(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
noInterrupts();
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(sReg, sBit); // sendPin Register low
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to input (pullups are off)
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to OUTPUT
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(rReg, rBit); // pin is now LOW AND OUTPUT
|
||||
delayMicroseconds(10);
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to input (pullups are off)
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(sReg, sBit); // sendPin High
|
||||
interrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
while ( !DIRECT_READ(rReg, rBit) && (total < CS_Timeout_Millis) ) { // while receive pin is LOW AND total is positive value
|
||||
total++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//Serial.print("SenseOneCycle(1): "); Serial.println(total);
|
||||
|
||||
if (total > CS_Timeout_Millis) {
|
||||
return -2; // total variable over timeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set receive pin HIGH briefly to charge up fully - because the while loop above will exit when pin is ~ 2.5V
|
||||
noInterrupts();
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(rReg, rBit);
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to OUTPUT - pin is now HIGH AND OUTPUT
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(rReg, rBit);
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to INPUT (pullup is off)
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(sReg, sBit); // sendPin LOW
|
||||
interrupts();
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FIVE_VOLT_TOLERANCE_WORKAROUND
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(rReg, rBit);
|
||||
DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(rReg, rBit);
|
||||
delayMicroseconds(10);
|
||||
DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(rReg, rBit); // receivePin to INPUT (pullup is off)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
while ( DIRECT_READ(rReg, rBit) && (total < CS_Timeout_Millis) ) { // while receive pin is HIGH AND total is less than timeout
|
||||
total++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
//Serial.print("SenseOneCycle(2): ");
|
||||
//Serial.println(total);
|
||||
|
||||
if (total >= CS_Timeout_Millis) {
|
||||
return -2; // total variable over timeout
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,234 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
CapacitiveSense.h v.04 - Capacitive Sensing Library for 'duino / Wiring
|
||||
https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
http://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_CapacitiveSensor.html
|
||||
http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2008 Paul Bagder All rights reserved.
|
||||
Version 05 by Paul Stoffregen - Support non-AVR board: Teensy 3.x, Arduino Due
|
||||
Version 04 by Paul Stoffregen - Arduino 1.0 compatibility, issue 146 fix
|
||||
vim: set ts=4:
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// ensure this library description is only included once
|
||||
#ifndef CapacitiveSensor_h
|
||||
#define CapacitiveSensor_h
|
||||
|
||||
#if ARDUINO >= 100
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#include "WProgram.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Direct I/O through registers and bitmask (from OneWire library)
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR__)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portInputRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint8_t
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (((*(base)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+1)) &= ~(mask), (*((base)+2)) &= ~(mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+1)) |= (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) ((*((base)+2)) &= ~(mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) ((*((base)+2)) |= (mask))
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__MK20DX128__) || defined(__MK20DX256__) || defined(__MK66FX1M0__) || defined(__MK64FX512__)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portOutputRegister(pin))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (1)
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint8_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (*((base)+512))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) (*((base)+640) = 0)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) (*((base)+640) = 1)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) (*((base)+256) = 1)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) (*((base)+128) = 1)
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__MKL26Z64__)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portOutputRegister(pin))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint8_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) ((*((base)+16) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) (*((base)+20) &= ~(mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) (*((base)+20) |= (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) (*((base)+8) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) (*((base)+4) = (mask))
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAM3X8E__)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (&(digitalPinToPort(pin)->PIO_PER))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (((*((base)+15)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+5)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+4)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) ((*((base)+13)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) ((*((base)+12)) = (mask))
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__PIC32MX__)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portModeRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (((*(base+4)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0) //PORTX + 0x10
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) ((*(base+2)) = (mask)) //TRISXSET + 0x08
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) ((*(base+1)) = (mask)) //TRISXCLR + 0x04
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) ((*(base+8+1)) = (mask)) //LATXCLR + 0x24
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) ((*(base+8+2)) = (mask)) //LATXSET + 0x28
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP8266)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portOutputRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (((*(base+6)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0) //GPIO_IN_ADDRESS
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) ((*(base+5)) = (mask)) //GPIO_ENABLE_W1TC_ADDRESS
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) ((*(base+4)) = (mask)) //GPIO_ENABLE_W1TS_ADDRESS
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) ((*(base+2)) = (mask)) //GPIO_OUT_W1TC_ADDRESS
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) ((*(base+1)) = (mask)) //GPIO_OUT_W1TS_ADDRESS
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
// runs extremely slow/unreliable on Arduino Zero - help wanted....
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) portModeRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin))
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, mask) (((*((base)+8)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+1)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, mask) ((*((base)+2)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, mask) ((*((base)+5)) = (mask))
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, mask) ((*((base)+6)) = (mask))
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(RBL_NRF51822)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (0)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (pin)
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, pin) nrf_gpio_pin_read(pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, pin) nrf_gpio_pin_clear(pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, pin) nrf_gpio_pin_set(pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, pin) nrf_gpio_cfg_input(pin, NRF_GPIO_PIN_NOPULL)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, pin) nrf_gpio_cfg_output(pin)
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(__arc__)
|
||||
|
||||
#include "scss_registers.h"
|
||||
#include "portable.h"
|
||||
#include "avr/pgmspace.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define GPIO_ID(pin) (g_APinDescription[pin].ulGPIOId)
|
||||
#define GPIO_TYPE(pin) (g_APinDescription[pin].ulGPIOType)
|
||||
#define GPIO_BASE(pin) (g_APinDescription[pin].ulGPIOBase)
|
||||
#define DIR_OFFSET_SS 0x01
|
||||
#define DIR_OFFSET_SOC 0x04
|
||||
#define EXT_PORT_OFFSET_SS 0x0A
|
||||
#define EXT_PORT_OFFSET_SOC 0x50
|
||||
|
||||
/* GPIO registers base address */
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) ((volatile uint32_t *)g_APinDescription[pin].ulGPIOBase)
|
||||
#define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) pin
|
||||
#define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
|
||||
#define IO_REG_ASM
|
||||
|
||||
static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
|
||||
IO_REG_TYPE directRead(volatile IO_REG_TYPE *base, IO_REG_TYPE pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
IO_REG_TYPE ret;
|
||||
if (SS_GPIO == GPIO_TYPE(pin)) {
|
||||
ret = READ_ARC_REG(((IO_REG_TYPE)base + EXT_PORT_OFFSET_SS));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ret = MMIO_REG_VAL_FROM_BASE((IO_REG_TYPE)base, EXT_PORT_OFFSET_SOC);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ((ret >> GPIO_ID(pin)) & 0x01);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
|
||||
void directModeInput(volatile IO_REG_TYPE *base, IO_REG_TYPE pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (SS_GPIO == GPIO_TYPE(pin)) {
|
||||
WRITE_ARC_REG(READ_ARC_REG((((IO_REG_TYPE)base) + DIR_OFFSET_SS)) & ~(0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin)),
|
||||
((IO_REG_TYPE)(base) + DIR_OFFSET_SS));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
MMIO_REG_VAL_FROM_BASE((IO_REG_TYPE)base, DIR_OFFSET_SOC) &= ~(0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
|
||||
void directModeOutput(volatile IO_REG_TYPE *base, IO_REG_TYPE pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (SS_GPIO == GPIO_TYPE(pin)) {
|
||||
WRITE_ARC_REG(READ_ARC_REG(((IO_REG_TYPE)(base) + DIR_OFFSET_SS)) | (0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin)),
|
||||
((IO_REG_TYPE)(base) + DIR_OFFSET_SS));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
MMIO_REG_VAL_FROM_BASE((IO_REG_TYPE)base, DIR_OFFSET_SOC) |= (0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
|
||||
void directWriteLow(volatile IO_REG_TYPE *base, IO_REG_TYPE pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (SS_GPIO == GPIO_TYPE(pin)) {
|
||||
WRITE_ARC_REG(READ_ARC_REG(base) & ~(0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin)), base);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
MMIO_REG_VAL(base) &= ~(0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
|
||||
void directWriteHigh(volatile IO_REG_TYPE *base, IO_REG_TYPE pin)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (SS_GPIO == GPIO_TYPE(pin)) {
|
||||
WRITE_ARC_REG(READ_ARC_REG(base) | (0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin)), base);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
MMIO_REG_VAL(base) |= (0x01 << GPIO_ID(pin));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define DIRECT_READ(base, pin) directRead(base, pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_INPUT(base, pin) directModeInput(base, pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_MODE_OUTPUT(base, pin) directModeOutput(base, pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_LOW(base, pin) directWriteLow(base, pin)
|
||||
#define DIRECT_WRITE_HIGH(base, pin) directWriteHigh(base, pin)
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// some 3.3V chips with 5V tolerant pins need this workaround
|
||||
//
|
||||
#if defined(__MK20DX256__)
|
||||
#define FIVE_VOLT_TOLERANCE_WORKAROUND
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief Class that stores state and functions for the capacitive sensor on CircuitPlayground boards
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
class CPlay_CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
{
|
||||
// user-accessible "public" interface
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// methods
|
||||
CPlay_CapacitiveSensor(uint8_t sendPin = 0, uint8_t receivePin = 0);
|
||||
long capacitiveSensorRaw(uint8_t samples);
|
||||
long capacitiveSensor(uint8_t samples);
|
||||
void set_CS_Timeout_Millis(unsigned long timeout_millis);
|
||||
void reset_CS_AutoCal();
|
||||
void set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(unsigned long autoCal_millis);
|
||||
// library-accessible "private" interface
|
||||
private:
|
||||
// variables
|
||||
int error;
|
||||
unsigned long leastTotal;
|
||||
unsigned int loopTimingFactor;
|
||||
unsigned long CS_Timeout_Millis;
|
||||
unsigned long CS_AutocaL_Millis;
|
||||
unsigned long lastCal;
|
||||
unsigned long total;
|
||||
IO_REG_TYPE sBit; // send pin's ports and bitmask
|
||||
volatile IO_REG_TYPE *sReg;
|
||||
IO_REG_TYPE rBit; // receive pin's ports and bitmask
|
||||
volatile IO_REG_TYPE *rReg;
|
||||
// methods
|
||||
int SenseOneCycle(void);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibCPE.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Combines all of the necessary libraries for implementing IR transmit and receive
|
||||
* on the Adafruit Circuit Playground Express. Similar to the IRLibAll.h in the
|
||||
* regular IRLib2.xx.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_CPE_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_CPE_H
|
||||
#include "IRLibDecodeBase.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibSendBase.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P01_NEC.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P02_Sony.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P03_RC5.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P04_RC6.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P05_Panasonic_Old.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P06_JVC.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P07_NECx.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P08_Samsung36.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P09_GICable.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P10_DirecTV.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P11_RCMM.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLib_P12_CYKM.h"
|
||||
//include additional protocols here
|
||||
#include "IRLibCombo.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibRecvPCI.h"
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_CPE_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibCombo.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This file is for creating a customer decode or send class which contains only
|
||||
* the protocols that you will actually use. At the top of your sketch you should
|
||||
* include the Send and/or Decode base modules followed by at least one or more
|
||||
* protocol module. Then conclude with this module.
|
||||
* WARNING: The lowest numbered protocol which you are using MUST be included first.
|
||||
* The remaining protocol modules technically could be in any order however we
|
||||
* recommend that you maintain numerical order because you might at some point
|
||||
* comment out the top one and then the lowest would not be first causing an error.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Here is an example...
|
||||
*
|
||||
* #include <IRLibSendBase.h> //Only include if you are sending
|
||||
* #include <IRLibDecodeBase.h> //Only include if you are decoding
|
||||
* #include <IRLib_Pxx_protocol_name.h> //Include at least one protocol
|
||||
* #include <IRLib_Pxx_another_name.h> //Include as many as you want
|
||||
* #include <IRLibCombo.h> //Include this file
|
||||
* IRdecode My_Decoder; //declare an instance of the decoder if needed
|
||||
* IRsend My_Sender; //declarative sense of the sending routine if needed
|
||||
* //The rest of your code goes here
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_COMBO_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_COMBO_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_HASHRAW_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_RAW
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_HASH
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_HASH
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_RAW
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_01_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_02_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_03_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_04_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_05_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_06_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_07_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_08_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_09_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_10_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_11_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_12_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_13_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_14_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
//Add additional protocols 15, 16, etc. above.
|
||||
|
||||
//Note protocol 90- 99 for sample code that will be unsupported in the final version.
|
||||
//See IRLibProtocols/unsupported/IRLib_P90_Unsupported.h for details
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_90_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_90
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_90
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_90
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_90
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_91_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_92_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* You may add additional protocols by copying and modifying the previous six lines.
|
||||
* You must also add appropriate macros in each segment below. Be sure to maintain
|
||||
* numerical order. Also the final entry in each list MUST BE the Hash_Raw version.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecode:
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_90 //Add additional 15, 16 etc. above this
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
PV_IR_DECODE_HASH //Must be last one.
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_90 //Add additional 15, 16 etc. above this
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
IR_DECODE_HASH //Must be last one.
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_12_H
|
||||
void dumpResults(bool verbose=true) {
|
||||
if(protocolNum==12) {
|
||||
IRdecodeCYKM::dumpResults();
|
||||
if(verbose)IRdecodeBase::dumpResults(true);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
IRdecodeBase::dumpResults(verbose);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsend:
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_90 //Add additional 15, 16 etc. above this
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
PV_IR_SEND_RAW //Must be last one.
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint8_t protocolNum, uint32_t data, uint16_t data2=0, uint8_t khz=38) {
|
||||
if(khz==0)khz=38;
|
||||
switch(protocolNum) {
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_13
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_14
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_90 //Add additional 15, 16 etc. above this
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_91
|
||||
IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_92
|
||||
IR_SEND_RAW //Must be last one.
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_COMBO_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibDecodeBase.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module contains the base classes for decoding. You will not create instances
|
||||
* of these classes, rather you will use them as base classes in creating derived
|
||||
* protocol specific decoders.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "IRLibDecodeBase.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h"
|
||||
|
||||
IRdecodeBase::IRdecodeBase(void) {
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=false; //turned on by enableIRIn.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeBuffer=recvGlobal.recvBuffer;//default buffer
|
||||
ignoreHeader=false;
|
||||
resetDecoder();
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Reinitialize the decoder clearing out previous data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRdecodeBase::resetDecoder(void) {
|
||||
protocolNum= UNKNOWN;
|
||||
value=0;
|
||||
address=0;
|
||||
bits=0;
|
||||
};
|
||||
void IRdecodeBase::dumpResults(bool verbose) {
|
||||
int i;uint32_t Extent;int interval;
|
||||
if((protocolNum>89) || (protocolNum<=LAST_PROTOCOL)) {
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Decoded ")); Serial.print(Pnames(protocolNum));
|
||||
Serial.print(F("(")); Serial.print(protocolNum,DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F("): Value:")); Serial.print(value, HEX);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" Adrs:" )); Serial.print(address, HEX);
|
||||
};
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" (")); Serial.print(bits, DEC); Serial.print(F(" bits) "));
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.didAutoResume) Serial.print(F("Auto Resumed"));
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
if(!verbose)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Raw samples(")); Serial.print(recvGlobal.decodeLength, DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F("): Gap:")); Serial.println(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[0], DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" Head: m")); Serial.print(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1], DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" s")); Serial.println(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2], DEC);
|
||||
int LowSpace= 32767; int LowMark= 32767;
|
||||
int HiSpace=0; int HiMark= 0;
|
||||
Extent=recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1]+recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2];
|
||||
for (i = 3; i < recvGlobal.decodeLength; i++) {
|
||||
Extent+=(interval= recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[i]);
|
||||
if (i % 2) {
|
||||
LowMark=min(LowMark, interval); HiMark=max(HiMark, interval);
|
||||
Serial.print(i/2-1,DEC); Serial.print(F(":m"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
if(interval>0)LowSpace=min(LowSpace, interval); HiSpace=max (HiSpace, interval);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" s"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.print(interval, DEC);
|
||||
int j=i-1;
|
||||
if ((j % 2)==1)Serial.print(F("\t"));
|
||||
if ((j % 4)==1)Serial.print(F("\t "));
|
||||
if ((j % 8)==1)Serial.println();
|
||||
if ((j % 32)==1)Serial.println();
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Extent=")); Serial.println(Extent,DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Mark min:")); Serial.print(LowMark,DEC);Serial.print(F("\t max:")); Serial.println(HiMark,DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Space min:")); Serial.print(LowSpace,DEC);Serial.print(F("\t max:")); Serial.println(HiSpace,DEC);
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* We use a generic routine because most protocols have the same basic structure.
|
||||
* Previous versions of this method would handle protocols with variable marks
|
||||
* or variable spaces. However we have discovered that only Sony protocol uses
|
||||
* variable marks so we have stripped out that portion of the code. This changes
|
||||
* the number of necessary parameters. We no longer need markOne and markZero
|
||||
* because they are both the same which we will pass in markData. Note this new
|
||||
* version will handle up to 48 bits putting the most significant 16 bits in
|
||||
* "this.address" in the least significant 32 bits in "this.data". We could have
|
||||
* allowed for 64 bit but we have not seen generic protocols that large.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool IRdecodeBase::decodeGeneric(uint8_t expectedLength,
|
||||
uint16_t headMark, uint16_t headSpace, uint16_t markData,
|
||||
uint16_t spaceOne, uint16_t spaceZero) {
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
// If "expectedLenght" or "headMark" or "headSpace" are zero or if "ignoreHeader"
|
||||
// is true then don't perform these tests. This is because some protocols need
|
||||
// to do their own custom header work.
|
||||
uint64_t data = 0;
|
||||
bufIndex_t Max=recvGlobal.decodeLength-1;
|
||||
if (expectedLength) {
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength != expectedLength) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!ignoreHeader) {
|
||||
if (headMark) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],headMark)) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(headMark);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (headSpace) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],headSpace)) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(headSpace);
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset=3;//skip initial gap plus two header items
|
||||
while (offset < Max) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH (recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],markData)) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(markData);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],spaceOne)) {
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (MATCH (recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],spaceZero)) {
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(spaceZero);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits = (offset - 1) / 2 -1;//didn't encode stop bit
|
||||
// Success
|
||||
value = (uint32_t)data; //low order 32 bits
|
||||
address = (uint16_t) (data>>32); //high order 16 bits
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* These MATCH methods used to be macros but we saved nearly
|
||||
* 800 bytes of program space by making them actual methods.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
bool IRdecodeBase::MATCH(int16_t val,int16_t expected){
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_USE_PERCENT
|
||||
return (val >= (uint16_t)(expected*(1.0-PERCENT_TOLERANCE/100.0)))
|
||||
&& (val <= (uint16_t)(expected*(1.0+PERCENT_TOLERANCE/100.0)));
|
||||
#else
|
||||
return ABS_MATCH(val,expected,DEFAULT_ABS_TOLERANCE);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool IRdecodeBase::ABS_MATCH(int16_t val,int16_t expected,int16_t tolerance){
|
||||
return (val >= (expected-tolerance)) && (val <= (expected+tolerance));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* The RC5 and RC6 and similar protocols used phase encoding and leave a
|
||||
* routine to extract zeros and ones. This routine gets one undecoded
|
||||
* level at a time from the raw buffer. personally The RC5/6 decoding
|
||||
* is easier if the data is broken into time intervals.
|
||||
* E.g. if the buffer has MARK for 2 time intervals and SPACE for 1,
|
||||
* successive calls to getRClevel will return MARK, MARK, SPACE.
|
||||
* The variables "offset" and "used" are updated to keep track of the
|
||||
* current position. The variable "t1" is the time interval for a single
|
||||
* bit in microseconds. Returns ERROR if the measured time interval is
|
||||
* not a multiple of "t1".
|
||||
*/
|
||||
IRdecodeRC::RCLevel IRdecodeRC::getRClevel(uint8_t *used, const uint16_t t1) {
|
||||
if (offset >= recvGlobal.decodeLength) {
|
||||
// After end of recorded buffer, assume SPACE.
|
||||
return SPACE;
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint16_t width = recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset];
|
||||
IRdecodeRC::RCLevel val;
|
||||
if ((offset) % 2) val=MARK; else val=SPACE;
|
||||
uint8_t avail;
|
||||
if (MATCH(width, t1)) {
|
||||
avail = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (MATCH(width, 2*t1)) {
|
||||
avail = 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (MATCH(width, 3*t1)) {
|
||||
avail = 3;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if((ignoreHeader) && (offset==1) && (width<t1)){
|
||||
avail =1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return ERROR;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
(*used)++;
|
||||
if (*used >= avail) {
|
||||
*used = 0;
|
||||
(offset)++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibDecodeBase.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module contains the base classes for decoding. You will not create instances
|
||||
* of these classes, rather you will use them as base classes in creating derived
|
||||
* protocol specific decoders.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
#define IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
#include "IRLibGlobals.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibProtocols.h"
|
||||
|
||||
// Base class for decoding raw results
|
||||
class IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
IRdecodeBase(void);
|
||||
uint8_t protocolNum; // NEC, SONY, RC5, UNKNOWN etc.
|
||||
uint32_t value; // Decoded value
|
||||
uint16_t address; // Additional data for protocols using more than 32 bits
|
||||
uint8_t bits; // Number of bits in decoded value
|
||||
bool ignoreHeader; // Relaxed header detection allows AGC to settle
|
||||
bool decodeGeneric(uint8_t expectedLength, uint16_t headMark, uint16_t headSpace,
|
||||
uint16_t markData, uint16_t spaceOne, uint16_t spaceZero);
|
||||
void dumpResults(bool verbose=true);//full dump of all timing values
|
||||
bool MATCH(int16_t val,int16_t expected);
|
||||
bool ABS_MATCH(int16_t val,int16_t expected,int16_t tolerance);
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
virtual void resetDecoder(void); // Initializes the decoder
|
||||
bufIndex_t offset; // Index into decodeBuffer used various places
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Base class used by RC5 and RC6 protocols
|
||||
class IRdecodeRC: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
enum RCLevel {MARK, SPACE, ERROR};//used by decoders for RC5/RC6
|
||||
RCLevel getRClevel(uint8_t *used, const uint16_t t1);
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
uint8_t nBits;
|
||||
uint8_t used;
|
||||
uint32_t data;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* The remainder of this file a variety of default values and macros which are
|
||||
* used internally. They used to be in a separate file IRLibMatch.h but it's easier
|
||||
* to include them here. You need not worry about them unless you are creating
|
||||
* your own decoding routines. See the documentation how to implement new protocols
|
||||
* for a more detailed explanation of these definitions and routines.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Originally all timing comparisons for decoding were based on a percent of the
|
||||
* target value. However when target values are relatively large, the percent tolerance
|
||||
* is too much. In some instances an absolute tolerance is needed. In order to maintain
|
||||
* backward compatibility, the default will be to continue to use percent. If you wish
|
||||
* to default to an absolute tolerance, you should comment out the line below.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define IRLIB_USE_PERCENT
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* These are some miscellaneous definitions that are needed by the decoding routines.
|
||||
* You need not include this file unless you are creating custom decode routines
|
||||
* which will require these macros and definitions. Even if you include it, you probably
|
||||
* don't need to be intimately familiar with the internal details.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define TOPBIT 0x80000000
|
||||
#define PERCENT_TOLERANCE 25 // percent tolerance in measurements
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_ABS_TOLERANCE 75 //absolute tolerance in microseconds
|
||||
/* If you insert #define IRLIB_TRACE in your sketch before including this file,
|
||||
* various debugging routines will be enabled in the dumpResults() method.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_TRACE
|
||||
void IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(const __FlashStringHelper * s) {Serial.print(F("Attempting ")); Serial.print(s); Serial.println(F(" decode:"));};
|
||||
void IRLIB_TRACE_MESSAGE(const __FlashStringHelper * s) {Serial.print(F("Executing ")); Serial.println(s);};
|
||||
uint8_t IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(const __FlashStringHelper * s) { Serial.print(F(" Protocol failed because ")); Serial.print(s); Serial.println(F(" wrong.")); return false;};
|
||||
uint8_t IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(const __FlashStringHelper * s, uint8_t index, uint16_t value, uint16_t expected) {
|
||||
IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(s); Serial.print(F("Error occurred with decodeBuffer[")); Serial.print(index,DEC); Serial.print(F("]=")); Serial.print(value,DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" expected:")); Serial.println(expected,DEC); return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#define RAW_COUNT_ERROR IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(F("number of raw samples"));
|
||||
#define HEADER_MARK_ERROR(expected) IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(F("header mark"),1,recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],expected);
|
||||
#define HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(expected) IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(F("header space"),2,recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],expected);
|
||||
#define DATA_MARK_ERROR(expected) IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(F("data mark"),offset,recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],expected);
|
||||
#define DATA_SPACE_ERROR(expected) IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(F("data space"),offset,recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],expected);
|
||||
#define TRAILER_BIT_ERROR(expected) IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(F("RC6 trailer bit length"),offset,recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],expected);
|
||||
#define BIT_COUNT_ERROR IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(F("invalid number of bits"));
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(s)
|
||||
#define IRLIB_TRACE_MESSAGE(s)
|
||||
#define IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(s) false
|
||||
#define IRLIB_DATA_ERROR_MESSAGE(s,i,v,e) false
|
||||
#define RAW_COUNT_ERROR false
|
||||
#define HEADER_MARK_ERROR(expected) false
|
||||
#define HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(expected) false
|
||||
#define DATA_MARK_ERROR(expected) false
|
||||
#define DATA_SPACE_ERROR(expected) false
|
||||
#define TRAILER_BIT_ERROR(expected) false
|
||||
#define BIT_COUNT_ERROR false
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibGlobals.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This file replaces the previous IRLibRData.h file. It contains definition of global
|
||||
* items which are used by both the receiver and decoding classes. They have to be
|
||||
* declared global in scope because they are accessed by the ISR and you cannot pass
|
||||
* parameters nor objects to an ISR routine.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* In general, applications would not include this file. Unless you are creating your own
|
||||
* customized receiver class apart from the provided IRrcev, IRrcevPCI, or IRrcevLoop
|
||||
* classes, you can ignore the contents of this file.
|
||||
* The RECV_BUF_LENGTH is the only item you would ever modify unless you are completely
|
||||
* rewriting how the system works in general.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLibGlobals_h
|
||||
#define IRLibGlobals_h
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/* Timing data is stored in a buffer by the receiver object. It is an array of
|
||||
* uint16_t that should be at least 100 entries as defined by this default below.
|
||||
* However some IR sequences will require longer buffers especially those used for
|
||||
* air conditioner controls. In general we recommend you keep this value below 255
|
||||
* so that the index into the array can remain 8 bits. This library can handle larger
|
||||
* arrays however it will make your code longer in addition to taking more RAM.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define RECV_BUF_LENGTH 100
|
||||
#if (RECV_BUF_LENGTH > 255)
|
||||
typedef uint16_t bufIndex_t;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
typedef uint8_t bufIndex_t;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Receiver states. This previously was enum but changed it to uint8_t
|
||||
// to guarantee it was a single atomic 8-bit value.
|
||||
#define STATE_UNKNOWN 0
|
||||
#define STATE_READY_TO_BEGIN 1
|
||||
#define STATE_TIMING_MARK 2
|
||||
#define STATE_TIMING_SPACE 3
|
||||
#define STATE_FINISHED 4
|
||||
#define STATE_RUNNING 5
|
||||
typedef uint8_t currentState_t;
|
||||
/* The structure contains information used by the ISR routines. Because we cannot
|
||||
* pass parameters to an ISR, it must be global. Values which can be changed by
|
||||
* the ISR but are accessed outside the ISR must be volatile.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
//These next 4 fields are initialized by the receiver class and unlikely to change once
|
||||
//they have been initialized. Only change them on the fly at your own peril.
|
||||
uint8_t recvPin; // pin number or interrupt number for receiver
|
||||
bool enableAutoResume; //ISR can copy data to decodeBuffer and restart by itself
|
||||
uint16_t frameTimeout; //Maximum length of a SPACE before we decide the frame has ended
|
||||
//Used by IRrecv only
|
||||
uint16_t frameTimeoutTicks;// = frameTimeout/USEC_PER_TICKS
|
||||
bool enableBlinkLED;
|
||||
|
||||
//These fields are both read and written inside and outside ISRs. Must be volatile.
|
||||
volatile bool decoderWantsData; //tells ISR previous decode is finished. Buffer available.
|
||||
volatile bool newDataAvailable; //ISR flag informs getResults that data is available.
|
||||
volatile bool didAutoResume; //ISR tells getResults we already copied, just do math.
|
||||
//The buffers are filled with timing values by the ISRs. The recvLength is the number of
|
||||
//entries when the frame is complete. See the note at the end of this file about buffers.
|
||||
volatile uint16_t recvBuffer[RECV_BUF_LENGTH];
|
||||
// volatile uint16_t* recvBuffer;
|
||||
volatile bufIndex_t recvLength;
|
||||
//These next two fields are how the receiver communicates with the decoder. Previously
|
||||
//this was accomplished by passing to the receiver a pointer to the decoder in getResults.
|
||||
//However with auto resume we now may need to communicate before getResults is called.
|
||||
//The decoderBuffer pointer is maintained by the decoder. It points to where the
|
||||
//decoder wants the data put by the receiver. It will point to either recvGlobal.recvBuffer
|
||||
//or an external buffer provided by the user via useExtnBuf. The decodeLength
|
||||
//is set by the receiver telling the decoder the data length.
|
||||
volatile uint16_t* decodeBuffer;
|
||||
volatile bufIndex_t decodeLength;
|
||||
//This field accumulates the elapsed time of a MARK or SPACE. IRrecv uses it only inside
|
||||
//the ISR however IRrecvPCI accesses it outside the ISR. Therefore it is volatile
|
||||
//and because it is multi-byte it will need atomic guards when accessed outside the ISR.
|
||||
volatile uint32_t timer; // state timer, counts 50uS ticks.(and other uses)
|
||||
//Used by both IRrecv and IRrecvPCI.
|
||||
volatile currentState_t currentState; // state machine Legal values defined above.
|
||||
}
|
||||
recvGlobal_t;
|
||||
extern recvGlobal_t recvGlobal; //declared in IRLibRecvBase.cpp
|
||||
|
||||
/**** NOTE CONCERNING BUFFER NAMES AND VOLATILITY
|
||||
* In versions of IRLib prior to 2.0 we had the capability to declare an external
|
||||
* buffer so that the receiver could resume receiving while the decoding was taking place.
|
||||
* However it was up to the decoder to notice that the data had been received via a call to
|
||||
* getResults() and it had to tell the receiver to resume. Starting with version 2.0
|
||||
* it is now possible that the receiver can automatically copy the data to the external
|
||||
* buffer and auto resume. Rather than using names like rawbuf1 and rawbuf2 we have come
|
||||
* up with a new naming system. Also irparams wasn't the most descriptive name
|
||||
* ever conceived. Here is our new naming system which we hope is slightly less confusing.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* First irparams was a structure that contained global variables used by the receiver ISR.
|
||||
* They should not be part of the receiver class because you can't pass parameters
|
||||
* to an ISR. We think recvGlobal is a better name.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Previously the ISR did not need access to any external buffer so it only needed one
|
||||
* buffer and one length variable. If there was an external buffer, only the decoder
|
||||
* needed to access it. Now the receiver and ISR needs access to that external buffer
|
||||
* in order to implement auto resume. Therefore the extra buffer needs to be linked
|
||||
* to recvGlobal as well. The receiver puts the data in recvGlobal.recvBuffer and it's
|
||||
* length is in recvGlobal.recvLength. It is for the receiver's internal use.
|
||||
* Additionally we have "decodeBuffer" and "decodeLength" which
|
||||
* are defined as where the decoder wants the receiver to put its data. The decoder
|
||||
* decides where decodeBuffer points. The receiver puts the data at that address
|
||||
* and has no idea where it points. The receiver puts the length in decodeLength.
|
||||
* It is the receiver's responsibility to copy the data from recvBuffer to decodeBuffer.
|
||||
* The math is always done in getResults however deciding when to do the copying is
|
||||
* a bit more complicated. If we are doing auto resume, we do a bufcpy to copy as
|
||||
* quickly as possible and defer the math until the actual poll to getResults.
|
||||
* The getResults needs to know whether it should copy or just do the math in place.
|
||||
* If you determine that by the flag didAutoResume.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Now we tackle the volatile issue of "volatile". Aptly named because it starts flame wars.
|
||||
* In general the rule is, if data is to be accessed inside and outside an ISR you need to
|
||||
* add the volatile qualifier to its definition. This ensures that the compiler does not
|
||||
* optimize the code in such a way that a bad copy of a variable might be used. It forces
|
||||
* the compiler to fetch the data every time he uses it and not to store it in a register.
|
||||
* We are going to presume that our ISRs never interrupt themselves. I believe the volatile
|
||||
* qualifier may not be necessary because the decoder is only accessing the data once the
|
||||
* receiver is finished working with it. The only items that really need to be volatile
|
||||
* are some of the flags. However making the buffer volatile does not seem to measurably
|
||||
* slowdown the decoding process (I ran some tests). So as part of "good programming
|
||||
* practices we are marking the buffers and lengths as volatile just in case. We need not
|
||||
* use atomic blocks to access the buffer except in very rare cases.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define DEBUG_VALUE(l, v) Serial.print(l); Serial.print(":"); Serial.println(v,DEC);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibHardware.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* We need a way for the sending object to communicate with the receiving object.
|
||||
* Sending an IR signal can disable further receiving because the timer needed for the 50us
|
||||
* interrupts is used to modulate the frequency of the PWM output signal. We need a flag
|
||||
* for the send object to inform you receive object that this occurred.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Some applications do sending only and would only require you to include IRLibSendBase.h
|
||||
* while others only do receiving/decoding and would include IRLibRecvBase.h but not
|
||||
* IRLibSendBase.h. The only include file that is used by both sending and receiving is
|
||||
* the IRLibHardware.h which was formerly called IRLibTimer.h. Therefore we put the flag
|
||||
* in this newly created IRLibHardware.cpp module. That way a send only can put the flag
|
||||
* here whether or not there is a receiver. Similarly the receiver can check the flag
|
||||
* whether or not there is a sender.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The below is a global flag IRLib_didIROut that gets set true with every call to enableIROut.
|
||||
* Then any call to IRrecv::enableIRIn checks this to see if it needs to restart the ISR.
|
||||
* Regardless IRrecv::enableIRIn will always reset it it false for the next time.
|
||||
* Note as always if you try to send while in the middle of receiving, the partially received
|
||||
* data is lost. If the application wishes to create a system where the sending waits until
|
||||
* the receiver is idle, the programmer can implement such a system themselves and deal with
|
||||
* the consequences.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The bottom line is the application no longer needs to figure out if it needs to
|
||||
* call enableIRIn or the "resume" method. There is no more "resume". You always do
|
||||
* enableIRIn after every decode and the system handles it.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h"
|
||||
uint8_t IRLib_didIROut=false;
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibHardware.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This file was formally called IRLibTimer.h but we have renamed it because it more
|
||||
* accurately reflects the fact that it contains all of the hardware specific defines.
|
||||
* It contains mostly definitions for 8-bit AVR processors. More advanced processors such as
|
||||
* SAMD21 definitions will now be defined in a separate processor specific header file.
|
||||
* NOTE: IRLibHardware.cpp is not related to hardware. See the comments in that file
|
||||
* to explain why it was created and what purpose it serves.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* This file has been significantly reconfigured for version 1.5 and greater. It now
|
||||
* allows you use a different timer for input versus output. This also allows you to
|
||||
* use no timers whatsoever by using the IRrecvPCI or IRrecvLoop for input and
|
||||
* bit-bang routines for output. Note the various "Teensy" sections have not been tested.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLibHardware_h
|
||||
#define IRLibHardware_h
|
||||
|
||||
#include "Arduino.h"
|
||||
|
||||
//This is a default for AVRs. SAMD21 will override it.
|
||||
#define IR_CLEAR_INTERRUPT {} //clear interrupt flag
|
||||
|
||||
// defines for setting and clearing register bits
|
||||
#ifndef cbi
|
||||
#define cbi(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) &= ~_BV(bit))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef sbi
|
||||
#define sbi(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) |= _BV(bit))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* In this section we attempt to detect your hardware type and give you the choice of
|
||||
* various hardware timers to change the PWM frequency for output. In each hardware
|
||||
* section below you should un-comment only one of the choices. The defines also
|
||||
* specify the output pin number. DO NOT change the pin number unless you're using
|
||||
* non-standard hardware that would require you to do so. If you wish to use the
|
||||
* bit-bang PWM output, you will specify that AFTER this section as an override.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* Arduino Mega */
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 11
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER2 9
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER3 5
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER4 6
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER5 46
|
||||
|
||||
/* Teensy 1.0 */
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_AT90USB162__)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 17
|
||||
|
||||
/* Teensy 2.0 versus Leonardo These boards use the same chip but the
|
||||
* pinouts are different.*/
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__)
|
||||
#ifdef CORE_TEENSY
|
||||
// it's Teensy 2.0
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 14
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER3 9
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER4_HS 10
|
||||
#else
|
||||
/* it's probably Leonardo */
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 9
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER3 5
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER4_HS 13
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Teensy++ 1.0 & 2.0 */
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_AT90USB646__) || defined(__AVR_AT90USB1286__)
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 25
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER2 1
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER3 16
|
||||
|
||||
/* Sanguino */
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega644__)
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 13
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER2 14
|
||||
|
||||
/* Arduino Zero, M0, M0 Pro, Feather M0 etc. */
|
||||
#elif defined (__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
// All of the settings can be found in IRLibSAMD21.h
|
||||
#include "IRLibSAMD21.h"
|
||||
/* Pinoccio Scout */
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega256RFR2__)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER3 3
|
||||
|
||||
/* Arduino Duemilanove, Diecimila, LilyPad, Mini, Fio, etc */
|
||||
#else
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_TIMER1 9
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_TIMER2 3
|
||||
#endif //end of setting IR_SEND_TIMER based on hardware detection
|
||||
|
||||
/* If you want to use bit-bang PWM output, you should un-comment the line below.
|
||||
* The definition must include the pin number for bit-bang output. This could be any
|
||||
* available digital output pin. It need not be a designated PWM pin.
|
||||
* NOTE: By un-commenting this line, you are forcing the library to ignore
|
||||
* hardware detection and timer specifications above. The bit-bang frequency
|
||||
* code is not as accurate as using a hardware timer but it is more flexible and
|
||||
* less hardware platform dependent.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_BIT_BANG 3 //Be sure to set this pin number if you un-comment
|
||||
|
||||
/* This is a fudge factor that adjusts bit-bang timing. Feel free to experiment
|
||||
* for best results.*/
|
||||
#define IR_BIT_BANG_OVERHEAD 10
|
||||
|
||||
/* We are going to presume that you want to use the same hardware timer to control
|
||||
* the 50 microsecond interrupt used by the IRrecv receiver class as was specified
|
||||
* above in the hardware detection section for sending. Even if you specified bit-bang
|
||||
* for sending, the definitions above have selected a default sending timer for you based
|
||||
* on hardware detection. If that is correct, then do nothing below. However if you do
|
||||
* wish to specify an IR_RECV_TIMER different than the IR_SEND_TIMER selected by the code
|
||||
* above, then you should un-comment the IR_RECV_TIMER_OVERRIDE and also un-comment one
|
||||
* and only one of the following IR_RECV_TIMERx lines below that.
|
||||
* NOTE: You are responsible for ensuring that the timer you are specifying is
|
||||
* available on your hardware. You should only choose timers which are shown as available
|
||||
* for your hardware platform as shown in the defines in the IR_SEND_TIMER section above.
|
||||
* NOTE: This discussion does not apply to SAMD 21 processors.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER_OVERRIDE
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER1
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER2
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER3
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER4
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER4_HS
|
||||
//#define IR_RECV_TIMER5
|
||||
|
||||
// Miscellaneous defines needed for computations below
|
||||
#ifdef F_CPU
|
||||
#define SYSCLOCK F_CPU // main Arduino clock
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define SYSCLOCK 16000000 // main Arduino clock
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Everything below this point is a computation based on user settings above.
|
||||
* In all likelihood you would never need to modify anything below this point
|
||||
* unless you are adding some completely new feature or seriously modifying
|
||||
* the behavior of existing features. In other words don't try this at home.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#if !defined(IR_RECV_TIMER_OVERRIDE)
|
||||
#if defined(IR_SEND_TIMER1)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER1
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER2)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER2
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER3)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER3
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER4)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER4
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER4_HS)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER4_HS
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER5)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TIMER5
|
||||
#elif defined(__SAMD21G18A__)//handle this one a little differently
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_TC3
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Unable to set IR_RECV_TIMER"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(IR_SEND_BIT_BANG) //defines for bit-bang output
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_BIT_BANG
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START unsigned int jmax=time/iLength;\
|
||||
for(unsigned int j=0;j<jmax;j++) {\
|
||||
digitalWrite(IR_SEND_BIT_BANG, HIGH); delayMicroseconds(onTime);\
|
||||
digitalWrite(IR_SEND_BIT_BANG, LOW); delayMicroseconds(offTime);}
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) float Length=1000.0/(float)khz;\
|
||||
iLength=int(Length+0.5); onTime=int(Length/3.0); \
|
||||
offTime=iLength-onTime-IR_BIT_BANG_OVERHEAD-(val<40);
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER1) // defines for timer1 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR1A |= _BV(COM1A1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR1A &= ~(_BV(COM1A1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint16_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR1A = _BV(WGM11); TCCR1B = _BV(WGM13) | _BV(CS10); \
|
||||
ICR1 = pwmval; OCR1A = pwmval / 3; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC1A_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC1A_PIN /* Teensy */
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER2) // defines for timer2 (8 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR2A |= _BV(COM2B1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR2A &= ~(_BV(COM2B1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint8_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR2A = _BV(WGM20); TCCR2B = _BV(WGM22) | _BV(CS20); \
|
||||
OCR2A = pwmval; OCR2B = pwmval / 3; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC2B_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC2B_PIN /* Teensy */
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER2
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER3) // defines for timer3 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR3A |= _BV(COM3A1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR3A &= ~(_BV(COM3A1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint16_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR3A = _BV(WGM31); TCCR3B = _BV(WGM33) | _BV(CS30); \
|
||||
ICR3 = pwmval; OCR3A = pwmval / 3; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC3A_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC3A_PIN /* Teensy */
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER3
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER4_HS) // defines for timer4 (10 bits, high speed option)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR4A |= _BV(COM4A1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR4A &= ~(_BV(COM4A1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint16_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR4A = (1<<PWM4A); TCCR4B = _BV(CS40); \
|
||||
TCCR4C = 0; TCCR4D = (1<<WGM40); \
|
||||
TCCR4E = 0; TC4H = pwmval >> 8; \
|
||||
OCR4C = pwmval; TC4H = (pwmval / 3) >> 8; OCR4A = (pwmval / 3) & 255; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC4A_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC4A_PIN /* Teensy */
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER4_HS
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER4) // defines for timer4 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR4A |= _BV(COM4A1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR4A &= ~(_BV(COM4A1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint16_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR4A = _BV(WGM41); TCCR4B = _BV(WGM43) | _BV(CS40); \
|
||||
ICR4 = pwmval; OCR4A = pwmval / 3; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC4A_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC4A_PIN
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER4
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_SEND_TIMER5) // defines for timer5 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START (TCCR5A |= _BV(COM5A1))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP (TCCR5A &= ~(_BV(COM5A1)))
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) ({ \
|
||||
const uint16_t pwmval = SYSCLOCK / 2000 / (val); \
|
||||
TCCR5A = _BV(WGM51); TCCR5B = _BV(WGM53) | _BV(CS50); \
|
||||
ICR5 = pwmval; OCR5A = pwmval / 3; })
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_OC5A_PIN)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN CORE_OC5A_PIN
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN IR_SEND_TIMER5
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#elif defined(IRLibSAMD21_h) // Used for SAMD 21
|
||||
/* All of these definitions have been moved to IRLibSAMD21.h
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#else // unknown timer
|
||||
#error "Internal code configuration error, no known IR_SEND_TIMER# defined\n"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* This section sets up the 50 microsecond interval timer used by the
|
||||
* IRrecv receiver class. The various timers have already been selected
|
||||
* earlier in this file. Theoretically you could change the 50 but it has not been tested.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define USEC_PER_TICK 50 // microseconds per clock interrupt tick
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(IR_RECV_TIMER1) // defines for timer1 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK1 = _BV(OCIE1A))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK1 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER1_COMPA_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR1A = 0; TCCR1B = _BV(WGM12) | _BV(CS10); \
|
||||
OCR1A = SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000; TCNT1 = 0; })
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_RECV_TIMER2) // defines for timer2 (8 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK2 = _BV(OCIE2A))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK2 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER2_COMPA_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_COUNT_TOP (SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000)
|
||||
#if (IR_RECV_COUNT_TOP < 256)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR2A = _BV(WGM21); TCCR2B = _BV(CS20); \
|
||||
OCR2A = IR_RECV_COUNT_TOP; TCNT2 = 0; })
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR2A = _BV(WGM21); TCCR2B = _BV(CS21); \
|
||||
OCR2A = IR_RECV_COUNT_TOP / 8; TCNT2 = 0; })
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_RECV_TIMER3) // defines for timer3 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK3 = _BV(OCIE3A))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK3 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER3_COMPA_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR3A = 0; TCCR3B = _BV(WGM32) | _BV(CS30); \
|
||||
OCR3A = SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000; TCNT3 = 0; })
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_RECV_TIMER4_HS) // defines for timer4 (10 bits, high speed option)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK4 = _BV(TOIE4))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK4 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER4_OVF_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR4A = 0; TCCR4B = _BV(CS40); \
|
||||
TCCR4C = 0; TCCR4D = 0; TCCR4E = 0; \
|
||||
TC4H = (SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000) >> 8; \
|
||||
OCR4C = (SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000) & 255; \
|
||||
TC4H = 0; TCNT4 = 0; })
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_RECV_TIMER4) // defines for timer4 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK4 = _BV(OCIE4A))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK4 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER4_COMPA_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR4A = 0; TCCR4B = _BV(WGM42) | _BV(CS40); \
|
||||
OCR4A = SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000; TCNT4 = 0; })
|
||||
|
||||
#elif defined(IR_RECV_TIMER5) // defines for timer5 (16 bits)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR (TIMSK5 = _BV(OCIE5A))
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR (TIMSK5 = 0)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME ISR(TIMER5_COMPA_vect,ISR_NOBLOCK)
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() ({ \
|
||||
TCCR5A = 0; TCCR5B = _BV(WGM52) | _BV(CS50); \
|
||||
OCR5A = SYSCLOCK * USEC_PER_TICK / 1000000; TCNT5 = 0; })
|
||||
#elif defined(IRLibSAMD21_h) //for SAMD 21
|
||||
/* All of these definitions have been moved to IRLibSAMD21.h
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS()
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#else // unknown timer
|
||||
#error "Internal code configuration error, no known IR_RECV_TIMER# defined\n"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
//Cannot use blinking LED on 13 if that's the output pin.
|
||||
#if (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==13)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED -1
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON()
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF()
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
// defines for blinking the LED
|
||||
#ifndef BLINKLED
|
||||
#if defined(CORE_LED0_PIN)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED CORE_LED0_PIN
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON() (digitalWrite(CORE_LED0_PIN, HIGH))
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF() (digitalWrite(CORE_LED0_PIN, LOW))
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED 13
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON() (PORTB |= B10000000)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF() (PORTB &= B01111111)
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega644__)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED 0
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON() (PORTD |= B00000001)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF() (PORTD &= B11111110)
|
||||
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32u4__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega328__)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED 13
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON() (PORTB |= B00100000)
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF() (PORTB &= B11011111)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define BLINKLED 13
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_ON() (digitalWrite(13, HIGH))
|
||||
#define BLINKLED_OFF() (digitalWrite(13, LOW))
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
extern uint8_t IRLib_didIROut;//See the explanation in IRLibHardware.cpp
|
||||
#endif //IRLibHardware_h
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibProtocols.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module enumerates the various supported protocols and defines a program memory
|
||||
* string used by the dump routines or your sketches to display the name of a protocol.
|
||||
* It is used by both Send and Decode sections of the code but not Receive.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "IRLibProtocols.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Returns a pointer to a flash stored string that is the name of the protocol received.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const __FlashStringHelper *Pnames(uint8_t type) {
|
||||
if(type>89) return F("Unsup");
|
||||
if(type>LAST_PROTOCOL) type=UNKNOWN;
|
||||
// You can add additional strings before the entry for hash code.
|
||||
const __FlashStringHelper *Names[LAST_PROTOCOL+1]={
|
||||
F("Unknown"),F("NEC"),F("Sony"),F("RC5"),F("RC6"),F("Panasonic Old"),F("JVC"),
|
||||
F("NECx"),F("Samsung36"),F("G.I.Cable"),F("DirecTV"),F("rcmm"),F("CYKM")
|
||||
//,F("Additional_13")//expand or edit these
|
||||
};
|
||||
return Names[type];
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibProtocols.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module enumerates the various supported protocols and defines a program memory
|
||||
* string used by the dump routines or your sketches to display the name of a protocol.
|
||||
* It is used by both Send and Decode sections of the code but not Receive.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIBPROTOCOLS_H
|
||||
#define IRLIBPROTOCOLS_H
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define UNKNOWN 0
|
||||
#define NEC 1
|
||||
#define SONY 2
|
||||
#define RC5 3
|
||||
#define RC6 4
|
||||
#define PANASONIC_OLD 5
|
||||
#define JVC 6
|
||||
#define NECX 7
|
||||
#define SAMSUNG36 8
|
||||
#define GICABLE 9
|
||||
#define DIRECTV 10
|
||||
#define RCMM 11
|
||||
#define CYKM 12
|
||||
//#define ADDITIONAL_13 13 //add additional protocols here
|
||||
//#define ADDITIONAL_14 14
|
||||
#define LAST_PROTOCOL 12 //Be sure to update this when adding protocols
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Returns a pointer to a flash stored string that is the name of the protocol received.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const __FlashStringHelper *Pnames(uint8_t Type);
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Miscellaneous values used by both Send and Decode modules
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define TOPBIT 0x80000000
|
||||
|
||||
// Decoded value for NEC and others when a repeat code is received or to be sent
|
||||
#define REPEAT_CODE 0xffffffff
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBPROTOCOLS_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
|
||||
/* IRrecvBase.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This module contains the base class classes for receiving IR signals. You will not create
|
||||
* instances of this class, rather it is used as a base class for the 3 different
|
||||
* receiver classes. These are the original IRrecv which uses a 50us timer interrupt.
|
||||
* The IRrecvPCI version that uses pin change interrupts and IRrecvLoop which uses no timers
|
||||
* or interrupts. Each of these has its own .h and .cpp file.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The IRrecvLoop files are in this folder. However the other two receivers in their own
|
||||
* separate libraries. That is because their interrupt service routines can conflict
|
||||
* with other ISRs. The ISRs conflict would occur even if you did not create an instance
|
||||
* of their receiver classes. Similarly the frequency detection receiver which also uses
|
||||
* interrupts is also in a separate folder IRLibFreq.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "IRLibRecvBase.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* This structure contains all of the global variables used by the ISRs to communicate
|
||||
* with the receiver and decoder objects. You cannot pass parameters to an ISR so
|
||||
* these values must be global. The fields are defined in IRLibRecvBase.h
|
||||
*/
|
||||
recvGlobal_t recvGlobal;
|
||||
|
||||
// The base constructor receives the pin number
|
||||
IRrecvBase::IRrecvBase(uint8_t recvPin) {
|
||||
recvGlobal.recvPin = recvPin;
|
||||
init();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialization common to all three receiver classes
|
||||
void IRrecvBase::init(void) {
|
||||
//These first two lines would normally be done by the decoder
|
||||
//however in rare circumstances there is no decoder.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=false; //turned on by enableIRIn.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeBuffer=recvGlobal.recvBuffer;//default buffer
|
||||
recvGlobal.enableAutoResume=false;
|
||||
recvGlobal.frameTimeout=DEFAULT_FRAME_TIMEOUT;
|
||||
recvGlobal.frameTimeoutTicks=recvGlobal.frameTimeout/USEC_PER_TICK;
|
||||
markExcess=DEFAULT_MARK_EXCESS;
|
||||
recvGlobal.newDataAvailable=false;
|
||||
recvGlobal.enableBlinkLED=false;
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState=STATE_FINISHED;//i.e. Not running.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Turn on or off a blinking LED which indicates signal received. Usually pin 13.
|
||||
void blink13(bool enableBlinkLED){
|
||||
#if (BLINKLED>0)
|
||||
pinMode(BLINKLED,OUTPUT);
|
||||
recvGlobal.enableBlinkLED=enableBlinkLED;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Any receiver class must implement a getResults method that will return true when
|
||||
* a complete frame of data has been received. When your getResults determines that
|
||||
* the frame is complete, it must guarantee that there will be no further changes to
|
||||
* the data in the buffer or the length value. It can do that by either disabling
|
||||
* interrupts or putting the ISR in a state that ensures it will not
|
||||
* change those values. Then it must then call IRrecvBase::getResults. This base method
|
||||
* will then will perform some math on the values and copy them to the decodeBuffer.
|
||||
* Some receivers provide results in recvBuffer measured in ticks of some number of
|
||||
* microseconds while others return results in actual microseconds. If you use ticks then
|
||||
* you should pass a multiplier value in timePerTicks.
|
||||
* NOTE: Only call the base method if newDataAvailable is true.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool IRrecvBase::getResults(const uint16_t timePerTick) {
|
||||
//Conceptually the loop below copies data from the receiver buffer to the decode buffer
|
||||
//while performing some math. In some instances, the source and destination are the same.
|
||||
//The decoder has already set up decodeBuffer to point to the proper destination.
|
||||
//Here we need to figure out the source. If didAutoResume is true then the ISR has already
|
||||
//copied the data to decodeBuffer so it is both source and destination. In all
|
||||
//other circumstances the source is always recvGlobal.recvBuffer.
|
||||
recvGlobal.newDataAvailable=false;
|
||||
volatile uint16_t *Source;
|
||||
//DEBUG_VALUE("recvGlobal.didAutoResume",recvGlobal.didAutoResume);
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.didAutoResume) {
|
||||
Source=recvGlobal.decodeBuffer;
|
||||
recvGlobal.didAutoResume=false;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Source=recvGlobal.recvBuffer;
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeLength=recvGlobal.recvLength;//if auto resumed, was already copied
|
||||
}
|
||||
//If the receiver counts time intervals rather than actual microseconds we will multiply
|
||||
//the data by timePerTick. It also adjusts the data by adding or subtracting the
|
||||
//markExcess value. See the documentation on markExcess for details.
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=0; i<recvGlobal.decodeLength; i++) {
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[i]=Source[i]*timePerTick + ( (i % 2)? -markExcess:markExcess);
|
||||
}
|
||||
//Now that the decoder has its data it doesn't want any more until it tells you.
|
||||
//It will do so by calling enableIRIn.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=false;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* The user calls enableIRIn each time it is ready to receive data. Previously
|
||||
* this was only used to initialize the receiver once and subsequent calls were made
|
||||
* to a method called "resume". However it was confusing because you had to call
|
||||
* enableIRIn after a send because any sending would disable IRIn. It's simpler just to
|
||||
* always use enableIRIn even though parts of it are slightly redundant.
|
||||
* The interrupt driven receivers call this before enabling interrupts.
|
||||
* See the comments on IRrecv::enableIRIn() in IRLibRecv.cpp regarding auto resume.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvBase::enableIRIn(void) {
|
||||
//some IR receiver datesheets recommend pull-up resistors
|
||||
pinMode(recvGlobal.recvPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
|
||||
recvGlobal.recvLength = 0;
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState = STATE_READY_TO_BEGIN;
|
||||
IRLib_didIROut=false;//We reinitialized so reset until somebody does more output.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Even when not receiving data or waiting to receive data, the ISR may remain active
|
||||
* but remains in a do-nothing state. If the user wants to truly shut down the ISR
|
||||
* they can call this method. The derived method should disable the ISR and then call
|
||||
* this base method to the turn everything off.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvBase::disableIRIn(void) {
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=false;
|
||||
recvGlobal.didAutoResume=false;
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState=STATE_FINISHED;//i.e. Not running.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Normally recvGlobal.decodeBuffer points to recvGlobal.recvBuffer and therefore
|
||||
* decoding uses the same buffer as receiving. However you may want to resume
|
||||
* receiving while still decoding. To do so must specify a separate buffer for decoding.
|
||||
* You will declare the buffer as "uint16_t myBuffer[RECV_BUF_LENGHT];" in your sketch
|
||||
* then pass its address using the method below. Then IRrecvBase::getResults() will copy
|
||||
* timing values from its buffer to yours. The receiver will then automatically resume.
|
||||
* The receiver will not overwrite your buffer unless you have called enableIRIn()
|
||||
* to tell it that you have finished your decoding. In other words auto resume will only
|
||||
* occur once until you again call enableIRIn().
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvBase::enableAutoResume(uint16_t *P){
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeBuffer=(volatile uint16_t*)P;
|
||||
recvGlobal.enableAutoResume=true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// This had to be a method so that IRrecv::setFrameTimeout can compute
|
||||
// frameTimeoutTicks.
|
||||
void IRrecvBase::setFrameTimeout(uint16_t frameTimeout) {
|
||||
recvGlobal.frameTimeout=frameTimeout;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*********************
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The remaining functions below are not part of any class or object. They are global
|
||||
* so they can be called by the ISRs or for other reasons are not really tied to any
|
||||
* class or object.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*********************/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This function is called by both the 50us and PCI ISR in one of two circumstances:
|
||||
* 1) The SPACE was long enough that we are sure the frame is over and ready to process.
|
||||
* 2) The buffer overflowed we have to quit. The parameter is for debugging purposes only.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_IRrecvComplete(uint8_t Reason) {
|
||||
// Here we are finished. Let the world know there is new data available.
|
||||
recvGlobal.newDataAvailable=true;
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState=STATE_FINISHED;//this essentially pauses the receiver ISR
|
||||
//Now we need to see if we want to auto resume. We can only do that if it is enabled and
|
||||
//if the user is finished using the buffer from the previous capture and wants more data.
|
||||
//DEBUG_VALUE ("Reason completed", Reason)
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.enableAutoResume && recvGlobal.decoderWantsData) {
|
||||
//Here we do the actual auto resume. We will copy the data using memcpy because it
|
||||
//should be very quick. Any calculations will be handled by the getResults method but
|
||||
//not here.
|
||||
memcpy((void *)recvGlobal.decodeBuffer, (const void*)recvGlobal.recvBuffer,recvGlobal.recvLength*sizeof(uint16_t));
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeLength=recvGlobal.recvLength;
|
||||
// We have just copied the data to the decoder so it's not going to want more until
|
||||
// it tells us that it is ready for more.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=false;
|
||||
// Tell getResults that we auto resumed therefore the data has been copied but
|
||||
// still needs the math done.
|
||||
recvGlobal.didAutoResume=true;
|
||||
// Now we need to reset the index to the beginning and restart the state machine.
|
||||
recvGlobal.recvLength=0;
|
||||
//While we were doing the copy, the 50 us interrupt continued but the state machine
|
||||
//was paused in the STATE_FINISHED. Now we actually turn it back on till you get to
|
||||
//actually receive data.
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState= STATE_READY_TO_BEGIN;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* If your hardware is set up to do both output and input but your particular sketch
|
||||
* doesn't do any output, this method will ensure that your output pin is low
|
||||
* and doesn't turn on your IR LED or any output circuit.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_NoOutput (void) {
|
||||
#if defined(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN)
|
||||
pinMode(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, LOW); // When not sending PWM, we want it low
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Do the actual blinking off and on of the indicator LED. Called by the various
|
||||
* receiver ISRs
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_doBlink(void) {
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.enableBlinkLED) {
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.recvLength & 1) {
|
||||
BLINKLED_ON(); // turn pin 13 LED on
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
BLINKLED_OFF(); // turn pin 13 LED off
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibRecvBase.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This module contains the base class classes for receiving IR signals. You will not create
|
||||
* instances of this class, rather it is used as a base class for the 3 different
|
||||
* receiver classes. These are the original IRrecv which uses a 50us timer interrupt.
|
||||
* The IRrecvPCI version that uses pin change interrupts and IRrecvLoop which uses no timers
|
||||
* or interrupts. Each of these has its own .h and .cpp file.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The IRrecvLoop files are in this folder. However the other two receivers in their own
|
||||
* separate libraries. That is because their interrupt service routines can conflict
|
||||
* with other ISRs. The ISRs conflict would occur even if you did not create an instance
|
||||
* of their receiver classes. Similarly the frequency detection receiver which also uses
|
||||
* interrupts is also in a separate folder IRLibFreq.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLibRecvBase_h
|
||||
#define IRLibRecvBase_h
|
||||
#include "IRLibGlobals.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Below are default values for initializing various receiver parameters.
|
||||
* Each of these can be set using methods or variables in the base class
|
||||
* however these are the defaults if you do not specifically set them.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_BLINK_PIN LED_BUILTIN //NOTE: LED_BUILTIN is an Arduino constant
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_BLINK_ENABLED false
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_MARK_EXCESS 50
|
||||
#define DEFAULT_FRAME_TIMEOUT 7800 //maximum length of SPACE Sbefore we assume frame ended
|
||||
//DEFAULT_TIMEOUT should be 1.25*the_largest_space_any_valid_IR_protocol_might_have.
|
||||
//In IRremote library ir_Dish.cpp space they use DISH_RPT_SPACE 6200 while referenced says
|
||||
//about 6000. If we take 6200*1.25= 7750 rounded up we will use 7800. Previous IRLib
|
||||
//value was 10000 was probably too large. Thanks to Gabriel Staples for this note.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Base receiver class. Do not create instance. Only used as base for other
|
||||
* receiver classes. See documentation for description of each method or variable.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class IRrecvBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
IRrecvBase(void) {};
|
||||
IRrecvBase(uint8_t recvPin);
|
||||
bool getResults(const uint16_t timePerTicks=1);
|
||||
virtual void enableIRIn(void);
|
||||
virtual void disableIRIn(void);
|
||||
void enableAutoResume(uint16_t *P);
|
||||
void setFrameTimeout(uint16_t frameTimeout);
|
||||
void blink13(bool enableBlinkLED);
|
||||
uint16_t markExcess;
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
void init(void);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* The global functions below are not methods of any class because they either
|
||||
* do not directly relate to the classes or they must be global functions
|
||||
* so that they can appear inside and ISR. You cannot pass variables to ISR's
|
||||
* or you could not pass any object or methods to it. These functions have been
|
||||
* renamed to emphasize the fact that they are part of this library.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* This function does the actual blinking of an indicator LED. Must be global
|
||||
* so it can be used by ISRs
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_doBlink(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Some users create custom boards for input and output of IR signals and those boards are
|
||||
* connected to their Arduino even in the case when the sketch only does input. It is
|
||||
* theoretically possible that when running an <20>input only<6C> sketch that the output pin
|
||||
* could initialize high and your output LED would be on all the time. LED driver circuits
|
||||
* are sometimes designed to overdrive the LED because it is used only intermittently. If
|
||||
* it were to be accidentally left on continuously, it could burn out your circuit. If you
|
||||
* want to ensure that this does not happen you can call the function below.
|
||||
* NOTE: This used to be a method of the base receiver class but it really doesn't have
|
||||
* anything to do with receiving so we renamed it and made it a standalone function.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_NoOutput(void);
|
||||
|
||||
/* This function is called by both the 50us and PCI ISR in one of two circumstances:
|
||||
* 1) The SPACE was long enough that we are sure the frame is over and ready to process.
|
||||
* 2) The buffer overflowed we have to quit. The parameter is for debugging purposes only.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRLib_IRrecvComplete(uint8_t Reason);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLibRecvBase_h
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
/* IRrecvPCI.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This module implements the IRrecvPCI receiver class which uses pin change interrupts to
|
||||
* poll the input pin. This class gives more accurate results than the 50us timer based
|
||||
* IRrecv but it has other limitations. It uses the Arduino "attachInterrupt()" function
|
||||
* which can conflict with other libraries. Also unless you use an external buffer and
|
||||
* enable auto resume this receiver occasionally fails to receive the second of 2 quickly
|
||||
* sent frames. If you do not have sufficient RAM for a second buffer you should consider
|
||||
* using the other two available receiver classes.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This receiver is based in part on Arduino firmware for use with AnalysIR IR signal analysis
|
||||
* software for Windows PCs. Many thanks to the people at http://analysir.com for their
|
||||
* assistance in developing this section of code.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "IRLibRecvPCI.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h" //needed for IRLib_didIROut
|
||||
|
||||
void IRrecvPCI_Handler();//prototype for interrupt handler
|
||||
|
||||
/* Note that the constructor is passed the interrupt number rather than the pin number.
|
||||
* WARNING: These interrupt numbers which are passed to <20>attachInterrupt()<29> are not
|
||||
* necessarily identical to the interrupt numbers in the datasheet of the processor chip
|
||||
* you are using. Rather it is a numbering system to the <20>attachInterrupt()<29> Arduino
|
||||
* function. For more information on attachInterrupt see
|
||||
* http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt
|
||||
*/
|
||||
IRrecvPCI::IRrecvPCI(uint8_t pin) {
|
||||
init();
|
||||
intrNum=digitalPinToInterrupt(pin);
|
||||
recvGlobal.recvPin=pin;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initializes receiving and attaches the pin change interrupt handler. Call this to
|
||||
* initialize it again to resume receiving after completing the decoding. Previous versions
|
||||
* of IRLib had a "resume" method that you should use this in either initializing or resuming.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvPCI::enableIRIn(void) {
|
||||
//See comments on IRrecv::enableIRIn in "IRLibRecv.cpp" for explanation of this logic
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.newDataAvailable)
|
||||
return;
|
||||
recvGlobal.decoderWantsData=true;//otherwise he wouldn't have called
|
||||
if( (recvGlobal.currentState==STATE_FINISHED) || IRLib_didIROut ) {
|
||||
IRrecvBase::enableIRIn();
|
||||
recvGlobal.timer=micros();
|
||||
attachInterrupt(intrNum, IRrecvPCI_Handler, CHANGE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* Even when not sampling inputs and recording pulse timing, the ISR remains active
|
||||
* continues to interrupt every 50us however it remains in a do-nothing state. If
|
||||
* the user wants to truly shut down the ISR they can call this method.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvPCI::disableIRIn(void) {
|
||||
detachInterrupt(intrNum);
|
||||
IRrecvBase::disableIRIn();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Returns true if a frame of data is available in the buffer. Most of the
|
||||
* handling is done by the base method. Because the ISR only is active when the pin
|
||||
* is changing, it may not recognize the long gap at the end of the frame so we need to
|
||||
* test to see if we had a long gap. Because the ISR is active, we need to ensure
|
||||
* that it doesn't change any variables while we are in the middle of accessing them.
|
||||
* Unfortunately the ATOMIC_BLOCK macro that we used to use is not supported for
|
||||
* SAMD 21 platforms so we have to use "noInterrupts();" and "interrupts();"
|
||||
* This is only necessary for multibyte variables.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool IRrecvPCI::getResults(void) {
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.newDataAvailable) {
|
||||
IRrecvBase::getResults();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//ISR hasn't detected end of frame so if running we will take a peek
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.currentState==STATE_RUNNING) {
|
||||
//Only check for timeout if it is a SPACE
|
||||
if(digitalRead(recvGlobal.recvPin)) {//pin high means SPACE
|
||||
uint32_t changeTime; //time of the last change
|
||||
noInterrupts (); //Ensure atomic access of volatile variable
|
||||
changeTime=recvGlobal.timer;
|
||||
interrupts(); //restore interrupts
|
||||
if( (micros()-changeTime) > recvGlobal.frameTimeout) {
|
||||
IRLib_IRrecvComplete(3);
|
||||
IRrecvBase::getResults();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/* This is the interrupt handler used by this class. It is called every time the input
|
||||
* pin changes from high to low or from low to high. The initial state of the state machine
|
||||
* is STATE_READY_TO_BEGIN. It waits until it sees a MARK before it switches to
|
||||
* STATE_RUNNING. Each subsequent interrupt it computes the time since the previous
|
||||
* interrupt. If it notices a SPACE is especially long then it calls IRLib_IRrecvComplete
|
||||
* which sets the proper flags to say that we had received data and implements
|
||||
* auto resume if enabled. The state STATE_FINISHED means that interrupts are continuing
|
||||
* however the receiver isn't ready for more data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRrecvPCI_Handler(){
|
||||
uint32_t volatile changeTime=micros();
|
||||
uint32_t deltaTime=changeTime-recvGlobal.timer;
|
||||
switch(recvGlobal.currentState) {
|
||||
case STATE_FINISHED: return;
|
||||
case STATE_RUNNING:
|
||||
IRLib_doBlink();
|
||||
if( !(recvGlobal.recvLength & 1) ){
|
||||
if (deltaTime>recvGlobal.frameTimeout) {
|
||||
IRLib_IRrecvComplete(1);//all finished, reset and possibly do auto resume
|
||||
return;//don't record final space
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case STATE_READY_TO_BEGIN:
|
||||
if(digitalRead(recvGlobal.recvPin)) {//pin high means SPACE
|
||||
return;//don't start until we get a MARK
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
recvGlobal.currentState=STATE_RUNNING;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
};
|
||||
recvGlobal.recvBuffer[recvGlobal.recvLength]=deltaTime;
|
||||
recvGlobal.timer=changeTime;
|
||||
if(++recvGlobal.recvLength>=RECV_BUF_LENGTH) {//buffer overflows so we quit
|
||||
IRLib_IRrecvComplete(2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibRecvPCI.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You should include this header in your sketch if you're using the IRLibRecvPCI
|
||||
* receiver class which uses pin change interrupts to poll the input pin.
|
||||
* This version gives more accurate results than the 50us timer based IRrecv but it has
|
||||
* other limitations. It uses the Arduino "attachInterrupt()" function which can conflict
|
||||
* with other libraries. Also unless you use an external buffer and enable auto resume
|
||||
* this receiver occasionally fails to receive the second of 2 quickly sent frames.
|
||||
* If you do not have sufficient RAM for a second buffer you should consider using the
|
||||
* other two available receiver classes.
|
||||
* Applications that do sending only SHOULD NOT include this header.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This receiver is based in part on Arduino firmware for use with AnalysIR IR signal analysis
|
||||
* software for Windows PCs. Many thanks to the people at http://analysir.com for their
|
||||
* assistance in developing this section of code.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLibRecvPCI_h
|
||||
#define IRLibRecvPCI_h
|
||||
#include "IRLibRecvBase.h"
|
||||
|
||||
class IRrecvPCI: public IRrecvBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
IRrecvPCI(void){}; //Use only when receiver object is part of larger object.
|
||||
// Still must initialize using constructor below.
|
||||
IRrecvPCI(uint8_t pin);
|
||||
void enableIRIn(void); //call to initialize or resume receiving
|
||||
bool getResults(void); //returns true if new frame of data has been received
|
||||
void disableIRIn(void); //ISR runs continuously once started. Use this if you want to stop.
|
||||
private:
|
||||
uint8_t intrNum;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLibRecvPCI_h
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibSAMD21.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This type of content is normally stored in IRLibHardware.h but we have
|
||||
* moved at her because the SAMD21 support is significantly different than the
|
||||
* AVR 8-bit hardware support. Separating it out into a separate file
|
||||
* will make it easier to include comments and to maintain the code.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* See IRLibSAMD21.h for details about this implementation.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#if defined (__SAMD21G18A__)
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h"
|
||||
|
||||
//Save some typing
|
||||
#define IR_APD g_APinDescription[IR_SEND_PWM_PIN]
|
||||
|
||||
void initializeSAMD21PWM(uint16_t khz) {
|
||||
// Enable the port multiplexer for the PWM channel on pin
|
||||
PORT->Group[IR_APD.ulPort].PINCFG[IR_APD.ulPin].bit.PMUXEN = 1;
|
||||
// Connect the TCC timer to the port outputs - port pins are paired odd PMUXO and even PMUXE
|
||||
// F & E peripherals specify the timers: TCC0, TCC1 and TCC2
|
||||
PORT->Group[IR_APD.ulPort].PMUX[IR_APD.ulPin >> 1].reg |= IR_MUX_EF;
|
||||
|
||||
// Feed GCLK0 to TCC0 and TCC1
|
||||
REG_GCLK_CLKCTRL = GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN | // Enable GCLK0 to TCC0 and TCC1
|
||||
GCLK_CLKCTRL_GEN_GCLK0 | // Select GCLK0
|
||||
GCLK_CLKCTRL_ID_TCC0_TCC1; // Feed GCLK0 to TCC0 and TCC1
|
||||
syncGCLK; // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
// Normal (single slope) PWM operation: timers countinuously count up to PER
|
||||
// register value and then is reset to 0
|
||||
IR_TCCx->WAVE.reg |= TCC_WAVE_WAVEGEN_NPWM; // Setup single slope PWM on TCCx
|
||||
while (IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.WAVE); // Wait for synchronization
|
||||
|
||||
// Each timer counts up to a maximum or TOP value set by the PER register,
|
||||
// this determines the frequency of the PWM operation.
|
||||
uint32_t cc = F_CPU/(khz*1000) - 1;
|
||||
IR_TCCx->PER.reg = cc; // Set the frequency of the PWM on IR_TCCx
|
||||
while(IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.PER);
|
||||
|
||||
// The CCx register value corresponds to the pulsewidth in microseconds (us)
|
||||
IR_TCCx->CC[(IR_CCn & 0x03)].reg = cc/3; // Set the duty cycle of the PWM on TCC0 to 33%
|
||||
while(IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.IR_CCx);
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable IR_TCCx timer but do not turn on PWM yet. Will turn it on later.
|
||||
IR_TCCx->CTRLA.reg |= TCC_CTRLA_PRESCALER_DIV1; // Divide GCLK0 by 1
|
||||
while (IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.ENABLE);
|
||||
IR_TCCx->CTRLA.reg &= ~TCC_CTRLA_ENABLE; //initially off will turn on later
|
||||
while (IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.ENABLE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Setup the 50 microsecond timer hardware interrupt for the IRrecv class.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void initializeSAMD21timerInterrupt(void) {
|
||||
GCLK->CLKCTRL.reg = (uint16_t)(GCLK_CLKCTRL_CLKEN |
|
||||
GCLK_CLKCTRL_GEN_GCLK0 |
|
||||
GCLK_CLKCTRL_ID(IR_GCM));
|
||||
syncGCLK;
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.reg &= ~TC_CTRLA_ENABLE;
|
||||
syncTC;
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.reg = TC_CTRLA_SWRST;
|
||||
while (IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.bit.SWRST);
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.reg |= TC_CTRLA_MODE_COUNT16;
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.reg |= TC_CTRLA_WAVEGEN_MFRQ;
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CC[0].reg = F_CPU/(1000000/USEC_PER_TICK) - 1;
|
||||
syncTC;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibSAMD21.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This type of content is normally stored in IRLibHardware.h but we have
|
||||
* moved at her because the SAMD21 support is significantly different than the
|
||||
* AVR 8-bit hardware support. Separating it out into a separate file
|
||||
* will make it easier to include comments and to maintain the code.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* This file provides hardware support for the SAMD21G18A processor or as we
|
||||
* will refer to it simply as SAMD 21. This processor is used in the Arduino Zero,
|
||||
* Arduino M0, Arduino M0 Pro, and the Adafruit Feather M0 series boards as well as
|
||||
* the upcoming Adafruit Circuit Playground Express.
|
||||
* Most of the code has been adapted from messages on the Arduino.cc support forum
|
||||
* and from the code at:
|
||||
* https://github.com/manitou48/ZERO/tree/master/IRtest
|
||||
* Receiving is supported through all three receiver classes. As you would expect
|
||||
* the IRrecvLoop class can be used with any available input pin. The IRrecvPCI and
|
||||
* IRfrequency classes can be used on any pin that supports "attachInterrupt()".
|
||||
* Specifically that means everything except pin 4 on the Arduino Zero. And everything
|
||||
* except pin 2 on the boards from Arduino.org such as the Arduino M0, M0 Pro, and
|
||||
* Zero Pro. For details on supported pins see these links:
|
||||
* https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt
|
||||
* http://www.arduino.org/learning/reference/AttachInterrupt
|
||||
* Note that although we support Arduino.org hardware, you should only use the
|
||||
* Arduino.cc IDE for compiling your sketches.
|
||||
* Both sending and receiving use GCLK0 even though GCLK0-GCLK3 are generally reserved
|
||||
* the Arduino infrastructure. However we are using the default 48 MHz clock source
|
||||
* and a divisor of "1" so we aren't changing any of the GCLK0 set up. It's therefore
|
||||
* safe to use.
|
||||
* The IRrecv receiver class using a 50 microsecond timer interrupt is also supported.
|
||||
* It defaults to using hardware timer TC3 however TC4 and TC5 can also be used in case
|
||||
* of conflicts with other libraries. The IRrecv and IRrecvLoop classes should be able to use
|
||||
* any available input pin. Note that all of our example sketches used pin 2 for
|
||||
* receiver and pin 3 for frequency measurement. However pin 2 is not available for PCI
|
||||
* interrupts on the Arduino.org platforms and neither 2 nor 3 are available on the
|
||||
* Adafruit Feather M0 platforms. We are recommending using 5 and 6 for receiving and
|
||||
* frequency measurement respectively.
|
||||
* For sending, you can use any pin that supports PWM on your particular
|
||||
* platform. On Arduino Zero that means pins 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, or 13.
|
||||
* Additionally Arduino M0 Pro adds pins 2 and 7 to that list. In all cases the default
|
||||
* output pin is 9. The code automatically selects TCC0 or TCC1 based on pin number
|
||||
* as needed. It has been tested at frequencies of 36, 38, 39, 40 and 57 which
|
||||
* are the frequencies of our supported protocols.
|
||||
* As of this release the code has been tested on Arduino Zero, Arduino M0 Pro, and
|
||||
* Adafruit Feather M0 BLE version.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLibSAMD21_h
|
||||
#define IRLibSAMD21_h
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This section contains user changeable values. You can probably stick with the defaults
|
||||
* but if there are hardware conflicts with other libraries, you can change these values.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
//Choose PWM output pin number from among the following
|
||||
//Un-comment only one of these.
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 2
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 3
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 4
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 5
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 6
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 7
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 8
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 9
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 10
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 11
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 12
|
||||
//#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 13
|
||||
//Override default for Adafruit Circuit Playground Express
|
||||
#ifdef ARDUINO_SAMD_CIRCUITPLAYGROUND_EXPRESS
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_PIN 25
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
//Choose which timer counter to use for the 50 microsecond interrupt
|
||||
//Un-comment only one of these.
|
||||
#define IR_TCn 3
|
||||
//#define IR_TCn 4
|
||||
//#define IR_TCn 5
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Everything below this point should not be changed. It computes needed defines
|
||||
* based on the user set values above.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Saves us a lot of typing when synchronizing
|
||||
#define syncTC while (IR_TCx->COUNT16.STATUS.bit.SYNCBUSY)
|
||||
#define syncGCLK while (GCLK->STATUS.bit.SYNCBUSY)
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_SAMD_FEATHER_M0)
|
||||
#if ( (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN<5) || (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==7) || (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==8) )
|
||||
#error "Pin unsupported on Adafruit Feather M0"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
//Pins 8 and 9 use TCC1 and all others use TCC0
|
||||
#if ( (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==8) || (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==9) )
|
||||
#define IR_TCCx TCC1
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define IR_TCCx TCC0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
//Although there are 8 WO there are only 4 CC
|
||||
#define CC4 CC0
|
||||
#define CC5 CC1
|
||||
#define CC6 CC2
|
||||
#define CC7 CC3
|
||||
|
||||
//Set other values based on pin number
|
||||
#if (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==2)
|
||||
//NOTE: Arduino M0 Pro only
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
//PA08 E:TCC0-WO[0] F:TCC1-WO[2]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_E
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC0
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 0
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Pin 2 only available on Arduino M0 Pro"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==3)
|
||||
//PA09 E:TCC0-WO[1] F:TCC1-WO[3]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_E
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC1
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 1
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==4)
|
||||
//Arduino M0 Pro swaps pins 2 and 4
|
||||
#if(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
//Arduino M0 Pro
|
||||
//PA09 E:TC3-WO[0] F:TCC0-WO[4]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC4
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 4
|
||||
#else
|
||||
//Arduino Zero
|
||||
//PA08 E:TCC0-WO[0] F:TCC1-WO[2]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_E
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC0
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==5)
|
||||
//PA15 E:TC3-WO[1] F:TCC0-WO[5]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC5
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 5
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==6)
|
||||
//PA20 E:TC7-WO[0] F:TCC0-WO[6]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC6
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 6
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==7)
|
||||
//NOTE: Arduino M0 Pro only
|
||||
#if defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
//PA08 E:TC7-WO[1] F:TCC0-WO[7]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC7
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 7
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Pin 7 only available on Arduino M0 Pro"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==8)
|
||||
//PA06 E:TCC1-WO[0] F:--
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_E
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC0
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 0
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==9)
|
||||
//PA07 E:TCC1-WO[1] F:--
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_E
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC1
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 1
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==10)
|
||||
//PA18 E:TC3-WO[0] F:TCC0-WO[2]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC2
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 2
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==11)
|
||||
//PA16 E:TCC2-WO[0] F:TCC0-WO[6]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXE_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC6
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 6
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==12)
|
||||
//PA19 E:TC3-WO[1] F:TCC0-WO[3]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC3
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 3
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==13)
|
||||
//PA17 E:TCC2-WO[1] F:TCC0-WO[7]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC7
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 7
|
||||
#elif (IR_SEND_PWM_PIN==25)//Adafruit Circuit Playground Express only
|
||||
//PA23 E:TC4-WO[1] F:TCC0-WO[5]
|
||||
#define IR_MUX_EF PORT_PMUX_PMUXO_F
|
||||
#define IR_CCx CC5
|
||||
#define IR_CCn 5
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Invalid SAMD21 PWM pin"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Turns PWM on and off after already set up
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_START {IR_TCCx->CTRLA.reg |= TCC_CTRLA_ENABLE;\
|
||||
while (IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.ENABLE);}
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time) IRLibDelayUSecs(time)
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PWM_STOP {IR_TCCx->CTRLA.reg &= ~TCC_CTRLA_ENABLE;\
|
||||
while (IR_TCCx->SYNCBUSY.bit.ENABLE);}
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(val) initializeSAMD21PWM(val);
|
||||
|
||||
/* These are the definitions for setting up the 50 microsecond
|
||||
* timer interrupt for the IRrecv class.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#if (IR_TCn==3)
|
||||
#define IR_TCx TC3
|
||||
#define IR_GCM GCM_TCC2_TC3
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME void TC3_Handler()
|
||||
#define IR_IRQ TC3_IRQn
|
||||
#elif (IR_TCn==4)
|
||||
#define IR_TCx TC4
|
||||
#define IR_GCM GCM_TC4_TC5
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME void TC4_Handler()
|
||||
#define IR_IRQ TC4_IRQn
|
||||
#elif (IR_TCn==5)
|
||||
#define IR_TCx TC5
|
||||
#define IR_GCM GCM_TC4_TC5
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_INTR_NAME void TC5_Handler()
|
||||
#define IR_IRQ TC5_IRQn
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#error "Invalid IR_TCn value"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_ENABLE_INTR ({NVIC_EnableIRQ(IR_IRQ);\
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.INTENSET.reg = TC_INTENSET_OVF;\
|
||||
IR_TCx->COUNT16.CTRLA.reg |= TC_CTRLA_ENABLE; syncTC;})
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR IR_TCx->COUNT16.INTENCLR.reg = TC_INTENCLR_OVF;
|
||||
#define IR_RECV_CONFIG_TICKS() initializeSAMD21timerInterrupt()
|
||||
|
||||
//Clear interrupt
|
||||
#define IR_CLEAR_INTERRUPT IR_TCx->COUNT16.INTFLAG.bit.MC0 = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
//prototypes
|
||||
void initializeSAMD21PWM(uint16_t khz);
|
||||
void initializeSAMD21timerInterrupt(void);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLibSAMD21_h
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibSendBase.cpp
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module contains the base classes for sending. You will not create instances
|
||||
* of these classes, rather you will use them as base classes in creating derived
|
||||
* protocol specific decoders. Each protocol specific send class begins
|
||||
* by calling enableIROut(uint8_t kHz) to set the carrier frequency.
|
||||
* It then calls mark(int usec) and space(inc usec) to transmit marks and
|
||||
* spaces of varying length of microseconds in the manner which the protocol defines.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#include "IRLibSendBase.h"
|
||||
#include "IRLibHardware.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Most of the protocols have a header consisting of a mark/space of a particular length followed by
|
||||
* a series of variable length mark/space signals. Depending on the protocol they very the lengths of the
|
||||
* mark or the space to indicate a data bit of "0" or "1". Most also end with a stop bit of "1".
|
||||
* The basic structure of the sending and decoding these protocols led to lots of redundant code.
|
||||
* Therefore I have implemented generic sending and decoding routines. You just need to pass a bunch of customized
|
||||
* parameters and it does the work. This reduces compiled code size with only minor speed degradation.
|
||||
* You may be able to implement new protocols by simply passing the proper values to these generic routines.
|
||||
* The decoding routines do not encode stop bits. So you have to tell this routine whether or not to send one.
|
||||
* Some protocols have a fixed amount of space between frames while others require that the entire frame
|
||||
* be a particularly length despite the fact that the data transmission time may be veritable. Pass this
|
||||
* frame length of time the parameter maxExtent. It's default value is zero.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void IRsendBase::sendGeneric(uint32_t data, uint8_t numBits, uint16_t headMark, uint16_t headSpace,
|
||||
uint16_t markOne, uint16_t markZero, uint16_t spaceOne, uint16_t spaceZero,
|
||||
uint8_t kHz, bool useStop, uint32_t maxExtent) {
|
||||
extent=0;
|
||||
data = data << (32 - numBits);
|
||||
enableIROut(kHz);
|
||||
//Some protocols do not send a header when sending repeat codes. So we pass a zero value to indicate skipping this.
|
||||
if(headMark) mark(headMark);
|
||||
if(headSpace) space(headSpace);
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i <numBits; i++) {
|
||||
if (data & TOPBIT) {
|
||||
mark(markOne); space(spaceOne);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
mark(markZero); space(spaceZero);
|
||||
}
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(useStop) mark(markOne); //stop bit of "1"
|
||||
if(maxExtent) {
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_TRACE
|
||||
Serial.print("maxExtent="); Serial.println(maxExtent);
|
||||
Serial.print("extent="); Serial.println(extent);
|
||||
Serial.print("Difference="); Serial.println(maxExtent-extent);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
space(maxExtent-extent);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else space(spaceOne);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void IRsendBase::enableIROut(uint8_t khz) {
|
||||
//NOTE: the comments on this routine accompanied the original early version of IRremote library
|
||||
//which only used TIMER2. The parameters defined in IRLibTimer.h may or may not work this way.
|
||||
// Enables IR output. The khz value controls the modulation frequency in kilohertz.
|
||||
// The IR output will be on pin 3 (OC2B).
|
||||
// This routine is designed for 36-40KHz; if you use it for other values, it's up to you
|
||||
// to make sure it gives reasonable results. (Watch out for overflow / underflow / rounding.)
|
||||
// TIMER2 is used in phase-correct PWM mode, with OCR2A controlling the frequency and OCR2B
|
||||
// controlling the duty cycle.
|
||||
// There is no prescaling, so the output frequency is 16MHz / (2 * OCR2A)
|
||||
// To turn the output on and off, we leave the PWM running, but connect and disconnect the output pin.
|
||||
// A few hours staring at the ATmega documentation and this will all make sense.
|
||||
// See my Secrets of Arduino PWM at http://www.righto.com/2009/07/secrets-of-arduino-pwm.html for details.
|
||||
|
||||
// Disable the Timer2 Interrupt (which is used for receiving IR)
|
||||
IRLib_didIROut=true; //Tell the receiver we probably trashed his timer settings
|
||||
IR_RECV_DISABLE_INTR; //Timer2 Overflow Interrupt
|
||||
pinMode(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, LOW); // When not sending PWM, we want it low
|
||||
IR_SEND_CONFIG_KHZ(khz);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
IRsendBase::IRsendBase () {
|
||||
pinMode(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, OUTPUT);
|
||||
digitalWrite(IR_SEND_PWM_PIN, LOW); // When not sending PWM, we want it low
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//The Arduino built in function delayMicroseconds has limits we wish to exceed
|
||||
//Therefore we have created this alternative
|
||||
void IRLibDelayUSecs(uint16_t time) {
|
||||
if(time){if(time>16000) {delayMicroseconds(time % 1000); delay(time/1000); } else delayMicroseconds(time);};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void IRsendBase::mark(uint16_t time) {
|
||||
IR_SEND_PWM_START;
|
||||
IR_SEND_MARK_TIME(time);
|
||||
extent+=time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void IRsendBase::space(uint16_t time) {
|
||||
IR_SEND_PWM_STOP;
|
||||
IRLibDelayUSecs(time);
|
||||
extent+=time;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
/* IRLibSendBase.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module contains the base classes for sending. You will not create instances
|
||||
* of these classes, rather you will use them as base classes in creating derived
|
||||
* protocol specific decoders. Each protocol specific send class begins
|
||||
* by calling enableIROut(uint8_t kHz) to set the carrier frequency.
|
||||
* It then calls mark(int usec) and space(inc usec) to transmit marks and
|
||||
* spaces of varying length of microseconds in the manner which the protocol defines.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
#define IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#include "IRLibProtocols.h"
|
||||
|
||||
class IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
IRsendBase();
|
||||
void sendGeneric(uint32_t data, uint8_t numBits, uint16_t headMark, uint16_t headSpace,
|
||||
uint16_t markOne, uint16_t markZero, uint16_t spaceOne, uint16_t spaceZero,
|
||||
uint8_t kHz, bool stopBits, uint32_t maxExtent=0);
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
void enableIROut(uint8_t khz);
|
||||
void mark(uint16_t usec);
|
||||
void space(uint16_t usec);
|
||||
uint32_t extent;
|
||||
uint8_t onTime,offTime,iLength;//used by bit-bang output.
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
Copyright information for IRLib – an Arduino library for
|
||||
infrared encoding and decoding
|
||||
|
||||
IRLib2 is a collection of libraries which we will collectively referred
|
||||
to as the PACKAGE. The PACKAGE consists of all files in the IRLib2,
|
||||
IRLibFreq, IRLibRecv, IRLibRecvPCI, and IRLibProtocols folders.
|
||||
|
||||
The PACKAGE is Copyright (c) 2014-2017 by Chris Young
|
||||
|
||||
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
|
||||
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
||||
(at your option) any later version.
|
||||
|
||||
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
GNU General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
These files will be maintained at https://github.com/cyborg5/IRLib2
|
||||
Documentation and other support info at http://tech.cyborg5.com/irlib
|
||||
|
||||
This is an updated version of my original IRLib which is still available at
|
||||
https://github.com/cyborg5/IRLib which will not be updated after this
|
||||
PACKAGE has its first stable non-beta release.
|
||||
|
||||
Both libraries are derived from the original source code in a library called
|
||||
IRemote by Ken Shirriff which was covered by GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC
|
||||
LICENSE version 2.1. This package is covered by the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC
|
||||
LICENSE 3.0. See LICENSE.txt for a copy of that license or visit
|
||||
https://www.gnu.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
As I understand these licenses it is permissible to upgrade the license
|
||||
this way. Additionally this license change was made with the approval of
|
||||
Mr. Shirriff in an email conversation I had with him. In accord with his
|
||||
wishes and out of respect for his work, his original copyright message is
|
||||
shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* IRremote
|
||||
* Version 0.1 July, 2009
|
||||
* Copyright 2009 Ken Shirriff
|
||||
* For details, see http://www.righto.com/2009/08/multi-protocol-infrared-remote-library.html http://www.righto.com/
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Interrupt code based on NECIRrcv by Joe Knapp
|
||||
* http://www.arduino.cc/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1210243556
|
||||
* Also influenced by http://zovirl.com/2008/11/12/building-a-universal-remote-with-an-arduino/
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
We also acknowledge and thank the developers of the AnalysIR program. AnalysIR is a Windows-based application which allows you to graphically analyze IR input signals through an Arduino, Raspberry Pi or other microcontrollers systems. The frequency analysis and other PCI based versions of the program are based upon and inspired by their work. We value their input into the development of that portion of the code. You can find more about their software at http://analysir.com
|
||||
|
||||
We also knowledge and thank programmer Gabriel Staples contributed bug fixes and an earlier version of the auto resume feature. Although much of his code was rewritten it could not have been possible without his contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Other major contributors will be acknowledged in this file in the future.
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P00_HashRaw.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* If you have a protocol which is unsupported by this library, you can still receive
|
||||
* and transmit the data. You can store the raw data values in a buffer and retransmit the
|
||||
* data exactly as you received it. Of course it takes a lot of memory to store such data
|
||||
* so it is inefficient but it is better than nothing.
|
||||
* If all you need to do is detect a unique value for an unsupported protocol and you do
|
||||
* not need to resend the data, you can use the hash code decoder. It looks at the
|
||||
* array of raw timing values and create a 32 bit value based on the data. It is
|
||||
* highly likely to be unique however you cannot reverse engineer the process.
|
||||
* You cannot re-create the original data stream for 32 bit hash code.
|
||||
* This module also implements the raw send method. You have to have the original
|
||||
* timing values.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_HASHRAW_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HASHRAW_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_RAW case 0: IRsendRaw::send((uint16_t*)data,data2,khz); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_HASH if(IRdecodeHash::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_HASH ,public virtual IRdecodeHash
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_RAW ,public virtual IRsendRaw
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_HASH public virtual IRdecodeHash
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_RAW public virtual IRsendRaw
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
/* The first parameter to the "IRendRaw" method is a pointer to the first element of an
|
||||
* array of uint16_t values. These values are the raw timing values in microseconds. Note
|
||||
* it is possible to simply pass "(uint16_t*) &My_Decoder.decodeBuffer[1]" if you have just
|
||||
* received a code and wish to echo it. You have to point to the index "1" because index "0"
|
||||
* of that buffer contains the gap between successive frames data and it should be ignored.
|
||||
* If the frequency to be used in transmission is not specified, it defaults to 38kHz.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class IRsendRaw: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint16_t *buf, uint8_t len, uint8_t khz) {
|
||||
enableIROut(khz);
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
|
||||
if (i & 1) {
|
||||
space(buf[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
mark(buf[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
space(0); // Just to be sure
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
/* This Hash decoder is based on IRhashcode Copyright 2010 Ken Shirriff
|
||||
* For details see http://www.righto.com/2010/01/using-arbitrary-remotes-with-arduino.html
|
||||
* Use FNV hash algorithm: http://isthe.com/chongo/tech/comp/fnv/#FNV-param
|
||||
* Converts the raw code values into a 32-bit hash code.
|
||||
* Hopefully this code is unique for each button.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define FNV_PRIME_32 16777619
|
||||
#define FNV_BASIS_32 2166136261
|
||||
// Compare two tick values, return 0 if v1 is lower, 1 if equal, and 2 if v2 is higher
|
||||
#define TICKS_COMPARE(v1,v2) ( (v2< v1*0.8)?0:( (v1< v2*0.8)?2:1) )
|
||||
class IRdecodeHash: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
value = FNV_BASIS_32;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i+2 < recvGlobal.decodeLength; i++) {
|
||||
value = (value * FNV_PRIME_32) ^ TICKS_COMPARE(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[i], recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[i+2]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
protocolNum = UNKNOWN;
|
||||
bits= (recvGlobal.decodeLength-3)/2;//Estimated number of bits of unknown protocol
|
||||
//Note that value is always 32 bit hash code.
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_HASHRAW_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P01_NEC.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* NEC is an extremely common protocol. There are two variations NEC1 and NEC2.
|
||||
* They differ only in the way in which they handle repeat codes. If you hold a button
|
||||
* using NEC1 it does not repeat the same sequence. Rather it sends a special sequence
|
||||
* consisting of the usual header mark, a half-size header space, a normal mark.
|
||||
* When IRLib receives one of these special repeat sequences, it returns the
|
||||
* value REPEAT_CODE which is defined in IRLibProtocols.h as the value 0xffffffff. If you
|
||||
* send REPEAT_CODE, the send routine will create a special sequence for you.
|
||||
* NOTE that the timing for this special did sequence is nearly identical to a ditto
|
||||
* used by the G.I.Cable protocol and IRLib generally not distinguish between the two.
|
||||
* The header timing for G.I. Cable ditto is 8820,1960 and for NEC is 9024,2256
|
||||
* If you are using both protocols and you receive an NEC ditto immediately after
|
||||
* receiving a G.I.Cable then you should presume it is a G.I.Cable and vice versa.
|
||||
* Whether it is a normal code or a repeat code the entire frame has a 108ms extent.
|
||||
* The IRP notation for these protocols are:
|
||||
* NEC1: {38k,564}<1,-1|1,-3>(16,-8,D:8,S:8,F:8,~F:8,1,^108,(16,-4,1,^108)*)
|
||||
* NEC2: {38k,564}<1,-1|1,-3>(16,-8,D:8,S:8,F:8,~F:8,1,^108)+
|
||||
* Other protocols use the same timing and 32 bits of data but they interpret the data fields
|
||||
* differently. These include Apple and TiVo. Also Pioneer protocol is identical to NEC2
|
||||
* however uses 40k rather than 38k modulation. Pioneer sometimes requires a 2 frame
|
||||
* sequence of different data for a single pushbutton function. The optional 2nd
|
||||
* parameter to the "send" method allows you to change the frequency from the default 38.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_01_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_01_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01 case 1: if(data2==0)data2=38;IRsendNEC::send(data,data2); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01 if(IRdecodeNEC::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01 ,public virtual IRdecodeNEC
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01 ,public virtual IRsendNEC
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_01 public virtual IRdecodeNEC
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_01 public virtual IRsendNEC
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
class IRsendNEC: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint8_t kHz=38) {
|
||||
if (data==REPEAT_CODE) {
|
||||
enableIROut(kHz);
|
||||
mark (564* 16); space(564*4); mark(564);space(572);delay(97);//actually 97572us
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,32, 564*16, 564*8, 564, 564, 564*3, 564, kHz, true,108000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeNEC: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("NEC repeat"));
|
||||
// Check for repeat
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength == 4 && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],564*16) && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],564*4)
|
||||
&& MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[3],564)) {
|
||||
bits = 0;
|
||||
value = REPEAT_CODE;
|
||||
protocolNum = NEC;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("NEC"));
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(68, 564*16, 564*8, 564, 564*3, 564)) return false;
|
||||
protocolNum = NEC;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_01_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P02_Sony.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Sony is backwards from most protocols. It uses a variable length mark and a fixed length
|
||||
* space rather than a fixed mark and a variable space. Our generic send will still work
|
||||
* however we need a custom decoding routine because it's difficult to get the generic
|
||||
* decoder to handle a variable length mark without cluttering up the code to much.
|
||||
* According to the protocol you must send Sony commands at least three times so we
|
||||
* automatically do it here. Sony can be 8, 12, 15, or 20 bits in length.
|
||||
* The 8 bit version uses a shorter trailing space at the end. The signal is modulated
|
||||
* at 40 kHz however most 38 kHz receivers are broad enough to receive it.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_02_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_02_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02 case 2: IRsendSony::send(data,data2); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02 if(IRdecodeSony::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02 ,public virtual IRdecodeSony
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02 ,public virtual IRsendSony
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_02 public virtual IRdecodeSony
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_02 public virtual IRsendSony
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendSony: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint8_t nbits) {
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=0; i<3;i++){
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,nbits, 600*4, 600, 600*2, 600, 600, 600, 40, false,45000);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeSony: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
virtual bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("Sony"));
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
if(recvGlobal.decodeLength!=2*8+2 && recvGlobal.decodeLength!=2*12+2 && recvGlobal.decodeLength!=2*15+2
|
||||
&& recvGlobal.decodeLength!=2*20+2) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
if(!ignoreHeader) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],600*4)) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(600*4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset=2;//skip initial gap plus header Mark.
|
||||
while (offset < recvGlobal.decodeLength) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],600)) return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(600);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],600*2)) {
|
||||
value = (value << 1) | 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],600)) {
|
||||
value <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else return DATA_MARK_ERROR(600);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits = (offset - 1) / 2;
|
||||
protocolNum = SONY;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_02_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P03_RC5.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* The RC5 protocol was invented by Phillips but is used by wide variety of manufacturers.
|
||||
* It uses a phase encoding of data bits. A space/mark pair indicates "1"
|
||||
* and a mark/space indicates a "0". It begins with a single "1" bit which is not encoded
|
||||
* in the data. The second highest order data bit is a toggle bit that indicates individual
|
||||
* keypresses. You must toggle this bit yourself when sending data. The protocol uses 36 kHz
|
||||
* modulation however 38 kHz receivers can typically receive the codes okay.
|
||||
* There are three supported varieties as follows:
|
||||
* RC5 13 bits, 36 kHz (default, most common variety.
|
||||
* RC5-F7 14 bits, 36 kHz
|
||||
* RC5-F7-57 14 bits, 57 kHz
|
||||
* There's also a 19 bit variety called RC5x that is not supported here but may be a separate
|
||||
* module eventually.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_03_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_03_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03 case 03: if(khz==38)khz=36; IRsendRC5::send(data,data2,khz); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03 if(IRdecodeRC5::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03 ,public virtual IRdecodeRC5
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03 ,public virtual IRsendRC5
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_03 public virtual IRdecodeRC5
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_03 public virtual IRsendRC5
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define RC5_T1 889
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
class IRsendRC5: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint8_t nBits=13, uint8_t kHz=36) {
|
||||
if(nBits==0)nBits=13;
|
||||
if(kHz==0)kHz=36;
|
||||
enableIROut(kHz);
|
||||
data = data << (32 - nBits);
|
||||
extent=0;
|
||||
mark(RC5_T1); // First start bit
|
||||
//Note: Original IRremote library incorrectly assumed second bit was
|
||||
//always a "1". Bit patterns from this decoder are not backward compatible
|
||||
//with patterns produced by the original library. Uncomment the following two
|
||||
//lines to maintain backward compatibility.
|
||||
//space(RC5_T1); // Second start bit
|
||||
//mark(RC5_T1); // Second start bit
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < nBits; i++) {
|
||||
if (data & TOPBIT) {
|
||||
space(RC5_T1); mark(RC5_T1);// 1 is space, then mark
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
mark(RC5_T1); space(RC5_T1);// 0 is mark, then space
|
||||
}
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
space(114000-extent); // Turn off at end
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
/* Note this decoder is a derived class from the IRdecodeRC base class
|
||||
* rather than IRdecodeBase. The base class defines the method "getRClevel"
|
||||
* which is common to both RC5 and RC6 protocols. It facilitates the decoding
|
||||
* of phase encoded data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
class IRdecodeRC5: public virtual IRdecodeRC {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
virtual bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("RC5"));
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength < 13) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
offset = 1; // Skip gap space
|
||||
data = 0;
|
||||
used = 0;
|
||||
// Get start bits
|
||||
if (getRClevel(&used, RC5_T1) != MARK) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(RC5_T1);
|
||||
//Note: Original IRremote library incorrectly assumed second bit was always
|
||||
// a "1". Bit patterns from this decoder are not backward compatible with
|
||||
// patterns produced by original library. Uncomment the following two lines
|
||||
// to maintain backward compatibility.
|
||||
//if (getRClevel(&used, RC5_T1) != SPACE) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(RC5_T1);
|
||||
//if (getRClevel(&used, RC5_T1) != MARK) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(RC5_T1);
|
||||
for (nBits = 0; offset < recvGlobal.decodeLength; nBits++) {
|
||||
RCLevel levelA = getRClevel(&used, RC5_T1);
|
||||
RCLevel levelB = getRClevel(&used, RC5_T1);
|
||||
if (levelA == SPACE && levelB == MARK) {
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1; // 1 bit
|
||||
} else if (levelA == MARK && levelB == SPACE) {
|
||||
data <<= 1; // zero bit
|
||||
} else return DATA_MARK_ERROR(RC5_T1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Success
|
||||
bits = nBits;
|
||||
value = data;
|
||||
protocolNum = RC5;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_03_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P04_RC6.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* The RC6 protocol was invented by Phillips but is used by wide variety of manufacturers.
|
||||
* Like the Phillips RC5 protocol it uses phased coding however the phase is backwards
|
||||
* from RC5. With RC6 a space/mark pair indicates "0" and a mark/space indicates a "1".
|
||||
* in the data. The protocol uses 36 kHz modulation however 38 kHz receivers can typically
|
||||
* receive the codes okay.
|
||||
* The protocol consists of a header followed by a "1" bit which is always on and we do not
|
||||
* encode. This is followed by a 3 bit OEM code that is usually 0 or 6. This is followed by
|
||||
* special trailer bit whose time is twice that of normal. It all but the 32-bit version,
|
||||
* the trailer bit also serves as a toggle bit. The toggle bit changes if the button was
|
||||
* pressed and released however remains the same if the button was held. You must toggle
|
||||
* this bit yourself when sending data and account for it when interpreting decoded values.
|
||||
* Next are the actual data bits. Varieties include 16, 20, 24, and 32 bit versions.
|
||||
* Because we encode the 3 OEM bits and the toggle bit, our actual bit lengths are 20, 24,
|
||||
* and 28 for the first three varieties. The 32-bit variety is different because it uses
|
||||
* OEM bits of 011 followed by a 0 in what is traditionally the toggle bit.
|
||||
* Because the 32-bit version is invariant in these first 4 bits, we do not encode them
|
||||
* and presume they are always "0110". The 32-bit version uses the highest order of the
|
||||
* data bits as a toggle bit. At this time the 16-bit version always uses OEM = 0 and
|
||||
* other known varieties always use OEM = 6 but we will only make that presumption for the
|
||||
* 32-bit version. Encoding the OEM bits allows for other OEM values to be used without
|
||||
* modifying the library. If we ever encounter a 32-bit version with an OEM other than 6
|
||||
* it will require a special modified encoder and decoder.
|
||||
* Here is a description of known varieties:
|
||||
* RC6-0-16: Original version by Phillips. 16 bits, we encode 20, toggle is 0x00010000
|
||||
* RC6-6-20: Used by some Sky and Sky+ remotes. 20 bits, we encode 24, toggle is 0x00100000
|
||||
* RC6-6-24: Also known as "Replay" protocol. 24 bits, we encode 28, toggle is 0x01000000
|
||||
* RC6-6-32: Also known as "MCE" protocol. 32 bits, we encode 32, toggle is 0x00008000
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_04_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_04_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04 case 04: IRsendRC6::send(data,data2); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04 if(IRdecodeRC6::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04 ,public virtual IRdecodeRC6
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04 ,public virtual IRsendRC6
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_04 public virtual IRdecodeRC6
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_04 public virtual IRsendRC6
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#define RC6_HDR_MARK 2666
|
||||
#define RC6_HDR_SPACE 889
|
||||
#define RC6_T1 444
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendRC6: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint8_t nBits=16) {
|
||||
if (nBits==0) nBits=16;
|
||||
enableIROut(36);
|
||||
uint64_t bigData = data;
|
||||
if (nBits==32) {
|
||||
bigData+=0xc00000000ull;//add OEM value
|
||||
nBits=36;
|
||||
};
|
||||
bigData=bigData << (64 - nBits);
|
||||
extent=0;
|
||||
mark(RC6_HDR_MARK); space(RC6_HDR_SPACE);
|
||||
mark(RC6_T1); space(RC6_T1);// start bit "1"
|
||||
uint16_t t;
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < nBits; i++) {
|
||||
if (i == 3) {
|
||||
t = 2 * RC6_T1; // double-wide trailer bit
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t = RC6_T1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (bigData & 0x8000000000000000ull) {
|
||||
mark(t); space(t);//"1" is a Mark/space
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
space(t); mark(t);//"0" is a space/Mark
|
||||
}
|
||||
bigData <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
space(107000-extent); // Turn off at end
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
/* Note this decoder is a derived class from the IRdecodeRC base
|
||||
* class rather than IRdecodeBase. The base class defines the
|
||||
* method "getRClevel" which is common to both RC5 and RC6 protocols.
|
||||
* It facilitates the decoding of phase encoded data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class IRdecodeRC6: public virtual IRdecodeRC {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
virtual bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("RC6"));
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
//Legal lengths range from 24 through 76 we went one bigger just in case.
|
||||
if( (recvGlobal.decodeLength < 23) || (recvGlobal.decodeLength > 77) )return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
// Initial mark
|
||||
if (!ignoreHeader) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1], RC6_HDR_MARK)) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(RC6_HDR_MARK);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2], RC6_HDR_SPACE)) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(RC6_HDR_SPACE);
|
||||
offset=3;//Skip gap and header
|
||||
data = 0;
|
||||
used = 0;
|
||||
// Get start bit (1)
|
||||
if (getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1) != MARK) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(RC6_T1);
|
||||
if (getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1) != SPACE) return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(RC6_T1);
|
||||
for (nBits = 0; offset < recvGlobal.decodeLength; nBits++) {
|
||||
RCLevel levelA, levelB; // Next two levels
|
||||
levelA = getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1);
|
||||
if (nBits == 3) {
|
||||
// T bit is double wide; make sure second half matches
|
||||
if (levelA != getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1)) return TRAILER_BIT_ERROR(RC6_T1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
levelB = getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1);
|
||||
if (nBits == 3) {
|
||||
// T bit is double wide; make sure second half matches
|
||||
if (levelB != getRClevel(&used, RC6_T1)) return TRAILER_BIT_ERROR(RC6_T1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (levelA == MARK && levelB == SPACE) { // reversed compared to RC5
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1; // 1 bit
|
||||
} else if (levelA == SPACE && levelB == MARK) {
|
||||
data <<= 1; // zero bit
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return DATA_MARK_ERROR(RC6_T1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Success
|
||||
if (nBits==36) {
|
||||
nBits=32;//OEM & trailer bits are discarded on 32-bit version
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//if ( (nBits!=20) || (nBits!=24) || (nBits!=28) ) return BIT_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits = nBits;
|
||||
value = data;
|
||||
protocolNum = RC6;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_04_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P05_Panasonic_Old.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This protocol #5 named "Panasonic_Old" is a 57 kHz protocol with 22 bits
|
||||
* of data. The second 11 bits are the bitwise logical complement of the first 11 bits.
|
||||
* The protocol is used by many cable boxes and DVR's made by Scientific Atlantic and
|
||||
* Cisco. They are common for Bright House and Time Warner cable systems.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_05_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_05_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05 case 5: IRsendPanasonic_Old::send(data); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05 if(IRdecodePanasonic_Old::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05 ,public virtual IRdecodePanasonic_Old
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05 ,public virtual IRsendPanasonic_Old
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_05 public virtual IRdecodePanasonic_Old
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_05 public virtual IRsendPanasonic_Old
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendPanasonic_Old: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data) {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,22, 833*4, 833*4, 833, 833, 833*3, 833,57, true);
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodePanasonic_Old: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
virtual bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("Panasonic_Old"));
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(48,833*4,833*4,833,833*3,833)) return false;
|
||||
// The protocol spec says that the first 11 bits described the device and function.
|
||||
// The next 11 bits are the same thing only it is the logical Bitwise complement.
|
||||
// Many protocols have such check features in their definition but our code typically
|
||||
// doesn't perform these checks. For example NEC's least significant 8 bits are the
|
||||
// complement of the next more significant 8 bits. While it's probably not necessary
|
||||
// to error check this, you can un-comment the next 4 lines of code to do this extra
|
||||
// checking.
|
||||
// long S1= (value & 0x0007ff); // 00 0000 0000 0111 1111 1111
|
||||
// long S2= (value & 0x3ff800)>> 11; // 11 1111 1111 1000 0000 0000
|
||||
// S2= (~S2) & 0x0007ff;
|
||||
// if (S1!=S2) return IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(F("inverted bit redundancy"));
|
||||
protocolNum = PANASONIC_OLD;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_05_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P06_JVC.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* JVC omits the mark/space header on repeat sending. Therefore we multiply
|
||||
* it by 0 if it's a repeat. The only device I had to test this protocol was
|
||||
* an old JVC VCR. It would only work if at least 2 frames are sent separated
|
||||
* by 45 time periods of "space". Therefore you should call this routine once
|
||||
* with "first=true" and it will send a first frame followed by one repeat
|
||||
* frame. If First==false, it will only send a single repeat frame.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_06_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_06_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06 case 06: IRsendJVC::send(data,(bool)data2); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06 if(IRdecodeJVC::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06 ,public virtual IRdecodeJVC
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06 ,public virtual IRsendJVC
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_06 public virtual IRdecodeJVC
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_06 public virtual IRsendJVC
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendJVC: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, bool first=true) {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data, 16,525*16*first, 525*8*first, 525, 525,525*3, 525, 38, true);
|
||||
space(525*45);
|
||||
if(first) {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data, 16,0,0, 525, 525,525*3, 525, 38, true);
|
||||
space(525*45);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeJVC: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
// JVC does not send any header if there is a repeat.
|
||||
// first try with the header. If that fails, try without.
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("JVC"));
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(36,525*16,525*8,525,525*3,525)) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("JVC Repeat"));
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength==34) {
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(0,525,0,525,525*3,525)) {
|
||||
return IRLIB_REJECTION_MESSAGE(F("JVC repeat failed generic"));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
//If this is a repeat code then IRdecodeBase::decodeGeneric fails to add the most significant bit
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],(525*3))) {
|
||||
value |= 0x8000;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],525)) return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(525);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
}
|
||||
address=(recvGlobal.decodeLength==36);
|
||||
protocolNum =JVC;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_06_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P07_NECx.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* NECx is a variation of NEC protocol. The only difference is in the timing of the
|
||||
* header. There are two variations NECx1 and NECx2. They differ only in the way in
|
||||
* which they handle repeat codes. If you hold a button using NECx1 it does not repeat
|
||||
* the same sequence. Rather it sends a special sequence consisting of the usual header
|
||||
* followed by a normal mark, a "1" bit, and then a long space with a 108ms extent. Note
|
||||
* this so-called "ditto" repeat code is slightly different than the one for regular NEC.
|
||||
* When IRLib receives one of these special repeat sequences, it returns the
|
||||
* value REPEAT_CODE which is defined in IRLibProtocols.h as the value 0xffffffff. If you
|
||||
* send REPEAT_CODE, the send routine will create a special sequence for you.
|
||||
* Whether it is a normal code or a repeat code the entire frame has a 108ms extent.
|
||||
* The IRP notation for these protocols are:
|
||||
* NECx1: {38k,564}<1,-1|1,-3>(8,-8,D:8,S:8,F:8,~F:8,1,^108,(8,-8,D:1,1,^108m)*)
|
||||
* NECx2: {38k,564}<1,-1|1,-3>(8,-8,D:8,S:8,F:8,~F:8,1,^108)+
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_07_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_07_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07 case 07: IRsendNECx::send(data); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07 if(IRdecodeNECx::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07 ,public virtual IRdecodeNECx
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07 ,public virtual IRsendNECx
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_07 public virtual IRdecodeNECx
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_07 public virtual IRsendNECx
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendNECx: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data) {
|
||||
if (data==REPEAT_CODE) {
|
||||
enableIROut(38);
|
||||
mark(564*8); space(564*8); mark(564);space(564);
|
||||
mark(564); space(412);delay(98);//actually 98412us
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,32, 564*8, 564*8, 564, 564, 564*3, 564, 38, true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeNECx: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
virtual bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("NECx"));
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
// Check for repeat
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength == 6 && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1], 564*8) && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],564*8)
|
||||
&& MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[3],564) && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[5],564)
|
||||
) {
|
||||
bits = 0;
|
||||
value = REPEAT_CODE;
|
||||
protocolNum = NECX;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(68, 564*8, 564*8, 564, 564*3, 564)) return false;
|
||||
protocolNum = NECX;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_07_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P08_Samsung36.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This 36 bit protocol is used by some Samsung devices such as Blu-ray players.
|
||||
* It consists of a 16 bit address and 20 bits of data with strange timing in between.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/* The IRP notation for this protocol is:
|
||||
* {38k,500}<1,-1|1,-3>(9,-9,D:8,S:8,1,-9,E:4,F:8,-68u,~F:8,1,-118)+
|
||||
* This means it uses 38k frequency. Base timing is multiples of 500.
|
||||
* A "0" is mark(500) space(500). A "1" is mark (500) space(500*3)
|
||||
* The header is mark(500*9) space(500*9).
|
||||
* The header is followed by 16 bit address (8 device, 8 sub device)
|
||||
* This is followed by a mark(500) space(500*9).
|
||||
* This is followed by 12 more bits (4+8)
|
||||
* This is followed by 68us of space. Actually this means that the space
|
||||
* of the last bit of that segment is simply 68us longer than normal.
|
||||
* This is followed by 8 more bits and a final stop bit.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_08_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_08_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08 case 8: IRsendSamsung36::send(data,data2); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08 if(IRdecodeSamsung36::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08 ,public virtual IRdecodeSamsung36
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08 ,public virtual IRsendSamsung36
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_08 public virtual IRdecodeSamsung36
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_08 public virtual IRsendSamsung36
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendSamsung36: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint32_t address) {
|
||||
data <<= 32-20;
|
||||
address <<= 32-16;
|
||||
enableIROut(38);
|
||||
mark(500*9); space(500*9); //Send header
|
||||
putBits (address, 16); //Send address 16 bits
|
||||
mark (500); space (500*9); //Send break
|
||||
putBits (data, 12); //Send 12 bits
|
||||
space(68); //Send tiny break
|
||||
data <<= 12;
|
||||
putBits (data, 8);mark(500); //Final eight bits and one stop bit
|
||||
space(118*500); //Lead out is 118 times the base time 500
|
||||
};
|
||||
private:
|
||||
/* Because not all of the data bits are contiguous in the stream,
|
||||
* we created this little routine to be called multiple times to send a
|
||||
* segment of the data.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void putBits (uint32_t data, uint8_t nbits) {
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < nbits; i++) {
|
||||
if (data & TOPBIT) {
|
||||
mark(500); space(500*3);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
mark(500); space(500);
|
||||
};
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeSamsung36: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("Samsung36"));
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength != 78) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],500*9)) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(500*9);
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],500*9)) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(500*9);
|
||||
offset=3; data=0;
|
||||
//Get first 16 bits
|
||||
if(!getBits(16*2+2))return false;
|
||||
//Skip middle header
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],500)) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(500);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],500*9)) return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(4400);
|
||||
//save first 16 bits in "address" and reset data
|
||||
offset++; address=data; data=0;
|
||||
//12 bits into this second segment, the space is extended by 68us.
|
||||
// so we adjust the value to its normal length without the extra 68us.
|
||||
recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[62]-=68;
|
||||
//Now get the remaining 20 bits
|
||||
if(!getBits(77))return false;
|
||||
bits =36; //set bit length
|
||||
value = data; //put remaining 20 bits in value
|
||||
protocolNum= SAMSUNG36;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
private:
|
||||
/* Because not all of the data bits are contiguous in the stream
|
||||
* we created this little routine to be called multiple times
|
||||
* to decode a segment of the data. Parameter "last_offset" is when we
|
||||
* stop decoding the segment.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
bool getBits(uint8_t last_offset) {
|
||||
while (offset < last_offset) {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],500)) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(500);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],500*3))
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1;
|
||||
else if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],500))
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
else return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(500*3);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
};
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
uint8_t offset;
|
||||
uint32_t data;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_08_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P09_GICable.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/* The G.I. Cable protocol is is used by many Motorola brand cable boxes manufactured by
|
||||
* General Instruments. The IRP notation for this protocol is
|
||||
* "{38.7k,490}<1,-4.5|1,-9>(18,-9,F:8,D:4,C:4,1,-84,(18,-4.5,1,-178)*) {C = -(D + F:4 + F:4:4)}"
|
||||
* It is a 16-bit code which uses an unusual "ditto" repeat sequence similar to NEC.
|
||||
* In fact it is so similar that IRLib generally not distinguish between the two.
|
||||
* The header timing for G.I. Cable ditto is 8820,1960 and for NEC is 9024,2256
|
||||
* If you are using both protocols and you receive an NEC ditto immediately after
|
||||
* receiving a G.I.Cable then you should presume it is a G.I.Cable and vice versa.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_09_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_09_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09 case 9: IRsendGICable::send(data); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09 if(IRdecodeGICable::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09 ,public virtual IRdecodeGICable
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09 ,public virtual IRsendGICable
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_09 public virtual IRdecodeGICable
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_09 public virtual IRsendGICable
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendGICable: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data) {
|
||||
if(data==REPEAT_CODE) {
|
||||
enableIROut(39);
|
||||
mark (490*18); space(2205);//actually "490*4.5"
|
||||
mark (490); space(220);delay(87);//actually 490*178 or "space(87220);"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,16, 490*18, 490*9, 490, 490, 490*9, 2205/*(4.5*490)*/, 39, true);
|
||||
space(37*490);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeGICable: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("G.I.cable"));
|
||||
// Check for repeat
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength == 4 && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1], 490*18) && MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],2205)
|
||||
&& MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[3],490)) {
|
||||
bits = 0;
|
||||
value = REPEAT_CODE;
|
||||
protocolNum=GICABLE;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(36, 18*490, 9*490, 490, 9*490, 2205/*(4.5*490)*/)) return false;
|
||||
protocolNum=GICABLE;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_09_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P10_DirecTV.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This module implements the protocol used by DirecTV. It comes in six different
|
||||
* varieties. It uses three different frequencies 38, 40, or 57 kHz. It also
|
||||
* uses two different varieties lead out times either 9000us or 30000us. The
|
||||
* default is 38 kHz and 30000us. Because the decoder does not usually detect
|
||||
* frequency and does not record the lead out time, you may have difficulty
|
||||
* determining which variety your device uses.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* According to http://www.hifi-remote.com/johnsfine/DecodeIR.html#DirecTV
|
||||
* The IRP notation for this protocol is:
|
||||
* {38k,600,msb}<1,-1|1,-2|2,-1|2,-2>(5,(5,-2,D:4,F:8,C:4,1,-50)+)
|
||||
* {C=7*(F:2:6)+5*(F:2:4)+3*(F:2:2)+(F:2)}
|
||||
* Unlike most protocols which use a fixed length mark and a variable length or
|
||||
* a variable length mark a fixed length space, this protocol varies both the
|
||||
* mark and the space. The stream is still a series of marks and spaces but the
|
||||
* length of either of those denotes a one or zero. A length of 1200us=logical 1
|
||||
* and length 600us=logical 0. So whereas the normal protocol requires both a mark
|
||||
* and a space to encode a single bit, this protocol encodes one bit in each mark
|
||||
* and space. It also makes changes to the length of the header mark to devote
|
||||
* repeat codes. The first header mark should be 6000us but repeat codes should
|
||||
* only be 3000us. The decode routine sets "address=true" if it is a first
|
||||
* and "address=false" otherwise.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_10_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_10_H
|
||||
/* When used with IRLibCombo.h the data2 value is a flag for repeat frame.
|
||||
* You can also optionally change the frequency. To change the lead out
|
||||
* time after you have created the instance of your sending object such as
|
||||
* IRsend My_Send;
|
||||
* you can change the leadout with
|
||||
* My_Send.longLeadOut= false;
|
||||
* The default value is true.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10 case 10: IRsendDirecTV::send(data,data2,khz); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10 if(IRdecodeDirecTV::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10 ,public virtual IRdecodeDirecTV
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10 ,public virtual IRsendDirecTV
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_10 public virtual IRdecodeDirecTV
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_10 public virtual IRsendDirecTV
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendDirecTV: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
IRsendDirecTV(void):longLeadOut(true){};
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, bool first=true, uint8_t khz=38) {
|
||||
enableIROut(khz);
|
||||
if(first) mark(6000); else mark(3000);
|
||||
space(1200);//Send header
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
|
||||
if (data & 0x8000) mark(1200); else mark(600);
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
if (data & 0x8000) space(1200); else space(600);
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
mark(600);
|
||||
space(longLeadOut?50*600:15*600);
|
||||
};
|
||||
bool longLeadOut;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeDirecTV: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("DirecTV"));
|
||||
if (recvGlobal.decodeLength != 20) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
//We use the "address" value as a repeat flag
|
||||
if(!ignoreHeader) {
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],3000)) {
|
||||
address=false;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],6000)) {
|
||||
return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(6000);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
address=true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],1200)) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(1200);
|
||||
uint32_t data=0; offset=3;
|
||||
while (offset < 18) {
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],1200)) {
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],600)) {
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return DATA_MARK_ERROR(1200);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],1200)) {
|
||||
data = (data << 1) | 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (MATCH (recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],600)) {
|
||||
data <<= 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(1200);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
bits = 16;
|
||||
value = data;
|
||||
protocolNum=DIRECTV;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_10_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P11_RCMM.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/* This module implements the Phillips RC-MM also known as Nokia Protocol. Is used by
|
||||
* AT&T U-Verse cable boxes. There are three different varieties that are 12, 24, or 32 bits.
|
||||
* According to http://www.hifi-remote.com/johnsfine/DecodeIR.html#Nokia
|
||||
* The IRP notation for these protocols are:
|
||||
* Nokia 12 bit: {36k,msb}<164,-276|164,-445|164,-614|164,-783>(412,-276,D:4,F:8,164,-???)+
|
||||
* Nokia 24-bit: {36k,msb}<164,-276|164,-445|164,-614|164,-783>(412,-276,D:8,S:8,F:8,164,-???)+
|
||||
* Nokia 32 bit: {36k,msb}<164,-276|164,-445|164,-614|164,-783>(412,-276,D:8,S:8,T:1X:7,F:8,164,^100m)+
|
||||
* Slightly different timing values are documented at
|
||||
* http://www.sbprojects.com/knowledge/ir/rcmm.php
|
||||
* We will use the timing from the latter reference.
|
||||
* Unlike most protocols which defined sequences for a logical "0" and "1", this protocol
|
||||
* encodes 2 bits per pulse. Therefore it encodes a logical "2" and "3" as well.
|
||||
* The length of the mark is constant but the length of the space denotes the bit values.
|
||||
* Note the 32-bit version uses a toggle bit of 0x8000 and as usual it is up to the end-user
|
||||
* to implement it outside the library routines.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define RCMM_HEAD_MARK 417
|
||||
#define RCMM_DATA_MARK 167
|
||||
#define RCMM_ZERO 278
|
||||
#define RCMM_ONE 444
|
||||
#define RCMM_TWO 611
|
||||
#define RCMM_THREE 778
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_11_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_11_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11 case 11: IRsendRCMM::send(data,data2); break;//data2 is the number of bits
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11 if(IRdecodeRCMM::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11 ,public virtual IRdecodeRCMM
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11 ,public virtual IRsendRCMM
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_11 public virtual IRdecodeRCMM
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_11 public virtual IRsendRCMM
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendRCMM: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data, uint8_t nBits= 12) {
|
||||
if (nBits==0) nBits=12;
|
||||
extent=0;
|
||||
data <<= (32 - nBits);
|
||||
nBits=nBits/2;
|
||||
enableIROut(36);
|
||||
mark(RCMM_HEAD_MARK); space(RCMM_ZERO);//Send header
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < nBits; i++) {
|
||||
mark(RCMM_DATA_MARK);
|
||||
switch (data & 0xC0000000UL) {//use the leftmost two bits
|
||||
case 0x00000000UL: space(RCMM_ZERO); break;
|
||||
case 0x40000000UL: space(RCMM_ONE); break;
|
||||
case 0x80000000UL: space(RCMM_TWO); break;
|
||||
case 0xC0000000UL: space(RCMM_THREE); break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
data <<= 2;
|
||||
};
|
||||
mark(RCMM_DATA_MARK);
|
||||
space(27778-extent);
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Normally IRLib uses a plus or minus percentage to determine if an interval matches the
|
||||
* desired value. However this protocol uses extremely long intervals of similar length.
|
||||
* For example using the default 25% tolerance the RCMM_TWO value 611 would be accepted for
|
||||
* anything between 458 and 763. The low end is actually closer to RCMM_ONE value of 444
|
||||
* and the upper range is closer to RCM_THREE value of 778. To implement this protocol
|
||||
* we created a new match routine ABS_MATCH which allows you to specify an absolute
|
||||
* number of microseconds of tolerance for comparison.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define RCMM_TOLERANCE 80
|
||||
class IRdecodeRCMM: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
resetDecoder();//This used to be in the receiver getResults.
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("RCMM"));
|
||||
if ( (recvGlobal.decodeLength!=(12+4)) && (recvGlobal.decodeLength!=(24+4)) && (recvGlobal.decodeLength!=(32+4)) ) return RAW_COUNT_ERROR;
|
||||
if (!ignoreHeader) if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[1],RCMM_HEAD_MARK)) return HEADER_MARK_ERROR(RCMM_HEAD_MARK);
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[2],RCMM_ZERO)) return HEADER_SPACE_ERROR(RCMM_ZERO);
|
||||
offset=3; uint32_t data=0;
|
||||
while (offset < (recvGlobal.decodeLength-1)) {
|
||||
if (!ABS_MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_DATA_MARK,RCMM_TOLERANCE)) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(RCMM_DATA_MARK);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
if (ABS_MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_ZERO, RCMM_TOLERANCE) ) { //Logical "0"
|
||||
data <<= 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (ABS_MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_ONE, RCMM_TOLERANCE) ) { //Logical "1"
|
||||
data = (data<<2) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (ABS_MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_TWO, RCMM_TOLERANCE) ) { //Logical "2"
|
||||
data = (data<<2) + 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (ABS_MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_THREE, RCMM_TOLERANCE) ) { //Logical "3"
|
||||
data = (data<<2) + 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else return DATA_SPACE_ERROR(RCMM_ZERO);
|
||||
offset++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!MATCH(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[offset],RCMM_DATA_MARK)) return DATA_MARK_ERROR(RCMM_DATA_MARK);
|
||||
bits = recvGlobal.decodeLength-4;//set bit length
|
||||
value = data;//put remaining bits in value
|
||||
protocolNum=RCMM;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_11_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,331 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P12_CYKM.h
|
||||
Chris Young keyboard mouse protocol
|
||||
See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for license information (spoilers it's GPL 3)
|
||||
|
||||
This library implements a custom protocol for IRLib to assist in creating
|
||||
Arduino based mouse and keyboard controls. Documentation will be updated soon.
|
||||
|
||||
Protocol information: Header 3100, 3100
|
||||
Zero bit: 650, 650,
|
||||
One bit: 650*3, 650, 38 kHz, stop=true
|
||||
15 bits of data which means 34 intervals of marks and spaces
|
||||
Description of bits high order to low order
|
||||
3 bits: Command: 3 bits
|
||||
0 mouse click
|
||||
1 mouse hold
|
||||
2 mouse move
|
||||
3 mouse and keyboard toggle
|
||||
4 keyboard hold
|
||||
5 keyboard write
|
||||
6 speed command
|
||||
7 Custom devices
|
||||
4 bits: Modifier one time use. Only valid for mouse click,
|
||||
mouse hold and keyboard write and hold not toggles
|
||||
1 Shift
|
||||
2 Control
|
||||
4 Alt
|
||||
8 GUI
|
||||
8 bits: data
|
||||
If mouse click or hold or toggle
|
||||
1 left click
|
||||
2 right click
|
||||
4 middle click
|
||||
If mouse move
|
||||
1 right, 2 left, 4 up, 8 down
|
||||
0x10 wheel up, 0x20 wheel down
|
||||
0x40 increase speed, 0x80 decrease speed
|
||||
If keyboard hold or key write then ASCII or Arduino code
|
||||
If speed command = absolute speed 0 to 255
|
||||
If Toggle 255= clear everything
|
||||
If custom devices… To be determined later.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define CYKM_MOUSE_CLICK 0x0000
|
||||
#define CYKM_MOUSE_HOLD 0x1000
|
||||
#define CYKM_MOUSE_MOVE 0x2000
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE 0x3000
|
||||
#define CYKM_KEY_HOLD 0x4000
|
||||
#define CYKM_KEY_WRITE 0x5000
|
||||
#define CYKM_SPEED 0x6000
|
||||
#define CYKM_CUSTOM_DEVICE 0x7000
|
||||
#define CYKM_SHIFT 0x100
|
||||
#define CYKM_CONTROL 0x200
|
||||
#define CYKM_ALT 0x400
|
||||
#define CYKM_GUI 0x800
|
||||
#define CYKM_LEFT_BUTTON 1
|
||||
#define CYKM_RIGHT_BUTTON 2
|
||||
#define CYKM_MIDDLE_BUTTON 4
|
||||
#define CYKM_DIR_RIGHT 0x01
|
||||
#define CYKM_DIR_LEFT 0x02
|
||||
#define CYKM_DIR_UP 0x04
|
||||
#define CYKM_DIR_DOWN 0x08
|
||||
#define CYKM_WHEEL_UP 0x10
|
||||
#define CYKM_WHEEL_DOWN 0x20
|
||||
#define CYKM_SPEED_INCREASE 0x40
|
||||
#define CYKM_SPEED_DECREASE 0x80
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_LEFT 0x01
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_RIGHT 0x02
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_MIDDLE 0x04
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_SHIFT 0x08
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_CONTROL 0x10
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_ALT 0x20
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_GUI 0x40
|
||||
#define CYKM_TOGGLE_RESET 0xff
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_12_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_12_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12 case 12: IRsendCYKM::send(data); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12 if(IRdecodeCYKM::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12 ,public virtual IRdecodeCYKM
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12 ,public virtual IRsendCYKM
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_12 public virtual IRdecodeCYKM
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_12 public virtual IRsendCYKM
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_DUE) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
#include <Keyboard.h>
|
||||
#include <Mouse.h>
|
||||
#include <HID.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendCYKM: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void send(uint32_t data) {
|
||||
sendGeneric(data,15, 3100, 3100, 650, 650, 650*3, 650, 38, true);
|
||||
delay(10);
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeCYKM: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("CYKM"));
|
||||
if(!decodeGeneric(34,3100,3100,650,650*3,650)) return false;
|
||||
protocolNum = CYKM;
|
||||
parseValue();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
virtual void dumpResults(void){
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Gap=")); Serial.print(recvGlobal.decodeBuffer[0],DEC);
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" CYKM decoded:")); Serial.print(value,HEX);Serial.print(" ");
|
||||
switch (cmdType) {
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_CLICK: //deliberate fall through
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_HOLD:
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Mouse "));
|
||||
showMods();
|
||||
switch(cmdData) {
|
||||
case CYKM_LEFT_BUTTON: Serial.print(F("left"));break;
|
||||
case CYKM_RIGHT_BUTTON: Serial.print(F("right"));break;
|
||||
case CYKM_MIDDLE_BUTTON: Serial.print(F("middle"));break;
|
||||
default: Serial.println(F("ERROR"));
|
||||
};
|
||||
if (cmdType==CYKM_MOUSE_CLICK)Serial.println(F(" click")); else Serial.println(F(" hold"));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_MOVE:
|
||||
if(cmdData & (CYKM_DIR_RIGHT|CYKM_DIR_LEFT|CYKM_DIR_UP|CYKM_DIR_DOWN)){
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Mouse move "));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_RIGHT) Serial.print(F("right ")); else if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_LEFT) Serial.print(F("left "));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_UP) Serial.print(F("up ")); else if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_DOWN) Serial.print(F("down "));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if(cmdData & (CYKM_WHEEL_UP|CYKM_WHEEL_DOWN)){
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Mouse Wheel "));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_UP) Serial.print(F("up ")); else Serial.print(F("down "));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (cmdData & CYKM_SPEED_DECREASE) {
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Decrease speed from "));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (cmdData & CYKM_SPEED_INCREASE) {
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Increase speed from "));
|
||||
} else Serial.println(F("Mouse Move Error"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
Serial.println(mouseSpeed,DEC);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_TOGGLE:
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Toggle"));
|
||||
if(cmdData==CYKM_TOGGLE_RESET) {
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" clear all"));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_LEFT) Serial.print(F(" left button"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_RIGHT) Serial.print(F(" right button"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_MIDDLE) Serial.print(F(" middle button"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_SHIFT ) Serial.print(F(" shift key"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_CONTROL) Serial.print(F(" control key"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_ALT) Serial.print(F(" alt key"));
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_GUI) Serial.print(F(" GUI"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" Bits= "));Serial.println(toggleData,HEX);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_KEY_WRITE:
|
||||
case CYKM_KEY_HOLD:
|
||||
if (cmdType==CYKM_KEY_WRITE) {
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Key write"));showMods();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Key hold"));
|
||||
};
|
||||
Serial.print(F(" value:")); Serial.print(cmdData,HEX); Serial.print(" "); Serial.print(cmdData,DEC);
|
||||
if((cmdData>31) && (cmdData< 128)) {Serial.print(" '"); Serial.write(cmdData);Serial.print("'");};
|
||||
Serial.println();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_SPEED:
|
||||
Serial.print(F("Change speed to:")); Serial.println(cmdData,DEC);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_CUSTOM_DEVICE: Serial.print(F("Custom Device data:")); Serial.println(cmdData,HEX);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
void doMouseKeyboard(void){
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_DUE) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
int8_t Button;
|
||||
int8_t xDir=0; int8_t yDir=0; int8_t wDir=0;
|
||||
switch (cmdType) {
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_CLICK: //deliberate fall through
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_HOLD:
|
||||
doMods (true); //presses modifier key
|
||||
switch(cmdData) {
|
||||
case CYKM_LEFT_BUTTON: Button= MOUSE_LEFT; break;
|
||||
case CYKM_RIGHT_BUTTON: Button= MOUSE_RIGHT; break;
|
||||
case CYKM_MIDDLE_BUTTON: Button= MOUSE_MIDDLE; break;
|
||||
};
|
||||
//only release if this was a click and not a hold
|
||||
if (cmdType==CYKM_MOUSE_CLICK) {
|
||||
Mouse.click(Button); doMods(false);
|
||||
} else Mouse.press(Button);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_MOUSE_MOVE:
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_RIGHT) xDir=mouseSpeed; else if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_LEFT) xDir= -mouseSpeed;
|
||||
//NOTE: Upper left corner is 0, 0 and positive numbers go down
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_UP) yDir=-mouseSpeed; else if(cmdData & CYKM_DIR_DOWN) yDir= mouseSpeed;
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_WHEEL_UP) wDir=1; else if(cmdData & CYKM_WHEEL_DOWN) wDir= -1;
|
||||
if(xDir || yDir || wDir) {
|
||||
Mouse.move(xDir,yDir,wDir);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if ( (cmdData & CYKM_SPEED_DECREASE) && (mouseSpeed>0) ) mouseSpeed--;
|
||||
if ( (cmdData & CYKM_SPEED_INCREASE) && (mouseSpeed<=255) ) mouseSpeed++;
|
||||
};
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_TOGGLE:
|
||||
if(cmdData==CYKM_TOGGLE_RESET) {
|
||||
Mouse.release(MOUSE_LEFT);
|
||||
Mouse.release(MOUSE_RIGHT);
|
||||
Mouse.release(MOUSE_MIDDLE);
|
||||
Keyboard.releaseAll();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_LEFT) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_LEFT) Mouse.release(MOUSE_LEFT);else Mouse.press(MOUSE_LEFT);};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_RIGHT) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_RIGHT) Mouse.release(MOUSE_RIGHT);else Mouse.press(MOUSE_RIGHT);};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_MIDDLE) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_MIDDLE) Mouse.release(MOUSE_MIDDLE);else Mouse.press(MOUSE_MIDDLE);};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_SHIFT) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_SHIFT) Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_SHIFT);else Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_SHIFT);};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_CONTROL) {
|
||||
if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_CONTROL) Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_CTRL);else Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_CTRL);
|
||||
};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_ALT) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_ALT) Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_ALT);else Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_ALT);};
|
||||
if(cmdData & CYKM_TOGGLE_GUI) {if(toggleData & CYKM_TOGGLE_GUI) Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_GUI);else Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_GUI);};
|
||||
toggleData= toggleData ^ cmdData;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_KEY_WRITE:
|
||||
doMods(true); //press modifier key
|
||||
Keyboard.write(cmdData);
|
||||
doMods(false); //release modifier key
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_KEY_HOLD:
|
||||
doMods(true);//press modifier key
|
||||
Keyboard.press(cmdData);
|
||||
//Do not release modifier
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case CYKM_SPEED:
|
||||
mouseSpeed=cmdData;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
// case CYKM_CUSTOM_DEVICE:
|
||||
// break;
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
void doMouseKeyboard(uint16_t code) {
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_DUE) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
value=code;
|
||||
parseValue();
|
||||
doMouseKeyboard();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
uint8_t mouseSpeed;
|
||||
uint8_t toggleData;
|
||||
uint16_t cmdType;
|
||||
uint16_t cmdData;
|
||||
private:
|
||||
void showMods(void){
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_SHIFT) Serial.print(F(" shift"));
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_CONTROL) Serial.print(F(" control"));
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_ALT) Serial.print(F(" alt"));
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_GUI) Serial.print(F(" GUI"));
|
||||
};
|
||||
void doMods(bool Press){
|
||||
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_DUE) || defined(ARDUINO_SAM_ZERO)
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_SHIFT) {if(Press) Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_SHIFT); else Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_SHIFT);}
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_CONTROL) {if(Press) Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_CTRL); else Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_CTRL);}
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_ALT) {if(Press) Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_ALT); else Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_ALT);}
|
||||
if(value & CYKM_GUI) {if(Press) Keyboard.press(KEY_LEFT_GUI); else Keyboard.release(KEY_LEFT_GUI);}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
void parseValue(void) {
|
||||
cmdType= value & 0x7000; //highest order 3 bits command type
|
||||
cmdData= value & 0xff; //lowest order 8 bits command data
|
||||
//To get Shift,Control,Alt, GUI modifiers do (value & CYKM_SHIFT) etc.
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
/*
|
||||
If you have a board capable of using the "Keyboard.h" library
|
||||
such as a Leonardo then these defines are already defined.
|
||||
However suppose you want to transmit a signal for the up arrow
|
||||
from an Arduino Uno you would need to look up the value.
|
||||
We are going to presume that if KEY_LEFT_CTRL is not defined
|
||||
then none of the are defined so we will define here for your convenience.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#ifndef KEY_LEFT_CTRL
|
||||
#define KEY_LEFT_CTRL 0x80
|
||||
#define KEY_LEFT_SHIFT 0x81
|
||||
#define KEY_LEFT_ALT 0x82
|
||||
#define KEY_LEFT_GUI 0x83
|
||||
#define KEY_RIGHT_CTRL 0x84
|
||||
#define KEY_RIGHT_SHIFT 0x85
|
||||
#define KEY_RIGHT_ALT 0x86
|
||||
#define KEY_RIGHT_GUI 0x87
|
||||
#define KEY_UP_ARROW 0xDA
|
||||
#define KEY_DOWN_ARROW 0xD9
|
||||
#define KEY_LEFT_ARROW 0xD8
|
||||
#define KEY_RIGHT_ARROW 0xD7
|
||||
#define KEY_BACKSPACE 0xB2
|
||||
#define KEY_TAB 0xB3
|
||||
#define KEY_RETURN 0xB0
|
||||
#define KEY_ESC 0xB1
|
||||
#define KEY_INSERT 0xD1
|
||||
#define KEY_DELETE 0xD4
|
||||
#define KEY_PAGE_UP 0xD3
|
||||
#define KEY_PAGE_DOWN 0xD6
|
||||
#define KEY_HOME 0xD2
|
||||
#define KEY_END 0xD5
|
||||
#define KEY_CAPS_LOCK 0xC1
|
||||
#define KEY_F1 0xC2
|
||||
#define KEY_F2 0xC3
|
||||
#define KEY_F3 0xC4
|
||||
#define KEY_F4 0xC5
|
||||
#define KEY_F5 0xC6
|
||||
#define KEY_F6 0xC7
|
||||
#define KEY_F7 0xC8
|
||||
#define KEY_F8 0xC9
|
||||
#define KEY_F9 0xCA
|
||||
#define KEY_F10 0xCB
|
||||
#define KEY_F11 0xCC
|
||||
#define KEY_F12 0xCD
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_12_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
/* IRLib_P99_Additional.h
|
||||
* Part of IRLib Library for Arduino receiving, decoding, and sending
|
||||
* infrared signals. See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt for more information.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* This is dummy code that you can copy and rename and modify when implementing new protocols.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef IRLIB_PROTOCOL_99_H
|
||||
#define IRLIB_PROTOCOL_99_H
|
||||
#define IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_99 case 99: IRsendAdditional::send(data); break;
|
||||
#define IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_99 if(IRdecodeAdditional::decode()) return true;
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_99 ,public virtual IRdecodeAdditional
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_99 ,public virtual IRsendAdditional
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PV_IR_DECODE_PROTOCOL_99 public virtual IRdecodeAdditional
|
||||
#define PV_IR_SEND_PROTOCOL_99 public virtual IRsendAdditional
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
class IRsendAdditional: public virtual IRsendBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
void IRsendAdditional::send(uint32_t data) {
|
||||
//void IRsendAdditional::send(uint32_t data, uint32_t data2)//optional form
|
||||
/*********
|
||||
* Insert your code here.
|
||||
*********/
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBSENDBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
class IRdecodeAdditional: public virtual IRdecodeBase {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool IRdecodeAdditional::decode(void) {
|
||||
IRLIB_ATTEMPT_MESSAGE(F("Additional"));
|
||||
/*********
|
||||
* Insert your code here. Return false if it fails.
|
||||
* Don't forget to include the following lines or
|
||||
* equivalent somewhere in the code.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* bits = 32; //Substitute proper value here
|
||||
* value = data; //return data in "value"
|
||||
* protocolNum = ADDITIONAL; //set the protocol number here.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIBDECODEBASE_H
|
||||
|
||||
#define IRLIB_HAVE_COMBO
|
||||
|
||||
#endif //IRLIB_PROTOCOL_99_H
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
# IRLib2 A Library for Receiving, Decoding and Sending Infrared Signals Using Arduino.
|
||||
|
||||
IRLib2 is copyright 2017 by Chris Young. It it is a major rewrite of the original IRLib 1.x by Chris Young which in turn was based on IRremote by Ken Shirriff. See COPYRIGHT.txt for details.
|
||||
|
||||
This library is covered under the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 3. See LICENSE.txt for a copy of the license.
|
||||
|
||||
This somewhat stripped-down version has been customized for use with Circuit Playground Express. It contains only IRrecvPCI receiver class because that is the one we recommend for use with Circuit Playground Express. It is automatically configured to use the building IR input and output capabilities of this board.
|
||||
|
||||
The complete library is available on GitHub at https://github.com/cyborg5/IRLib2
|
||||
|
||||
In that archive see CHANGELOG.txt for recent changes. It also contains a detailed Users Manual consisting of a reference, several tutorials, and information on how to implement new protocols is available in .docx, .pdf and .epub formats in the IRLib2/manuals/ folder.
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
#CapacitiveSensor Library#
|
||||
|
||||
CapacitiveSensor lets you create sensors that can detect touch or proximity.
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.pjrc.com/teensy/td_libs_CapacitiveSensor.html
|
||||
|
||||
http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/CapacitiveSensor
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHQPqQ_5ulc
|
||||
|
||||
CapacitiveSensor was originally written by Paul Badger and is now maintained by Paul Stoffregen.
|
||||
|
||||
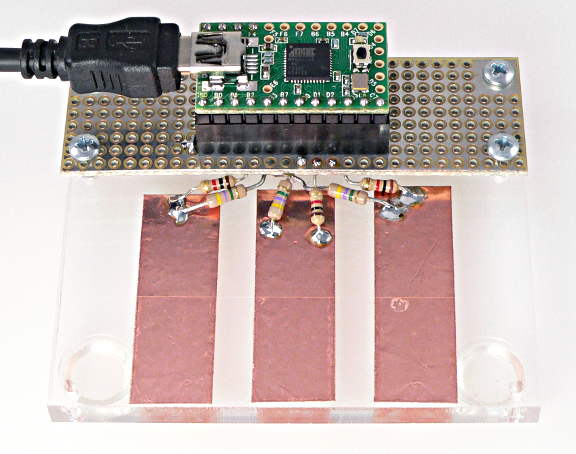
|
||||
438
arduino/libraries/Adafruit_Circuit_Playground/utility/ffft.S
Normal file
438
arduino/libraries/Adafruit_Circuit_Playground/utility/ffft.S
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,438 @@
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
;-----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
; Fixed-point FFT routines for megaAVRs (C)ChaN, 2005
|
||||
;-----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
; * This program is opened under license policy of following trems.
|
||||
;
|
||||
; Copyright (C) 2005, ChaN, all right reserved.
|
||||
;
|
||||
; * This program is a free software and there is NO WARRANTY.
|
||||
; * No restriction on use. You can use, modify and redistribute it for
|
||||
; personal, non-profit or commercial use UNDER YOUR RESPONSIBILITY.
|
||||
; * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice.
|
||||
;
|
||||
;-----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
;
|
||||
; void fft_input (const int16_t *array_src, complex_t *array_bfly);
|
||||
; void fft_execute (complex_t *array_bfly);
|
||||
; void fft_output (complex_t *array_bfly, uint16_t *array_dst);
|
||||
;
|
||||
; <array_src>: Wave form to be processed.
|
||||
; <array_bfly>: Complex array for butterfly operations.
|
||||
; <array_dst>: Spectrum output buffer.
|
||||
;
|
||||
; These functions must be called in sequence to do a DFT in FFT algorithm.
|
||||
; fft_input() fills the complex array with a wave form to prepare butterfly
|
||||
; operations. A hamming window is applied at the same time.
|
||||
; fft_execute() executes the butterfly operations.
|
||||
; fft_output() re-orders the results, converts the complex spectrum into
|
||||
; scalar spectrum and output it in linear scale.
|
||||
;
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
; THIS CODE HAS BEEN MODIFIED FROM ITS ORIGINAL FORM - it is pared down
|
||||
; to handle 64 points only, for the Circuit Playground microphone library.
|
||||
; Original FFFT code can be found on GitHub.
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
|
||||
.list
|
||||
|
||||
#define FFT_N 64
|
||||
#define FFT_B 6
|
||||
|
||||
#define T0L r0
|
||||
#define T0H r1
|
||||
#define T2L r2
|
||||
#define T2H r3
|
||||
#define T4L r4
|
||||
#define T4H r5
|
||||
#define T6L r6
|
||||
#define T6H r7
|
||||
#define T8L r8
|
||||
#define T8H r9
|
||||
#define T10L r10
|
||||
#define T10H r11
|
||||
#define T12L r12
|
||||
#define T12H r13
|
||||
#define T14L r14
|
||||
#define T14H r15
|
||||
#define AL r16
|
||||
#define AH r17
|
||||
#define BL r18
|
||||
#define BH r19
|
||||
#define CL r20
|
||||
#define CH r21
|
||||
#define DL r22
|
||||
#define DH r23
|
||||
#define EL r24
|
||||
#define EH r25
|
||||
#define XL r26
|
||||
#define XH r27
|
||||
#define YL r28
|
||||
#define YH r29
|
||||
#define ZL r30
|
||||
#define ZH r31
|
||||
|
||||
.macro ldiw dh,dl, abs
|
||||
ldi \dl, lo8(\abs)
|
||||
ldi \dh, hi8(\abs)
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro subiw dh,dl, abs
|
||||
subi \dl, lo8(\abs)
|
||||
sbci \dh, hi8(\abs)
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro addw dh,dl, sh,sl
|
||||
add \dl, \sl
|
||||
adc \dh, \sh
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro addd d3,d2,d1,d0, s3,s2,s1,s0
|
||||
add \d0, \s0
|
||||
adc \d1, \s1
|
||||
adc \d2, \s2
|
||||
adc \d3, \s3
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro subw dh,dl, sh,sl
|
||||
sub \dl, \sl
|
||||
sbc \dh, \sh
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro subd d3,d2,d1,d0, s3,s2,s1,s0
|
||||
sub \d0, \s0
|
||||
sbc \d1, \s1
|
||||
sbc \d2, \s2
|
||||
sbc \d3, \s3
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro lddw dh,dl, src
|
||||
ldd \dl, \src
|
||||
ldd \dh, \src+1
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro ldw dh,dl, src
|
||||
ld \dl, \src
|
||||
ld \dh, \src
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro stw dst, sh,sl
|
||||
st \dst, \sl
|
||||
st \dst, \sh
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro clrw dh, dl
|
||||
clr \dh
|
||||
clr \dl
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro lsrw dh, dl
|
||||
lsr \dh
|
||||
ror \dl
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro asrw dh, dl
|
||||
asr \dh
|
||||
ror \dl
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro lslw dh, dl
|
||||
lsl \dl
|
||||
rol \dh
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro pushw dh, dl
|
||||
push \dh
|
||||
push \dl
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro popw dh, dl
|
||||
pop \dl
|
||||
pop \dh
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro lpmw dh,dl, src
|
||||
lpm \dl, \src
|
||||
lpm \dh, \src
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro rjne lbl
|
||||
breq 99f
|
||||
rjmp \lbl
|
||||
99:
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro FMULS16 d3,d2,d1,d0 ,s1h,s1l, s2h,s2l ;Fractional Multiply (19clk)
|
||||
fmuls \s1h, \s2h
|
||||
movw \d2, T0L
|
||||
fmul \s1l, \s2l
|
||||
movw \d0, T0L
|
||||
adc \d2, EH ;EH: zero reg.
|
||||
fmulsu \s1h, \s2l
|
||||
sbc \d3, EH
|
||||
add \d1, T0L
|
||||
adc \d2, T0H
|
||||
adc \d3, EH
|
||||
fmulsu \s2h, \s1l
|
||||
sbc \d3, EH
|
||||
add \d1, T0L
|
||||
adc \d2, T0H
|
||||
adc \d3, EH
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
.macro SQRT32 ; 32bit square root (526..542clk)
|
||||
clr T6L
|
||||
clr T6H
|
||||
clr T8L
|
||||
clr T8H
|
||||
ldi BL, 1
|
||||
ldi BH, 0
|
||||
clr CL
|
||||
clr CH
|
||||
ldi DH, 16
|
||||
90: lsl T2L
|
||||
rol T2H
|
||||
rol T4L
|
||||
rol T4H
|
||||
rol T6L
|
||||
rol T6H
|
||||
rol T8L
|
||||
rol T8H
|
||||
lsl T2L
|
||||
rol T2H
|
||||
rol T4L
|
||||
rol T4H
|
||||
rol T6L
|
||||
rol T6H
|
||||
rol T8L
|
||||
rol T8H
|
||||
brpl 91f
|
||||
add T6L, BL
|
||||
adc T6H, BH
|
||||
adc T8L, CL
|
||||
adc T8H, CH
|
||||
rjmp 92f
|
||||
91: sub T6L, BL
|
||||
sbc T6H, BH
|
||||
sbc T8L, CL
|
||||
sbc T8H, CH
|
||||
92: lsl BL
|
||||
rol BH
|
||||
rol CL
|
||||
andi BL, 0b11111000
|
||||
ori BL, 0b00000101
|
||||
sbrc T8H, 7
|
||||
subi BL, 2
|
||||
dec DH
|
||||
brne 90b
|
||||
lsr CL
|
||||
ror BH
|
||||
ror BL
|
||||
lsr CL
|
||||
ror BH
|
||||
ror BL
|
||||
.endm
|
||||
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
; Constant Tables
|
||||
|
||||
.global tbl_window
|
||||
tbl_window: ; tbl_window[] = ... (This is a Hamming window)
|
||||
.dc.w 2621, 2693, 2910, 3270, 3768, 4401, 5161, 6042, 7036, 8132, 9320, 10588, 11926, 13318, 14753, 16216
|
||||
.dc.w 17694, 19171, 20634, 22069, 23462, 24799, 26068, 27256, 28352, 29345, 30226, 30987, 31619, 32117, 32477, 32694
|
||||
.dc.w 32766, 32694, 32477, 32117, 31619, 30987, 30226, 29345, 28352, 27256, 26068, 24799, 23462, 22069, 20634, 19171
|
||||
.dc.w 17694, 16216, 14753, 13318, 11926, 10588, 9320, 8132, 7036, 6042, 5161, 4401, 3768, 3270, 2910, 2693
|
||||
tbl_cos_sin: ; Table of {cos(x),sin(x)}, (0 <= x < pi, in FFT_N/2 steps)
|
||||
.dc.w 32767, 0, 32609, 3211, 32137, 6392, 31356, 9511, 30272, 12539, 28897, 15446, 27244, 18204, 25329, 20787
|
||||
.dc.w 23169, 23169, 20787, 25329, 18204, 27244, 15446, 28897, 12539, 30272, 9511, 31356, 6392, 32137, 3211, 32609
|
||||
.dc.w 0, 32766, -3211, 32609, -6392, 32137, -9511, 31356, -12539, 30272, -15446, 28897, -18204, 27244, -20787, 25329
|
||||
.dc.w -23169, 23169, -25329, 20787, -27244, 18204, -28897, 15446, -30272, 12539, -31356, 9511, -32137, 6392, -32609, 3211
|
||||
tbl_bitrev: ; tbl_bitrev[] = ...
|
||||
.dc.w 0*4, 32*4, 16*4, 48*4, 8*4, 40*4, 24*4, 56*4, 4*4, 36*4, 20*4, 52*4, 12*4, 44*4, 28*4, 60*4
|
||||
.dc.w 2*4, 34*4, 18*4, 50*4, 10*4, 42*4, 26*4, 58*4, 6*4, 38*4, 22*4, 54*4, 14*4, 46*4, 30*4, 62*4
|
||||
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
.global fft_input
|
||||
.func fft_input
|
||||
fft_input:
|
||||
pushw T2H,T2L
|
||||
pushw AH,AL
|
||||
pushw YH,YL
|
||||
|
||||
movw XL, EL ;X = array_src;
|
||||
movw YL, DL ;Y = array_bfly;
|
||||
clr EH ;Zero
|
||||
ldiw ZH,ZL, tbl_window ;Z = &tbl_window[0];
|
||||
ldiw AH,AL, FFT_N ;A = FFT_N;
|
||||
1: lpmw BH,BL, Z+ ;B = *Z++; (window)
|
||||
ldw CH,CL, X+ ;C = *X++; (I-axis)
|
||||
FMULS16 DH,DL,T2H,T2L, BH,BL, CH,CL ;D = B * C;
|
||||
stw Y+, DH,DL ;*Y++ = D;
|
||||
stw Y+, DH,DL ;*Y++ = D;
|
||||
subiw AH,AL, 1 ;while(--A)
|
||||
brne 1b ;/
|
||||
|
||||
popw YH,YL
|
||||
popw AH,AL
|
||||
popw T2H,T2L
|
||||
clr r1
|
||||
ret
|
||||
.endfunc
|
||||
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
.global fft_execute
|
||||
.func fft_execute
|
||||
fft_execute:
|
||||
pushw T2H,T2L
|
||||
pushw T4H,T4L
|
||||
pushw T6H,T6L
|
||||
pushw T8H,T8L
|
||||
pushw T10H,T10L
|
||||
pushw T12H,T12L
|
||||
pushw T14H,T14L
|
||||
pushw AH,AL
|
||||
pushw YH,YL
|
||||
|
||||
movw ZL, EL ;Z = array_bfly;
|
||||
ldiw EH,EL, 1 ;E = 1;
|
||||
ldiw XH,XL, FFT_N/2 ;X = FFT_N/2;
|
||||
1: ldi AL, 4 ;T12 = E; (angular speed)
|
||||
mul EL, AL ;
|
||||
movw T12L, T0L ;
|
||||
mul EH, AL ;
|
||||
add T12H, T0L ;/
|
||||
movw T14L, EL ;T14 = E;
|
||||
pushw EH,EL
|
||||
movw YL, ZL ;Z = &array_bfly[0];
|
||||
mul XL, AL ;Y = &array_bfly[X];
|
||||
addw YH,YL, T0H,T0L ;
|
||||
mul XH, AL ;
|
||||
add YH, T0L ;/
|
||||
pushw ZH,ZL
|
||||
2: clrw T10H,T10L ;T10 = 0 (angle)
|
||||
clr EH ;Zero reg.
|
||||
3: lddw AH,AL, Z+0 ;A = *Z - *Y; *Z++ += *Y;
|
||||
asrw AH,AL ;
|
||||
lddw DH,DL, Y+0 ;
|
||||
asrw DH,DL ;
|
||||
movw CL, AL ;
|
||||
subw AH,AL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
addw CH,CL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
stw Z+, CH,CL ;/
|
||||
lddw BH,BL, Z+0 ;B = *Z - *Y; *Z++ += *Y;
|
||||
asrw BH,BL ;
|
||||
lddw DH,DL, Y+2 ;
|
||||
asrw DH,DL ;
|
||||
movw CL, BL ;
|
||||
subw BH,BL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
addw CH,CL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
stw Z+, CH,CL ;/
|
||||
movw T0L, ZL
|
||||
ldiw ZH,ZL, tbl_cos_sin ;C = cos(T10); D = sin(T10);
|
||||
addw ZH,ZL, T10H,T10L ;
|
||||
lpmw CH,CL, Z+ ;
|
||||
lpmw DH,DL, Z+ ;/
|
||||
movw ZL, T0L
|
||||
FMULS16 T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, AH,AL, CH,CL ;*Y++ = A * C + B * D;
|
||||
FMULS16 T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L, BH,BL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
addd T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L;
|
||||
stw Y+, T4H,T4L ;/
|
||||
FMULS16 T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, BH,BL, CH,CL ;*Y++ = B * C - A * D;
|
||||
FMULS16 T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L, AH,AL, DH,DL ;
|
||||
subd T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L;
|
||||
stw Y+, T4H,T4L ;/
|
||||
addw T10H,T10L, T12H,T12L ;T10 += T12; (next angle)
|
||||
#if FFT_N >= 128
|
||||
sbrs T10H, FFT_B - 7 ;while(T10 < pi)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
sbrs T10L, FFT_B + 1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
rjmp 3b ;/
|
||||
ldi AL, 4 ;Y += X; Z += X; (skip split segment)
|
||||
mul XL, AL
|
||||
addw YH,YL, T0H,T0L ;
|
||||
addw ZH,ZL, T0H,T0L ;
|
||||
mul XH, AL ;
|
||||
add YH, T0L ;
|
||||
add ZH, T0L ;/
|
||||
ldi EL, 1 ;while(--T14)
|
||||
subw T14H,T14L, EH,EL ;
|
||||
rjne 2b ;/
|
||||
popw ZH,ZL
|
||||
popw EH,EL
|
||||
lslw EH,EL ;E *= 2;
|
||||
lsrw XH,XL ;while(X /= 2)
|
||||
adiw XL, 0 ;
|
||||
rjne 1b ;/
|
||||
|
||||
popw YH,YL
|
||||
popw AH,AL
|
||||
popw T14H,T14L
|
||||
popw T12H,T12L
|
||||
popw T10H,T10L
|
||||
popw T8H,T8L
|
||||
popw T6H,T6L
|
||||
popw T4H,T4L
|
||||
popw T2H,T2L
|
||||
; clr r1
|
||||
ret
|
||||
.endfunc
|
||||
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
.global fft_output
|
||||
.func fft_output
|
||||
fft_output:
|
||||
pushw T2H,T2L
|
||||
pushw T4H,T4L
|
||||
pushw T6H,T6L
|
||||
pushw T8H,T8L
|
||||
pushw T10H,T10L
|
||||
pushw AH,AL
|
||||
pushw YH,YL
|
||||
|
||||
movw T10L, EL ;T10 = array_bfly;
|
||||
movw YL, DL ;Y = array_output;
|
||||
ldiw ZH,ZL, tbl_bitrev ;Z = tbl_bitrev;
|
||||
clr EH ;Zero
|
||||
ldiw AH,AL, FFT_N / 2 ;A = FFT_N / 2; (plus only)
|
||||
1: lpmw XH,XL, Z+ ;X = *Z++;
|
||||
addw XH,XL, T10H,T10L ;X += array_bfly;
|
||||
ldw BH,BL, X+ ;B = *X++;
|
||||
ldw CH,CL, X+ ;C = *X++;
|
||||
FMULS16 T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, BH,BL, BH,BL ;T4:T2 = B * B;
|
||||
FMULS16 T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L, CH,CL, CH,CL ;T8:T6 = C * C;
|
||||
addd T4H,T4L,T2H,T2L, T8H,T8L,T6H,T6L;T4:T2 += T8:T6;
|
||||
SQRT32 ;B = sqrt(T4:T2);
|
||||
stw Y+, BH,BL ;*Y++ = B;
|
||||
subiw AH,AL, 1 ;while(--A)
|
||||
rjne 1b ;/
|
||||
|
||||
popw YH,YL
|
||||
popw AH,AL
|
||||
popw T10H,T10L
|
||||
popw T8H,T8L
|
||||
popw T6H,T6L
|
||||
popw T4H,T4L
|
||||
popw T2H,T2L
|
||||
clr r1
|
||||
ret
|
||||
.endfunc
|
||||
|
||||
;----------------------------------------------------------------------------;
|
||||
.global fmuls_f
|
||||
.func fmuls_f
|
||||
fmuls_f:
|
||||
movw CL, EL ;C = E;
|
||||
clr EH ;Zero
|
||||
FMULS16 ZH,ZL,XH,XL, CH,CL, DH,DL ;Z:X = C * D;
|
||||
movw EL, ZL
|
||||
clr r1
|
||||
ret
|
||||
.endfunc
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // __AVR__
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __SAMD21G18A__
|
||||
.cpu cortex-m0plus
|
||||
.fpu softvfp
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
181
arduino/libraries/Adafruit_Circuit_Playground/utility/talkie.cpp
Normal file
181
arduino/libraries/Adafruit_Circuit_Playground/utility/talkie.cpp
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
||||
// Talkie library
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 Peter Knight
|
||||
// This code is released under GPLv2 license.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define FS 8000 // Speech engine sample rate
|
||||
#define TICKS (FS / 40) // Speech data rate
|
||||
#define USEC ((1000000 + (FS / 2)) / FS) // Sample period (microseconds)
|
||||
|
||||
static const int16_t PROGMEM
|
||||
tmsK1[] = {0x82C0,0x8380,0x83C0,0x8440,0x84C0,0x8540,0x8600,0x8780,
|
||||
0x8880,0x8980,0x8AC0,0x8C00,0x8D40,0x8F00,0x90C0,0x92C0,
|
||||
0x9900,0xA140,0xAB80,0xB840,0xC740,0xD8C0,0xEBC0,0x0000,
|
||||
0x1440,0x2740,0x38C0,0x47C0,0x5480,0x5EC0,0x6700,0x6D40},
|
||||
tmsK2[] = {0xAE00,0xB480,0xBB80,0xC340,0xCB80,0xD440,0xDDC0,0xE780,
|
||||
0xF180,0xFBC0,0x0600,0x1040,0x1A40,0x2400,0x2D40,0x3600,
|
||||
0x3E40,0x45C0,0x4CC0,0x5300,0x5880,0x5DC0,0x6240,0x6640,
|
||||
0x69C0,0x6CC0,0x6F80,0x71C0,0x73C0,0x7580,0x7700,0x7E80};
|
||||
|
||||
static const int8_t PROGMEM
|
||||
tmsK3[] = {0x92,0x9F,0xAD,0xBA,0xC8,0xD5,0xE3,0xF0,
|
||||
0xFE,0x0B,0x19,0x26,0x34,0x41,0x4F,0x5C},
|
||||
tmsK4[] = {0xAE,0xBC,0xCA,0xD8,0xE6,0xF4,0x01,0x0F,
|
||||
0x1D,0x2B,0x39,0x47,0x55,0x63,0x71,0x7E},
|
||||
tmsK5[] = {0xAE,0xBA,0xC5,0xD1,0xDD,0xE8,0xF4,0xFF,
|
||||
0x0B,0x17,0x22,0x2E,0x39,0x45,0x51,0x5C},
|
||||
tmsK6[] = {0xC0,0xCB,0xD6,0xE1,0xEC,0xF7,0x03,0x0E,
|
||||
0x19,0x24,0x2F,0x3A,0x45,0x50,0x5B,0x66},
|
||||
tmsK7[] = {0xB3,0xBF,0xCB,0xD7,0xE3,0xEF,0xFB,0x07,
|
||||
0x13,0x1F,0x2B,0x37,0x43,0x4F,0x5A,0x66},
|
||||
tmsK8[] = {0xC0,0xD8,0xF0,0x07,0x1F,0x37,0x4F,0x66},
|
||||
tmsK9[] = {0xC0,0xD4,0xE8,0xFC,0x10,0x25,0x39,0x4D},
|
||||
tmsK10[] = {0xCD,0xDF,0xF1,0x04,0x16,0x20,0x3B,0x4D},
|
||||
chirp[] = {0x00,0x2A,0xD4,0x32,0xB2,0x12,0x25,0x14,
|
||||
0x02,0xE1,0xC5,0x02,0x5F,0x5A,0x05,0x0F,
|
||||
0x26,0xFC,0xA5,0xA5,0xD6,0xDD,0xDC,0xFC,
|
||||
0x25,0x2B,0x22,0x21,0x0F,0xFF,0xF8,0xEE,
|
||||
0xED,0xEF,0xF7,0xF6,0xFA,0x00,0x03,0x02,0x01};
|
||||
|
||||
static const uint8_t PROGMEM
|
||||
tmsEnergy[] = {0x00,0x02,0x03,0x04,0x05,0x07,0x0A,0x0F,
|
||||
0x14,0x20,0x29,0x39,0x51,0x72,0xA1,0xFF},
|
||||
tmsPeriod[] = {0x00,0x10,0x11,0x12,0x13,0x14,0x15,0x16,
|
||||
0x17,0x18,0x19,0x1A,0x1B,0x1C,0x1D,0x1E,
|
||||
0x1F,0x20,0x21,0x22,0x23,0x24,0x25,0x26,
|
||||
0x27,0x28,0x29,0x2A,0x2B,0x2D,0x2F,0x31,
|
||||
0x33,0x35,0x36,0x39,0x3B,0x3D,0x3F,0x42,
|
||||
0x45,0x47,0x49,0x4D,0x4F,0x51,0x55,0x57,
|
||||
0x5C,0x5F,0x63,0x66,0x6A,0x6E,0x73,0x77,
|
||||
0x7B,0x80,0x85,0x8A,0x8F,0x95,0x9A,0xA0};
|
||||
|
||||
static const uint8_t *ptrAddr;
|
||||
static uint16_t buf;
|
||||
static uint8_t bufBits;
|
||||
|
||||
static inline uint8_t rev(uint8_t a) { // Reverse bit sequence in 8-bit value
|
||||
a = ( a >> 4) | ( a << 4); // 76543210 -> 32107654
|
||||
a = ((a & 0xCC) >> 2) | ((a & 0x33) << 2); // 32107654 -> 10325476
|
||||
a = ((a & 0xAA) >> 1) | ((a & 0x55) << 1); // 10325476 -> 01234567
|
||||
return a;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static uint8_t getBits(uint8_t bits) {
|
||||
uint8_t value;
|
||||
if(bits > bufBits) {
|
||||
buf |= rev(pgm_read_byte(ptrAddr)) << (8 - bufBits);
|
||||
bufBits += 8;
|
||||
ptrAddr++; // Don't post-inc in pgm_read_byte! Is a macro.
|
||||
}
|
||||
value = buf >> (16 - bits);
|
||||
buf <<= bits;
|
||||
bufBits -= bits;
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define read8(base, bits) pgm_read_byte(&base[getBits(bits)]);
|
||||
#define read16(base, bits) pgm_read_word(&base[getBits(bits)]);
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
@brief speak the data at the passed location
|
||||
@param addr pointer to the data
|
||||
*/
|
||||
/**************************************************************************/
|
||||
void Adafruit_CPlay_Speaker::say(const uint8_t *addr) {
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t x0=0, x1=0, x2=0, x3=0, x4=0,
|
||||
x5=0, x6=0, x7=0, x8=0, x9=0,
|
||||
synthK1, synthK2, u0;
|
||||
uint16_t synthEnergy, synthRand = 1;
|
||||
int8_t synthK3, synthK4, synthK5, synthK6,
|
||||
synthK7, synthK8, synthK9, synthK10;
|
||||
uint8_t periodCounter=0, nextPwm = 0x7F, synthPeriod;
|
||||
uint8_t iCount = TICKS;
|
||||
uint32_t nowTime, prevTime=0;
|
||||
|
||||
if(!started) begin();
|
||||
|
||||
buf = bufBits = 0; // Reset 'ROM' reader (global stuff)
|
||||
ptrAddr = addr;
|
||||
|
||||
for(;;) {
|
||||
while(((nowTime = micros()) - prevTime) < USEC);
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
OCR4A = nextPwm;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, nextPwm);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
prevTime = nowTime;
|
||||
|
||||
if(++iCount >= TICKS) {
|
||||
// Read speech data, processing the variable size frames
|
||||
uint8_t energy;
|
||||
if((energy = getBits(4)) == 0) { // Rest frame
|
||||
synthEnergy = 0;
|
||||
} else if(energy == 0xF) { // Stop frame; silence
|
||||
#ifdef __AVR__
|
||||
TCCR4A = 0x7F;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
analogWrite(A0, 0x7F);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
synthEnergy = pgm_read_byte(&tmsEnergy[energy]);
|
||||
uint8_t repeat = getBits(1);
|
||||
synthPeriod = pgm_read_byte(&tmsPeriod[getBits(6)]);
|
||||
if(!repeat) { // A repeat frame uses last coefficients
|
||||
synthK1 = read16(tmsK1, 5); // All frames
|
||||
synthK2 = read16(tmsK2, 5); // use the first
|
||||
synthK3 = read8( tmsK3, 4); // 4 coefficients
|
||||
synthK4 = read8( tmsK4, 4);
|
||||
if(synthPeriod) {
|
||||
synthK5 = read8(tmsK5 , 4); // Voiced
|
||||
synthK6 = read8(tmsK6 , 4); // frames
|
||||
synthK7 = read8(tmsK7 , 4); // use
|
||||
synthK8 = read8(tmsK8 , 3); // six
|
||||
synthK9 = read8(tmsK9 , 3); // extra
|
||||
synthK10 = read8(tmsK10, 3); // coeffs
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
iCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(synthPeriod) { // Voiced source
|
||||
if(++periodCounter >= synthPeriod) periodCounter = 0;
|
||||
u0 = (periodCounter >= sizeof(chirp)) ? 0 :
|
||||
(pgm_read_byte(&chirp[periodCounter]) *
|
||||
(uint32_t)synthEnergy) >> 8;
|
||||
} else { // Unvoiced source
|
||||
synthRand = (synthRand >> 1) ^ ((synthRand & 1) ? 0xB800 : 0);
|
||||
u0 = (synthRand & 1) ? synthEnergy : -synthEnergy;
|
||||
}
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK10 * x9) +
|
||||
(synthK9 * x8)) >> 7;
|
||||
x9 = x8 + ((synthK9 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK8 * x7 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x8 = x7 + ((synthK8 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK7 * x6 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x7 = x6 + ((synthK7 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK6 * x5 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x6 = x5 + ((synthK6 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK5 * x4 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x5 = x4 + ((synthK5 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK4 * x3 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x4 = x3 + ((synthK4 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK3 * x2 ) >> 7);
|
||||
x3 = x2 + ((synthK3 * u0 ) >> 7);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK2 * (int32_t)x1 ) >> 15);
|
||||
x2 = x1 + ((synthK2 * (int32_t)u0 ) >> 15);
|
||||
u0 -= ((synthK1 * (int32_t)x0 ) >> 15);
|
||||
x1 = x0 + ((synthK1 * (int32_t)u0 ) >> 15);
|
||||
|
||||
if( u0 > 511) u0 = 511; // Output clamp
|
||||
else if(u0 < -512) u0 = -512;
|
||||
|
||||
x0 = u0;
|
||||
nextPwm = (u0 >> 2) + 0x80;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user